What Information is Included in a Job Background Check?

Overview and Types of Information in a Background Check
A background check is an essential step in the hiring process that allows employers to verify a candidate’s credentials and ensure they are the right fit for a role. By examining key aspects of a person’s history, such as employment, education, and criminal records, background checks help companies make informed decisions while maintaining workplace safety and compliance. This section provides an overview of what a background check entails and the types of information that may appear in one.
What Is a Background Check?
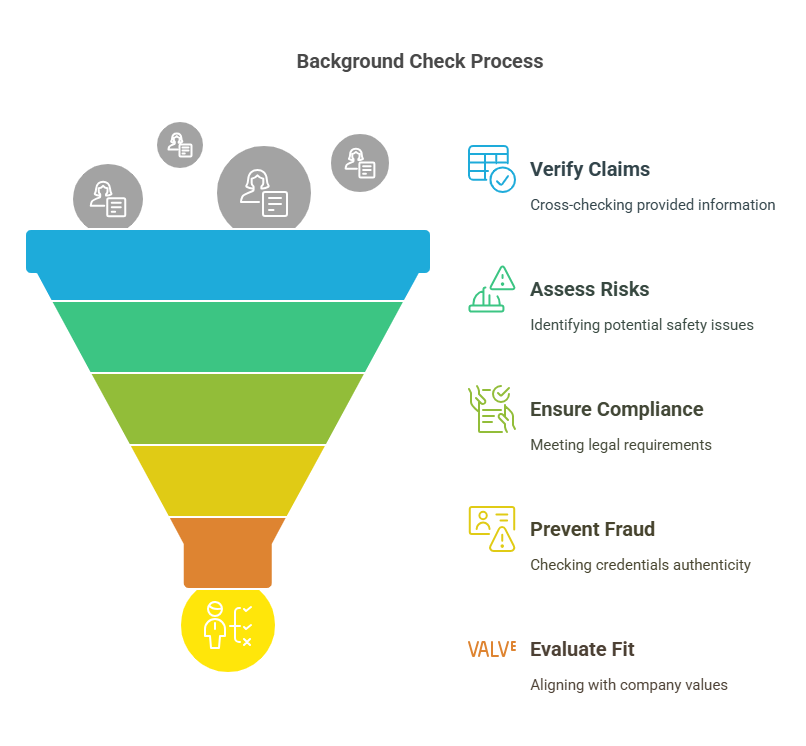
A background check is a systematic review of an individual’s past, conducted to verify the accuracy of their claims and uncover any potential red flags. Employers typically perform background checks during the hiring process to evaluate a candidate’s trustworthiness, qualifications, and suitability for a role.
Why Do Employers Conduct Background Checks?
- Workplace Safety: Ensures a safe environment by identifying potential risks, such as a history of violence or substance abuse.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meets legal and industry-specific requirements, such as background screenings for positions in healthcare, education, or finance.
- Fraud Prevention: Verifies credentials, preventing false claims regarding education, experience, or certifications.
- Cultural Fit: Helps ensure candidates align with company values and policies.
What Comes Up on a Background Check for a Job?
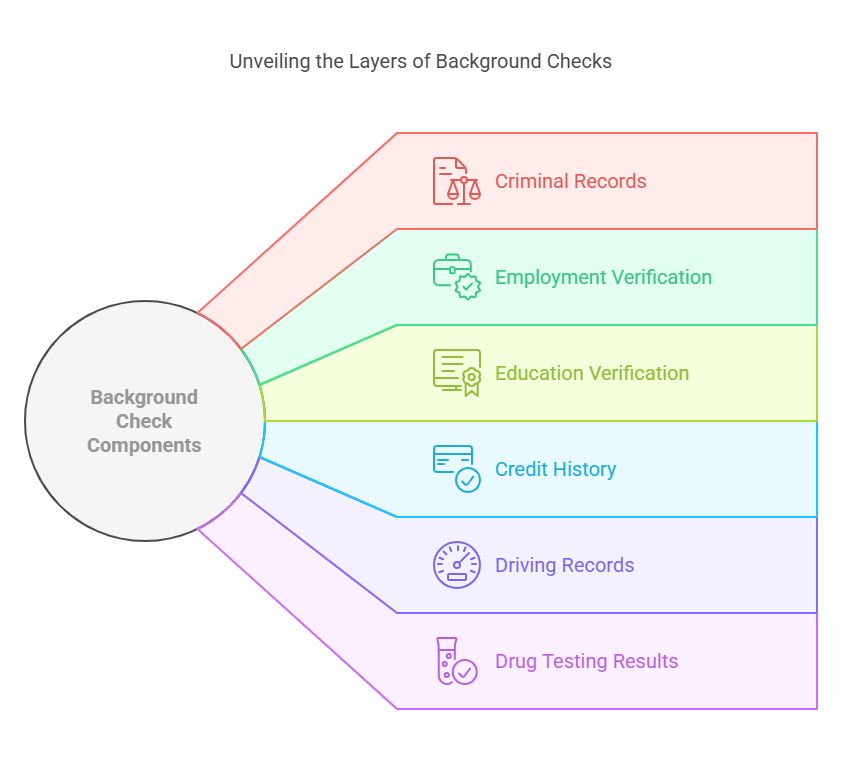
The information revealed during a background check varies depending on the role, industry, and level of scrutiny required. Below is a comprehensive list of the most common components of background checks:
1. Criminal Records
- Shows felony and misdemeanor convictions, arrests, pending charges, and, in some cases, dismissed cases.
- May include sex offender registry status or driving violations for roles requiring vehicle operation.
- Employers use this to evaluate potential risks related to workplace safety and compliance.
2. Employment Verification
- Confirms previous job titles, dates of employment, and reasons for leaving.
- Ensures candidates have the experience they claim on their resumes.
3. Education Verification
- Validates degrees, certifications, and institutions attended.
- Used to confirm qualifications required for specific roles.
4. Credit History
- Includes credit reports, debt, and financial responsibility.
- Commonly checked for roles involving financial management or access to sensitive data.
5. Driving Records
- Provides details about a candidate’s driving history, including accidents, violations, and license validity.
- Relevant for roles requiring driving or operating company vehicles.
6. Drug Testing Results
- Employers may request drug screening as part of a background check to ensure a drug-free workplace.
7. Identity Verification
- Confirms the candidate’s identity using Social Security numbers, passports, or other government-issued IDs.
- Prevents fraud or identity theft.
8. Professional Licenses and Certifications
- Ensures licenses or certifications required for the job are valid and up-to-date.
- Common in healthcare, law, and technical fields.
9. References
- Employers may contact professional or personal references to assess a candidate’s skills, character, and work ethic.
10. Social Media and Online Presence
- Some employers review a candidate’s social media activity to assess professionalism and cultural alignment.
- Limited to publicly available information to avoid violating privacy laws.
Summary Table: Common Components of Background Checks
| Component | Details | Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Criminal Records | Felony/misdemeanor convictions, arrests, pending charges, sex offender status | Workplace safety, legal compliance |
| Employment Verification | Job titles, employment dates, reasons for leaving | Fraud prevention, resume accuracy |
| Education Verification | Degrees, certifications, and institutions attended | Qualification confirmation |
| Credit History | Debt, credit score, financial responsibility | Roles involving financial management |
| Driving Records | Accidents, violations, license validity | Driving-related roles |
| Drug Testing | Results of pre-employment drug screenings | Maintaining a drug-free workplace |
| Identity Verification | Government-issued IDs, Social Security number | Fraud prevention |
| Licenses/Certifications | Professional licenses required for the job | Industry compliance |
| References | Feedback from past supervisors or colleagues | Work ethic and cultural fit assessment |
| Social Media Review | Public posts, photos, and professional profiles | Professionalism and character evaluation |
Tailoring Background Checks to the Role
The scope of a background check often depends on the specific job being offered. For example:
- Healthcare Roles: Focus on criminal records, licenses, and certifications.
- Finance Positions: Emphasize credit history and employment verification.
- Transportation Jobs: Require detailed driving record reviews.
How Background Checks Are Conducted and Their Importance
The process of conducting background checks involves multiple steps and varies depending on the job role, employer requirements, and the type of information being verified. In this section, we’ll explore how background checks are conducted, the timelines involved, and why they are essential for hiring. Additionally, we’ll discuss the benefits of professional background check services, including a look at Precise Hire and how they streamline this critical process.
How Background Checks Are Conducted
Employers may perform background checks in-house or partner with professional services to gather and verify information. The process generally follows these key steps:
1. Candidate Consent
Before initiating a background check, employers must obtain written consent from the candidate. This is required by law under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) and ensures transparency in the hiring process.
2. Collecting Candidate Information
Employers request personal details from the candidate, such as:
- Full name
- Date of birth
- Social Security number
- Employment and education history
This information is critical for accurate identification and verification.
3. Selecting Screening Components
The employer determines the scope of the background check based on the role’s requirements. For example:
- Basic Roles: Employment and education verification, identity checks.
- High-Risk Positions: Criminal records, credit history, drug testing, and professional license verification.
4. Information Gathering and Verification
Employers or screening providers use various methods to collect and verify data, such as:
- Accessing public records (e.g., criminal records or driving history).
- Contacting previous employers or educational institutions.
- Running credit checks through authorized credit reporting agencies.
5. Reviewing Results
Once the data is collected, the employer or screening provider reviews the findings to determine whether the candidate meets the role’s requirements.
How Long Do Background Checks Take?
Timelines for background checks depend on the complexity of the screening process. Here’s an approximate breakdown:
- Basic Checks: 1–3 business days (identity, employment, and education verification).
- Comprehensive Checks: 5–10 business days (criminal records, credit history, and references).
- Delays: May occur due to incomplete information, difficulty contacting institutions, or holidays.
Importance of Background Checks in Hiring
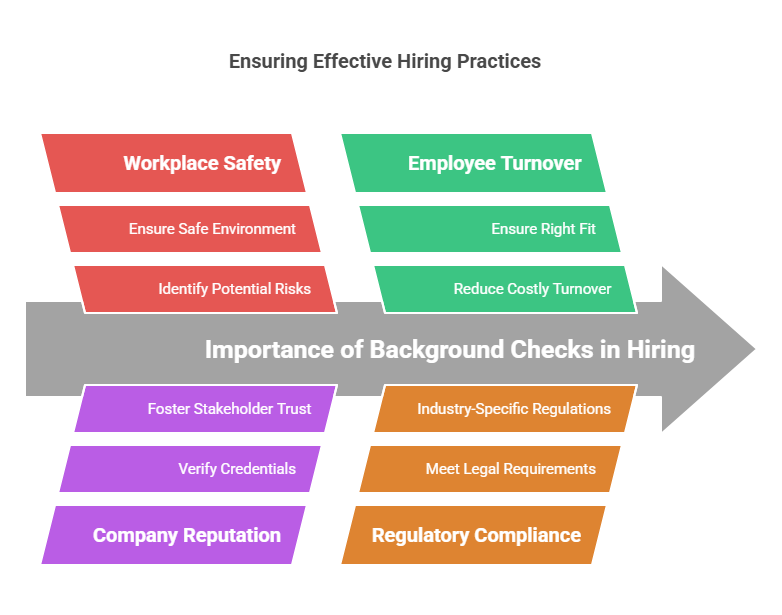
Background checks are critical to ensuring the success of a hiring process. Below are the key reasons employers prioritize background screenings:
1. Workplace Safety
- Background checks help identify potential risks, such as violent behavior or substance abuse, ensuring a safe environment for employees and customers.
2. Protecting Company Reputation
- Hiring employees with verified credentials and a clean history protects the company’s reputation and fosters trust among stakeholders.
3. Reducing Turnover
- Verifying a candidate’s qualifications and work history ensures the right fit for the role, reducing costly turnover.
4. Regulatory Compliance
- Many industries, such as healthcare, finance, and transportation, require background checks to meet federal, state, and industry-specific regulations.
5. Fraud Prevention
- Background checks prevent fraudulent claims on resumes, such as false degrees or inflated job titles.
DIY Background Checks vs. Professional Screening Services
Employers may consider conducting background checks internally (DIY) or using professional services. Below is a comparison of both approaches:
| Aspect | DIY Background Checks | Professional Screening Services |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Prone to errors due to lack of expertise. | High accuracy with trained professionals. |
| Compliance | Risk of non-compliance with laws like the FCRA. | Full compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. |
| Time Efficiency | Time-consuming, especially for in-depth checks. | Faster processing due to established systems. |
| Cost | May appear cheaper upfront but costly if errors occur. | Cost-effective when considering accuracy and time savings. |
| Access to Records | Limited access to public records and databases. | Extensive access to verified databases. |
Why Choose Professional Screening Services Like Precise Hire?
Precise Hire is a leading provider of background check services, offering reliable, accurate, and legally compliant solutions. Here’s why employers trust Precise Hire:
1. Streamlined Process
Precise Hire uses advanced technology to automate background screenings, ensuring fast and efficient results.
2. Comprehensive Reports
Their detailed reports include all necessary components, such as criminal records, employment verification, and credit checks, tailored to each role’s requirements.
3. FCRA Compliance
Precise Hire adheres to all federal and state laws, ensuring employers avoid legal risks while conducting screenings.
4. Expert Support
Their team of professionals assists employers at every step, from selecting screening components to interpreting results.
5. Candidate-Friendly Approach
Precise Hire ensures a transparent and respectful process, maintaining a positive candidate experience throughout the screening.
The Benefits of Professional Background Checks
- Saves Time: Delegating screening tasks to experts frees up HR teams for other priorities.
- Reduces Risk: Accurate and thorough checks prevent costly hiring mistakes.
- Ensures Compliance: Professional services ensure adherence to laws and regulations, avoiding penalties.
- Improves Candidate Quality: Comprehensive checks help identify the best-fit candidates for the role.
Legal Aspects of Background Checks
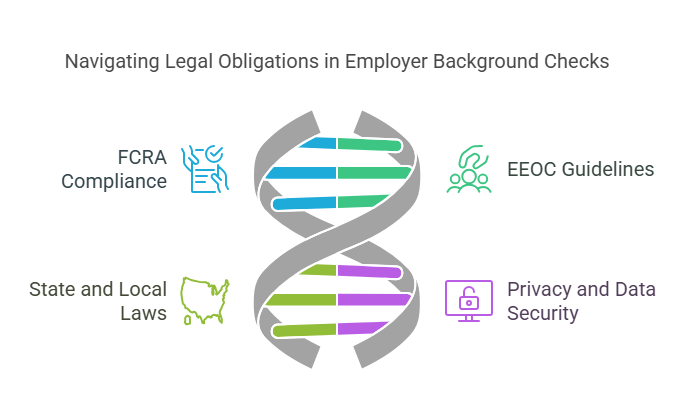
Employers must comply with laws and regulations that govern how background checks are conducted. Failure to follow these rules can result in fines, lawsuits, or reputational damage.
1. Compliance with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)
The FCRA is a federal law that outlines the rights of candidates and the obligations of employers when conducting background checks. Key requirements include:
- Written Consent: Employers must obtain written permission from the candidate before performing a background check.
- Disclosure: Candidates must be informed of the purpose of the background check and how the information will be used.
- Adverse Action Process: If the background check leads to a decision not to hire, employers must provide a copy of the report and notify the candidate of their rights.
2. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) Guidelines
Employers must ensure their background check policies comply with the EEOC guidelines, which prohibit discrimination. For example:
- Avoid blanket policies that disqualify candidates based on criminal history without considering the relevance to the job.
- Apply screening practices consistently to all candidates to prevent claims of bias.
3. State and Local Laws
Background check regulations vary by state and city. Employers should:
- Be aware of “Ban the Box” laws, which restrict inquiries about criminal history on initial job applications.
- Follow state-specific rules for reporting criminal records, such as time limits on certain convictions.
4. Privacy and Data Security
Employers must handle background check information with care to protect candidates’ privacy. Key practices include:
- Storing data securely to prevent unauthorized access.
- Sharing results only with individuals directly involved in the hiring process.
FAQs About Background Checks for a Job
Candidates and employers often have questions about background checks. Here are five frequently asked questions, with detailed answers to clarify common concerns:
What Comes Up on a Background Check for a Job?
A background check may include:
- Criminal records
- Employment and education verification
- Credit history (if relevant)
- Driving records
- Drug test results
- Identity verification
The specific components depend on the job role and industry.
How Long Do Background Checks Take?
The timeframe varies depending on the scope of the check:
- Basic checks (identity, employment, and education): 1–3 business days.
- Comprehensive checks (criminal records, credit history, and references): 5–10 business days.
Delays can occur if there’s difficulty verifying information or accessing records.
What Happens If a Background Check Reveals a Criminal Record?
Employers must evaluate the relevance of the record to the job. Factors to consider include:
- The nature and severity of the offense.
- The time elapsed since the conviction.
- Whether the offense directly impacts the candidate’s ability to perform job duties.
Candidates may also have an opportunity to explain or dispute the findings.
Can Background Checks Show False Information?
Yes, errors can occur in background reports, such as outdated or inaccurate data.
- Candidates have the right to dispute incorrect information with the reporting agency.
- Employers should use reputable screening providers, such as Precise Hire, to ensure accuracy.
Are Background Check Results Confidential?
Yes, results are confidential and should only be shared with authorized individuals involved in the hiring process.
- Unauthorized disclosure can violate privacy laws and lead to legal consequences.
What Comes Up on a Background Check for a Job?
A background check may include:
- Criminal records
- Employment and education verification
- Credit history (if relevant)
- Driving records
- Drug test results
- Identity verification
The specific components depend on the job role and industry.
How Long Do Background Checks Take?
The timeframe varies depending on the scope of the check:
- Basic checks (identity, employment, and education): 1–3 business days.
- Comprehensive checks (criminal records, credit history, and references): 5–10 business days.
Delays can occur if there’s difficulty verifying information or accessing records.
What Happens If a Background Check Reveals a Criminal Record?
Employers must evaluate the relevance of the record to the job. Factors to consider include:
- The nature and severity of the offense.
- The time elapsed since the conviction.
- Whether the offense directly impacts the candidate’s ability to perform job duties.
Candidates may also have an opportunity to explain or dispute the findings.
Can Background Checks Show False Information?
Yes, errors can occur in background reports, such as outdated or inaccurate data.
- Candidates have the right to dispute incorrect information with the reporting agency.
- Employers should use reputable screening providers, such as Precise Hire, to ensure accuracy.
Are Background Check Results Confidential?
Yes, results are confidential and should only be shared with authorized individuals involved in the hiring process.
- Unauthorized disclosure can violate privacy laws and lead to legal consequences.
Conclusion
Background checks are a critical part of the hiring process, helping employers verify candidates’ qualifications and ensure workplace safety. However, they must be conducted in compliance with legal requirements and with respect for candidates’ rights.
Key Takeaways:
- Background checks reveal information such as criminal records, employment history, education verification, and more.
- The process must comply with laws like the FCRA, EEOC guidelines, and relevant state and local regulations.
- Common FAQs address issues like timelines, accuracy, and the handling of sensitive information.
Why Choose Precise Hire? For accurate, efficient, and legally compliant background checks, professional services like Precise Hire offer invaluable support. With advanced technology, expert guidance, and a commitment to compliance, Precise Hire ensures employers can make informed hiring decisions with confidence.
