Tenant Screening Checklist: Essential Guide for Landlords and Property Managers

Tenant Screening Checklist: Why It’s Essential for Landlords and Property Managers
Introduction to Tenant Screening
Tenant screening is a vital part of the rental process, and it’s essential for landlords and property managers to conduct a thorough screening to ensure they are renting to responsible tenants. This process involves assessing various aspects of a prospective tenant’s background to gauge their suitability for the property. Tenant screening typically includes checking financial responsibility, rental history, and personal behavior to ensure the tenant is reliable and trustworthy. The goal is to find tenants who will respect the property, pay rent on time, and cause minimal issues for other tenants or neighbors.
By following a structured tenant screening checklist, landlords can mitigate risks, avoid legal issues, and create a more stable, profitable rental business.
Why Tenant Screening is Crucial

Tenant screening helps protect landlords from the following risks:
- Non-Payment of Rent: Screening helps identify tenants with a history of late payments or non-payment, reducing the likelihood of future rent-related issues.
- Property Damage: Tenants with a record of damaging rental properties or causing disturbances can be avoided through proper screening.
- Eviction: Evicting tenants is a lengthy, expensive process. Screening reduces the chances of having to deal with tenants who may eventually be evicted for failing to meet rental agreements.
- Legal Challenges: Inadequate screening can lead to discrimination claims or issues with tenant rights. By following a structured process, landlords can ensure they are compliant with the law.
Screening tenants thoroughly helps landlords build a secure, reliable tenant base, ensuring both financial stability and peace of mind.
Key Components of a Tenant Screening Checklist
A comprehensive tenant screening checklist is an essential tool for landlords to ensure that they are making informed, consistent decisions. The following are key components typically included in a screening process:
- Credit Report: To assess financial responsibility and ability to pay rent on time.
- Criminal Background Check: To identify any criminal history that may affect the safety of other tenants or the property.
- Rental History: To confirm the tenant’s history of renting, including any issues with previous landlords.
- Employment Verification: To ensure the tenant has stable income and employment.
- Income Verification: To verify the tenant’s income and ensure they can afford the rent.
- Eviction History: To identify any past evictions that could indicate potential problems.
- Personal References: To gain insight into the tenant’s character from previous acquaintances.
Each of these components is important in ensuring that the tenant is a good fit for the property and the landlord.
Types of Information Needed for Tenant Screening
When conducting tenant screening, landlords typically request the following types of information from prospective tenants:
- Personal Information: Name, contact information, and identification details.
- Rental History: Information about previous rentals, including landlord contact information and rental duration.
- Employment Details: Employer name, position, and duration of employment.
- Financial Information: Income details, including pay stubs or bank statements, to verify the tenant’s ability to pay rent.
- Criminal and Eviction History: Consent to check criminal records and eviction history to ensure tenant reliability.
Having a clear and organized tenant screening checklist ensures that all necessary information is collected and that no critical details are overlooked during the evaluation process.
How to Conduct a Thorough Tenant Screening: A Complete Checklist for Landlords
Detailed Tenant Screening Checklist
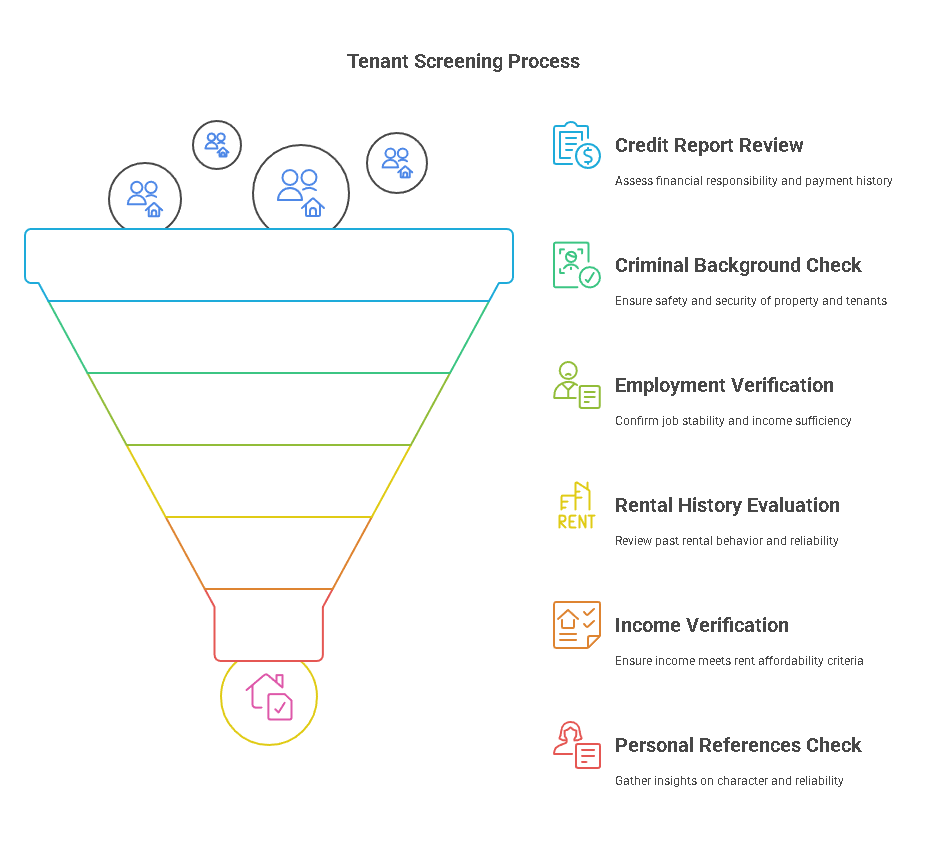
Tenant screening is a systematic process that involves verifying the information provided by a prospective tenant. Below is a detailed tenant screening checklist to guide landlords and property managers in evaluating potential tenants:
- Credit Report:
- Why it’s important: A credit report helps assess the tenant’s financial responsibility. A tenant with a high credit score is more likely to pay rent on time, while a low credit score may indicate a history of missed or late payments.
- What to look for: Review their payment history, outstanding debts, and credit utilization. Focus on any negative marks like bankruptcies, collections, or late payments.
- Criminal Background Check:
- Why it’s important: A criminal background check ensures that the tenant has no history of violent or destructive behavior that could pose a risk to the property or other tenants.
- What to look for: Look for convictions related to theft, violence, or property damage. Landlords may also check if there are any ongoing criminal cases that might affect the tenant’s stability.
- Employment Verification:
- Why it’s important: Verifying employment confirms the tenant’s financial stability and their ability to pay rent consistently.
- What to look for: Ensure the tenant has a stable job with a sufficient income to cover rent and living expenses. This can be verified through pay stubs or employer contact details.
- Rental History:
- Why it’s important: Previous rental behavior provides insight into how the tenant might behave in your property.
- What to look for: Ask previous landlords about the tenant’s payment history, how they maintained the property, and whether there were any issues with eviction.
- Income Verification:
- Why it’s important: Ensuring the tenant’s income meets a certain threshold (typically 2.5 to 3 times the rent) guarantees that they can afford to pay the rent.
- What to look for: Review pay stubs, bank statements, or tax returns to verify the tenant’s income.
- Eviction History:
- Why it’s important: A history of eviction may indicate that the tenant has difficulty adhering to rental agreements.
- What to look for: Check if the tenant has ever been evicted or if there are any ongoing legal disputes related to their rental history.
- Personal References:
- Why it’s important: Personal references can provide additional insight into the tenant’s character and reliability.
- What to look for: Contact at least two personal references to verify the tenant’s character, work ethic, and stability.
Explaining Each Step of the Checklist
- Credit Report: The credit report helps gauge the tenant’s overall financial responsibility. Tenants with excellent credit scores are likely to be punctual with rent payments, while those with poor scores may require a higher deposit or more strict lease terms. A report with a score of 700+ is generally considered good.
- Criminal Background Check: Criminal background checks are essential for ensuring tenant safety. While certain criminal records, like minor offenses, may not be grounds for rejection, violent crimes or theft may make a tenant unsuitable for rental. It is important to check both state and national records.
- Employment Verification: Verifying employment ensures the tenant has the income to pay rent and confirms their financial stability. If a tenant cannot provide sufficient proof of income, they may be deemed unqualified, or a larger security deposit might be required.
- Rental History: Reviewing rental history helps identify any potential red flags, such as frequent moves or disputes with previous landlords. A tenant with a strong rental history and positive references is likely to be a good fit for your property.
- Income Verification: Income verification ensures the tenant can comfortably afford the rent. It’s essential that the tenant’s monthly income is enough to cover the rent and any additional living expenses. If the income is borderline, you may want to ask for a larger deposit or a co-signer.
- Eviction History: Tenants with an eviction history may pose risks, as they might be prone to violating lease terms. While past evictions do not automatically disqualify tenants, you should evaluate the reasons for eviction and whether the tenant has taken steps to resolve past issues.
- Personal References: Personal references provide additional context about the tenant’s behavior, responsibility, and character. Be sure to contact at least two personal references to gain a holistic view of the tenant.
Precisehire’s Services for Tenant Screening
Precisehire offers comprehensive background screening services that can assist landlords and property managers in conducting thorough tenant evaluations. By using Precisehire, landlords can access up-to-date credit reports, criminal background checks, eviction histories, and income verification tools to ensure their tenants are reliable and trustworthy.
Precisehire’s platform simplifies the tenant screening process, ensuring compliance with local, state, and federal regulations while providing fast, accurate, and secure results.
Comparison of Tenant Screening Tools
| Screening Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Online Tenant Screening Services | Fast, easy to use, accessible anytime | May be expensive for landlords with limited budgets |
| Traditional Screening Methods | Provides a personal touch, customizable | Time-consuming, labor-intensive |
| Professional Screening Services (e.g., Precisehire) | Accurate, legal-compliant, comprehensive | May incur service fees, requires subscription |
Legal Considerations in Tenant Screening
Tenant screening is a vital part of the rental process, but it is also heavily regulated. Landlords and property managers must adhere to both federal and state laws to ensure they are screening tenants legally and fairly. Below are some important legal considerations when conducting tenant screenings:
- Fair Housing Act (FHA):
- The Fair Housing Act prohibits discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, national origin, familial status, and disability. Landlords must ensure their tenant screening process is free from any bias related to these characteristics. This means that landlords cannot reject tenants based solely on race, gender, or other protected categories.
- Consent for Screening:
- Before conducting any background checks (including credit, criminal history, or eviction records), landlords must obtain the tenant’s written consent. This is required by the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) when using third-party services for background checks. Tenants must be made aware of what information will be collected and how it will be used.
- Use of Criminal History:
- While landlords can use criminal background checks to ensure tenant safety, they must be cautious in how they use this information. Some states have laws regarding the use of criminal history in housing decisions, especially regarding convictions that are no longer relevant or have occurred many years ago. Discrimination based on arrest records, without a conviction, is also illegal under some circumstances.
- Eviction History:
- Similar to criminal background checks, eviction history can be an important factor in tenant screening. However, landlords must be mindful that they cannot automatically reject tenants based solely on a past eviction, especially if the eviction was related to nonpayment of rent, which may have been caused by temporary financial hardship.
- Data Protection and Privacy:
- Tenant screening involves the collection of sensitive personal information, including social security numbers, financial data, and criminal records. Landlords must protect this data and comply with applicable data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe (if applicable) or state-specific regulations in the U.S.
By ensuring compliance with these laws, landlords can avoid costly legal issues and provide equal opportunities for all potential tenants.
Frequently Asked Questions
What information can a landlord legally request from a potential tenant?
Landlords can legally request information such as the tenant’s name, date of birth, contact details, employment history, income verification, rental history, references, and consent to conduct background checks (including credit, criminal, and eviction records). However, they cannot request discriminatory information, such as details about a tenant’s race, religion, or sexual orientation.
How long does the tenant screening process take?
The time it takes to complete tenant screening can vary depending on the depth of the checks. A basic credit and criminal background check might take a few days, while more comprehensive screenings, including verifying rental history and employment, could take up to a week. Using professional tenant screening services like Precisehire can speed up this process by providing fast, comprehensive reports.
Can a landlord reject a tenant based on criminal history?
Yes, landlords can reject tenants based on criminal history, but they must be careful not to discriminate against tenants with arrests but no convictions or against tenants whose convictions are irrelevant (e.g., a minor offense that occurred many years ago). Some states and cities have "ban the box" laws that restrict landlords from considering criminal history in certain situations. Landlords should review their state and local laws to ensure compliance.
How can landlords protect themselves from discrimination claims during screening?
To protect themselves from discrimination claims, landlords should apply the same screening criteria consistently to all applicants and document every step of the process. It is also important to stay informed about Fair Housing Act requirements and avoid any biases during the screening process. Using standardized screening forms and services like Precisehire can help ensure fairness and consistency.
How can landlords protect themselves from discrimination claims during screening?
To protect themselves from discrimination claims, landlords should apply the same screening criteria consistently to all applicants and document every step of the process. It is also important to stay informed about Fair Housing Act requirements and avoid any biases during the screening process. Using standardized screening forms and services like Precisehire can help ensure fairness and consistency.
What should a landlord do if a tenant has a bad credit history but provides a large deposit?
A tenant with a poor credit history may still be considered if they offer a larger security deposit or provide a co-signer or guarantor. Landlords can weigh the risks of accepting a tenant with bad credit against the benefits of securing a larger deposit. However, landlords should clearly define their policies on credit requirements and be transparent with tenants about what factors influence their decision.
Conclusion
Tenant screening is a critical process that helps landlords choose responsible tenants while protecting their property and investment. By following a structured checklist and adhering to legal requirements, landlords can ensure they are selecting tenants who are likely to pay rent on time, respect the property, and contribute to a positive rental experience.
The tenant screening process should be thorough, consistent, and legal. Landlords should also consider using reliable services like Precisehire for background checks, which streamline the process and provide accurate, up-to-date information for informed decision-making. Taking the time to properly screen tenants will help prevent potential legal issues and avoid future problems with rent collection, property maintenance, and tenant relationships.
By following a well-structured tenant screening checklist and staying informed about relevant legal aspects, landlords can successfully manage their rental properties and create a safe, stable living environment for all tenants.
