What Is KBA Identity Verification? A Complete Guide to Knowledge-Based Authentication

Introduction to KBA Identity Verification: What Is KBA Identity Verification?
In the age of digital transactions, protecting personal and financial information has become increasingly important. One of the most widely used methods for securing online services is Knowledge-Based Authentication (KBA). KBA is a form of identity verification that relies on the user answering specific questions to confirm their identity. These questions are typically based on personal information that only the legitimate user should know, such as financial or historical data.
KBA identity verification is commonly used in various industries to ensure the security of accounts and transactions. From online banking to e-commerce platforms and government services, KBA helps protect against fraud by validating the identity of individuals before they can access sensitive information or complete transactions. This method not only adds an additional layer of security but also prevents unauthorized access that could lead to identity theft or financial loss.
How KBA Works: The Process
KBA identity verification involves several steps to ensure that the person attempting to access an account or perform a transaction is indeed the rightful owner. Here’s a breakdown of how the process works:
- User Initiates the Verification Process: When a user tries to access a service or complete a transaction, they may be prompted to go through KBA to verify their identity. This step often follows an initial login or submission of personal information such as a name, date of birth, or address.
- Question Generation: Based on the user’s personal and financial history, KBA systems generate a set of questions. These questions are designed to be unique to the individual, and they are typically derived from publicly available records or data tied to financial transactions. The questions might include things like “What was the name of your first car?” or “Which bank issued your mortgage?”
- User Responses: The individual must answer these questions within a short time frame to prove they are who they claim to be. The answers are compared to the information in the system’s records.
- Verification Outcome: If the user answers correctly, they pass the KBA verification, and they are granted access. If the responses do not match or are incorrect, the user may be asked to retry the verification process, or in some cases, their access may be blocked.
The success of KBA relies heavily on the accuracy and relevance of the questions generated, ensuring they are only answerable by the legitimate user.
Why KBA is Used: Applications and Importance
KBA is crucial for various industries, particularly those that handle sensitive data. Some of the most common uses include:
- Banking and Financial Services: KBA is widely used in online banking to ensure that only the account holder can access their financial information, transfer funds, or perform other actions. It also plays a significant role in identity verification for loan applications, credit card approvals, and other financial transactions.
- E-Commerce and Online Shopping: Online retailers often use KBA to prevent fraud during transactions, particularly when the customer is making a high-value purchase or creating a new account.
- Government Services: Many government agencies use KBA to verify the identities of individuals when applying for services like social security, tax filings, or public benefits.
- Healthcare and Insurance: KBA is also used to protect patient information and ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive health records or insurance claims.
By employing KBA, organizations add an extra layer of protection that ensures only legitimate individuals can perform sensitive actions, minimizing the risk of identity fraud.
Types of KBA: Static and Dynamic
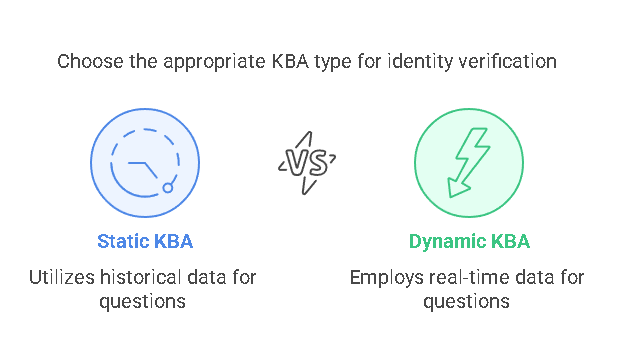
There are two primary types of KBA: Static KBA and Dynamic KBA. Both serve the same general purpose—identity verification—but differ in the way they generate questions.
- Static KBA: Static KBA uses historical data to generate questions that are based on the user’s past activities or information, such as previous addresses, loans, or credit card details. This type of KBA is more commonly used in the past, as it relies on data that is less likely to change over time.
- Dynamic KBA: Dynamic KBA generates questions based on real-time data, such as recent transactions, current credit card information, or recent purchases. This type of KBA is considered more secure because it uses up-to-date data, making it harder for fraudsters to guess the correct answers.
Dynamic KBA is becoming more common, particularly in industries where up-to-date information is vital for security.
Security Considerations: Why KBA is Secure
KBA provides several security benefits. The main advantage is that it involves personal knowledge that only the user should know, unlike passwords or PINs that can be easily stolen or guessed. The use of both static and dynamic questions further strengthens the security measures by reducing the chances of an unauthorized individual passing the verification process.
However, while KBA adds an extra layer of security, it is not without its potential flaws. One of the challenges with KBA is the risk of using information that can be found publicly. For example, details such as past addresses or previous employers may be accessible via social media or public records, making it possible for fraudsters to obtain this information and answer the questions incorrectly. Furthermore, if someone has had their identity stolen, they could also potentially answer the questions accurately and gain unauthorized access.
Comparison with Other Verification Methods
KBA is often compared with other identity verification methods such as two-factor authentication (2FA), biometric verification, and SMS verification. While each method serves the purpose of verifying an individual’s identity, they differ in their approach:
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA adds a second layer of security by requiring users to input a code sent to their mobile device or email. It’s a powerful method but still vulnerable if the user’s phone is compromised.
- Biometric Verification: This method uses physical characteristics such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or retinal scans to verify identity. Biometric data is harder to steal or fake than traditional knowledge-based methods.
- SMS Verification: SMS verification sends a one-time code to the user’s mobile phone. While convenient, this method can be vulnerable to SIM swapping, where a fraudster takes control of the user’s phone number.
KBA stands apart by asking questions that are specific to the individual’s personal or financial history, making it a good method for situations where other methods might not be as feasible or secure.
Limitations of KBA
Despite its advantages, KBA has some limitations. One of the primary concerns is the reliance on publicly available or previously recorded information. If fraudsters have access to a person’s public records, they could potentially answer the questions correctly and bypass the verification process. Additionally, if a person’s information is outdated or no longer accessible, they might fail the verification process, which could prevent them from completing important transactions.
Another limitation is that KBA relies on the assumption that the user’s identity is relatively stable. For individuals who have had significant life changes (e.g., a name change or relocation), KBA may not provide an accurate reflection of their identity.
KBA identity verification is an essential tool for securing digital transactions and protecting personal information. While it provides an added layer of protection against fraud, it’s important for organizations to carefully manage the process and consider potential vulnerabilities. As technology evolves, KBA may need to adapt, and its combination with other security measures, such as biometric verification, may become increasingly important.
Step-by-Step Process of KBA Identity Verification
The Knowledge-Based Authentication (KBA) identity verification process involves several critical steps to ensure that the individual seeking access is the legitimate user. Below is a detailed breakdown of the process:
1. Initial User Input
The process typically begins when the user submits basic personal information, such as their name, date of birth, address, or social security number. This data is essential to initiate the KBA process and allow the system to generate personalized questions. This personal information acts as a reference point for the KBA system, enabling it to cross-check the individual’s data against known databases containing relevant historical or real-time information.
2. Question Generation
After receiving the personal details, the KBA system uses advanced algorithms to generate a series of identity verification questions. These questions are derived from historical data, such as credit reports, financial transactions, and public records. The questions might be based on the following categories:
- Personal history: e.g., “What was the name of your high school?”
- Financial information: e.g., “Which company issued your mortgage?”
- Previous addresses: e.g., “What was your previous street address?”
- Banking information: e.g., “Which bank issued your first credit card?”
The system aims to generate questions that only the individual can answer accurately. For static KBA, the questions are based on historical data that may be years old, while dynamic KBA generates questions based on current or recent data that may reflect more recent financial events or activity.
3. User Response
Once the system generates the questions, the user is required to answer them in real time. The answers are typically entered on a secure platform, which ensures that sensitive information is not exposed during the process. Time constraints are often in place, allowing users only a few minutes to answer the questions.
The user’s responses are cross-checked against the database to verify their identity. The system often employs multiple rounds of questioning to verify the individual’s authenticity further. For example, if the first set of questions is answered correctly, the user may be prompted with additional questions to strengthen the verification process.
4. Verification Outcome
Once the user completes the questions, the system evaluates their responses. The outcome will either confirm the user’s identity or raise a flag if the answers do not align with the information in the database.
- Verification Success: If the user answers correctly, they are granted access to the service or transaction they were attempting to complete. This means that the KBA system has successfully authenticated the identity.
- Verification Failure: If the user fails to answer enough questions correctly, they are denied access. The system may provide an option to retry or request additional forms of verification. In some cases, users may be asked to undergo an alternate authentication method, such as biometric verification or 2FA (two-factor authentication).
5. Factors Affecting the KBA Process
Several factors can influence the success of the KBA identity verification process. These factors include the accuracy and currency of the personal data provided, as well as the quality of the information in the relevant databases.
Accuracy of Personal Data
The accuracy of the personal information submitted plays a significant role in determining the success of KBA. If the information provided is outdated or incorrect, the system may not be able to generate appropriate questions, or the questions may be based on inaccurate data, leading to verification failure.
Availability of Relevant Information
The KBA system relies on historical or real-time data from various sources such as financial institutions, credit bureaus, and government records. If the necessary data is not available, it can delay the process or cause questions to be inaccurately generated. For instance, if a person has recently moved or changed financial institutions, the system might fail to access updated records, thus leading to questions that are irrelevant or outdated.
Technology Used
The efficiency of the KBA system also depends on the technology behind the platform. Modern KBA systems are built with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms that enhance the accuracy and reliability of the questions asked. Faster systems can provide better response times, leading to smoother user experiences.
6. Challenges in KBA Verification
While KBA provides an effective means of identity verification, there are several challenges that can impede the process.
Difficulty Answering Questions
If users have difficulty recalling answers to the questions, they may fail the verification process. For example, a user may not remember their previous addresses or may not recognize the name of a bank from years ago. The challenge increases if the questions are too specific or if the user’s life has changed significantly (e.g., a name change or relocation).
Outdated or Inaccurate Information
KBA is highly dependent on the availability and accuracy of data. If an individual has experienced significant life changes (e.g., a name change or change of address), the KBA system may generate questions based on old information that no longer reflects the individual’s current identity. This can prevent successful verification.
Security Risks and Fraudulent Attempts
Though KBA is designed to be secure, it is not foolproof. Fraudsters who have access to public records or databases may be able to answer questions correctly, posing a potential security risk. Similarly, if a person’s identity has been stolen, fraudsters could potentially bypass KBA checks.
7. Best Practices for Users and Companies
For KBA to be effective, both users and companies need to follow best practices to ensure the verification process goes smoothly.
For Companies
- Maintain Updated Records: Organizations should ensure that the personal information they store about users is up-to-date. This is crucial for generating accurate questions and increasing the likelihood of successful verification.
- Use a Multi-Layered Approach: While KBA is effective, businesses should consider combining it with other verification methods, such as two-factor authentication or biometric verification, for enhanced security.
- Provide Clear Instructions: Users should be guided on how to answer KBA questions and what to do if they fail the verification process.
For Users
- Ensure Accurate Information: Users should ensure that their personal and financial information is correct and up-to-date with the organizations they interact with.
- Prepare for KBA: If users anticipate going through KBA verification, they should ensure that they have access to relevant personal or financial records, such as old addresses, loan information, or account details.
Comparison of KBA with Other Identity Verification Methods
To better understand KBA’s role in identity verification, let’s compare it with other widely used methods. Below is a comparison table:
| Verification Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| KBA (Knowledge-Based Authentication) | – Secure and reliable for many transactions. – Does not require physical hardware (e.g., fingerprint scanners). |
– Can be bypassed with stolen personal data. – May fail for users with outdated information. |
| Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) | – Provides an additional layer of security. – Easy to implement across various platforms. |
– Can be compromised if the second factor (e.g., phone number) is stolen. |
| Biometric Verification | – High level of security, difficult to replicate. – Quick and convenient. |
– Requires specialized hardware (fingerprint or facial scanners). – Can be invasive for some users. |
| SMS Verification | – Simple and quick for users. – Widely available on most devices. |
– Vulnerable to SIM swapping and phishing attacks. |
Precisehire Mention: How Precisehire Assists with KBA Verification
At Precisehire, we provide comprehensive background screening services, including KBA identity verification, to help businesses streamline their hiring and compliance processes. By leveraging advanced KBA solutions, we ensure that companies can easily verify the identities of potential employees or candidates without compromising security. Our KBA verification process is designed to deliver quick and reliable results, enhancing security while safeguarding user privacy.
Precisehire assists organizations in navigating the complexities of KBA verification and other identity verification techniques. With our expertise, businesses can rely on our services to ensure compliance with legal standards and secure sensitive information efficiently.
Incorporating KBA as part of your identity verification strategy helps protect against fraud and ensures that only legitimate individuals are granted access to sensitive data, financial accounts, and services. Whether you are looking for employee screening or consumer protection, Precisehire offers streamlined, effective, and legally compliant solutions tailored to your needs.
Legal Aspects of KBA Identity Verification
As KBA (Knowledge-Based Authentication) becomes a central tool for securing digital transactions, its implementation must align with various legal and regulatory frameworks to ensure compliance and privacy protection. The following legal aspects are essential to consider when using KBA identity verification.
Compliance with Laws and Regulations
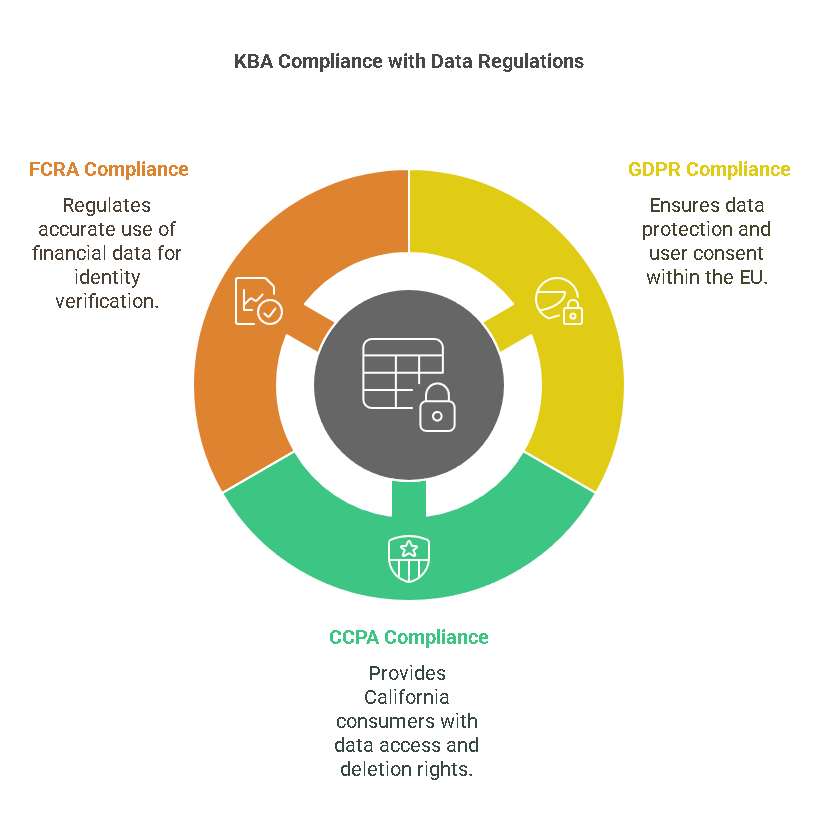
KBA identity verification must adhere to several privacy and data protection regulations to maintain users’ rights and ensure that personal information is handled securely. Some of the most relevant regulations include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) The GDPR governs the processing of personal data within the European Union (EU) and mandates strict rules regarding user consent, transparency, and data protection. Organizations using KBA must ensure they collect and process user data in a way that complies with GDPR requirements. For example, users must give explicit consent for their data to be used in the verification process, and organizations must provide access to data upon request.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) The CCPA applies to businesses in California and provides consumers with the right to access, delete, and opt out of the sale of their personal data. When using KBA verification, businesses must inform users about the data collection process and their rights under CCPA. Users must also be given an option to request that their data be deleted if they no longer wish to participate in the verification process.
- Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) The FCRA regulates how consumer information is collected, used, and shared by consumer reporting agencies. Since KBA often relies on financial and credit data to verify identities, organizations must ensure that they comply with FCRA guidelines. This includes ensuring the accuracy of the data used in the KBA process and obtaining user consent before accessing financial records.
Risks of Non-Compliance
Organizations that fail to comply with legal regulations when conducting KBA identity verification could face severe penalties, including fines and legal consequences. For example, non-compliance with GDPR could result in substantial financial penalties (up to 4% of global annual revenue), while violations of the FCRA could lead to lawsuits and significant reputational damage.
Additionally, failing to adhere to data protection laws can undermine the trust between businesses and consumers, leading to a loss of business and a damaged reputation. Organizations must ensure that they follow the relevant laws to mitigate legal risks and protect both their customers and their operations.
Data Protection and User Rights
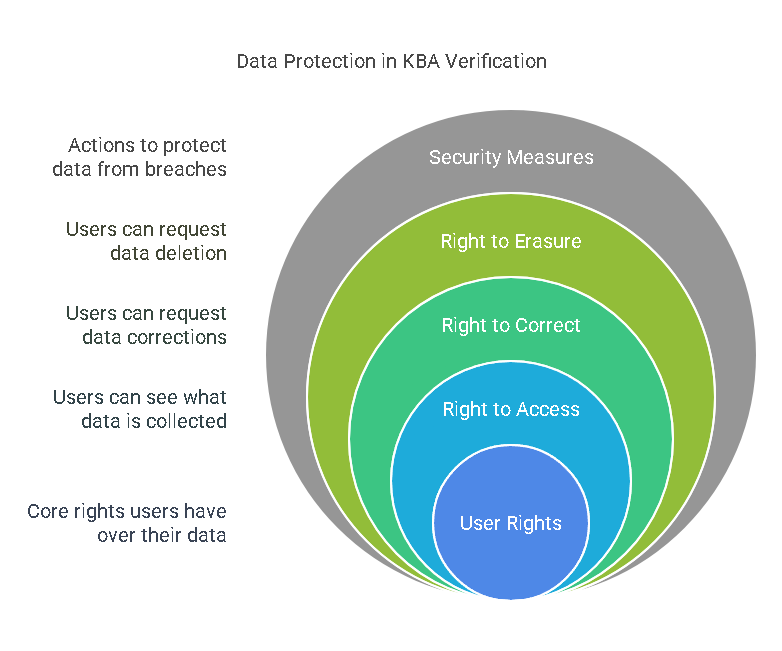
KBA verification involves collecting personal and sometimes sensitive data to authenticate identities. As such, it is critical that businesses protect this data from unauthorized access or breaches. Under data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA, users have specific rights regarding their personal information:
- Right to Access: Users have the right to know what personal data has been collected and how it will be used during the KBA process.
- Right to Correct: If a user believes that the data used in the KBA process is incorrect, they have the right to request corrections.
- Right to Erasure: Under certain conditions, users may request that their data be deleted, especially if they no longer wish to use the service or if their consent is withdrawn.
- Right to Restrict Processing: Users can request that their data be limited in how it is used, for example, if they believe the data is inaccurate or have concerns about its use.
Organizations using KBA verification must ensure that they provide users with the ability to exercise these rights in compliance with privacy laws.
Impact of Data Breaches
Data breaches present a significant risk when dealing with personal data in identity verification processes. In the event of a breach, sensitive information used for KBA—such as social security numbers, addresses, and financial data—could be exposed to unauthorized individuals. This could lead to identity theft, fraud, and reputational damage for the affected company.
Organizations must implement robust security measures, such as encryption, secure storage, and access controls, to protect users’ data. Additionally, they should have an incident response plan in place to address potential breaches promptly. Compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA requires that users are notified of data breaches within specific timeframes, further underscoring the importance of robust security practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about KBA Identity Verification
Below are some common questions related to KBA identity verification, along with clear answers to help users and organizations better understand the process.
What Types of Questions Are Asked in KBA Identity Verification?
KBA identity verification typically involves questions that only the legitimate user should be able to answer. These questions are derived from historical or real-time data and may include:
- Personal history questions, such as "What was the name of your high school?"
- Financial questions, such as "Which bank issued your mortgage?"
- Previous address questions, such as "What was the address of your first home?"
- Banking-related questions, such as "Which company issued your first credit card?"
The questions are designed to be specific and unique to each individual, ensuring that the person attempting verification is the rightful owner of the data.
Can KBA Be Used for All Types of Online Transactions?
KBA is widely used for online transactions that require strong identity verification, such as banking, e-commerce, and government services. However, it may not be suitable for all types of transactions, especially those that require higher levels of security, such as online banking transfers or access to highly sensitive accounts. In these cases, organizations might use additional verification methods, such as biometric authentication or two-factor authentication (2FA), in combination with KBA.
What Happens if I Fail the KBA Identity Verification?
If you fail to answer the KBA questions correctly, you may be denied access to the service or transaction you were attempting to complete. Some systems provide an option to retry, while others may offer alternative verification methods, such as 2FA, email verification, or biometric checks. In cases where you cannot verify your identity, you may need to contact the organization to resolve the issue.
How Accurate is KBA Identity Verification Compared to Other Methods?
KBA is a highly accurate and effective method for verifying identities, but it is not infallible. Its accuracy depends on the quality and availability of the data it uses, as well as the specific questions asked. Compared to other verification methods such as biometrics or SMS verification, KBA can be more susceptible to fraud if a person's data is compromised or outdated. Combining KBA with additional verification methods can increase its reliability.
How Can I Protect My Personal Information from Being Used in KBA Fraud?
To protect your personal information from being used in KBA fraud:
- Regularly monitor your credit reports and financial records to ensure no unauthorized activity has occurred.
- Use strong and unique passwords for your online accounts, and consider enabling multi-factor authentication where available.
- Be cautious about sharing personal information online and avoid posting sensitive details on social media.
- Immediately report any suspicious activity or unauthorized access to the appropriate authorities.
Conclusion
KBA identity verification plays a vital role in securing digital transactions and protecting against identity theft. While it offers numerous benefits in terms of user convenience and security, it must be implemented in compliance with privacy laws and regulations to ensure that users’ rights are respected. Businesses must take care to protect sensitive information during the KBA process and maintain up-to-date user records to avoid verification failures.
Precisehire helps businesses streamline their identity verification processes, including the use of KBA. With Precisehire’s expertise, companies can ensure they meet compliance standards, safeguard sensitive data, and protect their users from identity fraud.
By understanding the legal, technical, and practical aspects of KBA identity verification, businesses can enhance their security measures and offer a safer environment for users engaging in digital transactions.
