MTD Drug Screening Explained: Everything You Need to Know About Methadone Testing

Understanding MTD Drug Screening: Purpose, Process, and Applications
What is MTD Drug Screening?
MTD drug screening refers to the process of testing for methadone and related substances in an individual’s system. Methadone is a synthetic opioid medication commonly used in opioid substitution therapy (OST) to treat opioid addiction, such as heroin addiction. It works by blocking the effects of opioids and preventing withdrawal symptoms without producing the high associated with opioid misuse. This makes it a valuable tool in addiction treatment, particularly for individuals recovering from opioid dependency.
While methadone has beneficial uses, it also has the potential for abuse, especially when used outside of a prescribed treatment plan. This is where MTD drug screening becomes essential. MTD drug screening specifically targets methadone use in an individual’s system, providing insight into whether a person is adhering to their prescribed treatment or engaging in misuse.
MTD drug tests are commonly used by employers, healthcare providers, rehabilitation centers, legal systems, and courts to ensure that individuals are not under the influence of methadone when they are expected to be functioning at their best. This includes testing for compliance in addiction recovery programs, ensuring workplace safety, or meeting legal requirements in court-ordered programs. The results from an MTD drug test help decision-makers to determine the extent of methadone use in an individual’s system and take appropriate action based on the findings.
Why MTD Drug Screening is Important
MTD drug screening serves an important role in ensuring safety, compliance, and appropriate treatment monitoring. Below are some of the most common reasons why MTD drug screening is utilized:
1. Workplace Safety and Compliance
Employers in various industries may require drug testing as part of their hiring process or as a routine practice to maintain a safe, drug-free workplace. In particular, industries such as transportation, healthcare, and construction, where safety is a primary concern, need to ensure that employees are fit to work and are not under the influence of methadone or other drugs that may impair their judgment, reflexes, or decision-making abilities. Methadone, if used improperly, can cause drowsiness, slowed reaction times, and difficulty focusing—all of which can significantly affect job performance, particularly in safety-sensitive positions.
Workplace drug screening helps employers ensure that their employees are functioning at their best and following safety protocols. Additionally, for individuals who are undergoing methadone maintenance therapy (MMT) as part of opioid addiction treatment, MTD drug screening is important to confirm they are following their prescribed regimen rather than misusing methadone.
2. Rehabilitation and Treatment Monitoring
Rehabilitation centers that specialize in addiction recovery often utilize MTD drug screening to monitor patients’ adherence to their prescribed methadone treatment. Methadone is used to help individuals overcome opioid dependency by providing a controlled dose of the substance. Regular screening ensures that the patient is not using methadone beyond the prescribed dosage and is not using illegal opioids while participating in the recovery program.
In these settings, the focus of MTD drug screening is to maintain the effectiveness of the treatment and prevent misuse. Furthermore, if a patient tests positive for illicit methadone use or other opioids, it can help healthcare providers identify potential treatment issues or relapses early on.
3. Legal and Court-Ordered Drug Testing
In legal settings, especially in cases involving probation or parole, MTD drug screening may be required to ensure compliance with the terms of a court-ordered treatment plan. Individuals who have been convicted of opioid-related offenses, such as heroin addiction, may be ordered by the court to undergo methadone treatment and periodic drug screenings. These tests confirm whether the individual is adhering to their treatment plan and not engaging in substance abuse.
Additionally, MTD drug screening can be used to evaluate compliance with child custody agreements, probation conditions, or other legal proceedings. Courts rely on drug test results to determine whether an individual is following prescribed treatments and taking the necessary steps toward rehabilitation.
4. Healthcare Monitoring and Patient Care
Healthcare providers, including physicians and addiction specialists, use MTD drug screening to monitor the treatment progress of patients undergoing methadone maintenance therapy. This is particularly important for patients in long-term addiction treatment programs who require regular check-ins to ensure they are receiving the proper care and adhering to their treatment regimen. Methadone testing in healthcare settings helps providers determine whether the patient is taking their medication as prescribed or if adjustments are needed to the treatment plan.
Additionally, medical practitioners may utilize MTD drug screening to evaluate potential drug interactions or to determine whether a patient is misusing methadone by combining it with other illicit substances. This can guide healthcare providers in offering appropriate interventions and optimizing patient care.
What Does MTD Stand For?
The acronym MTD stands for “Methadone Drug Testing” in the context of drug screening. Methadone is a substance that, when misused, can have serious consequences. It is important to differentiate between prescribed methadone use in a therapeutic setting and its misuse. As methadone is often used in the treatment of opioid addiction, MTD drug screening plays an important role in ensuring that those who use methadone for recovery are doing so within the guidelines of their treatment plan.
MTD drug tests detect methadone in various biological samples, such as urine, saliva, or blood, depending on the type of test used. These tests are designed to detect recent use of methadone and, in some cases, may also detect other opioids or substances that can interfere with the treatment process.
Types of Methadone Drug Tests
There are several types of tests used to screen for methadone use, each with its advantages and limitations. The most common types of MTD drug tests include:
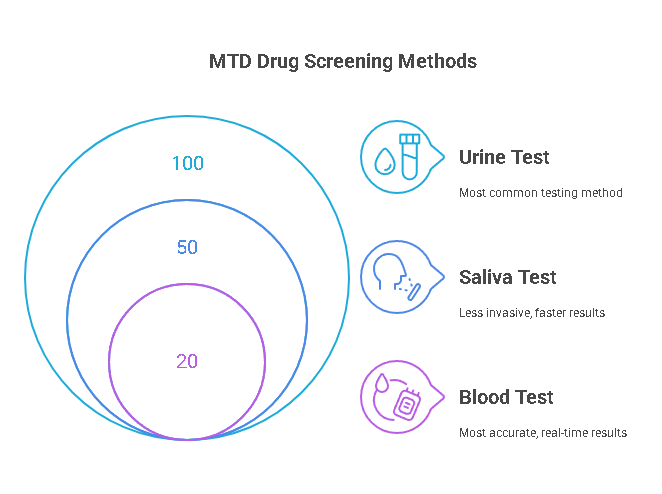
- Urine Drug Test: The most common and widely used method of drug testing, urine drug tests can detect methadone for up to seven days, depending on the frequency of use and the individual’s metabolism. Urine tests are cost-effective, easy to administer, and non-invasive, making them a preferred choice in many situations, such as workplace testing and rehabilitation monitoring.
- Blood Drug Test: Blood tests are more invasive and costly compared to urine tests. However, they provide an accurate and immediate snapshot of methadone levels in the bloodstream. Blood tests are typically used in situations where immediate results are necessary, or when more accurate data on recent use is required.
- Saliva Drug Test: Saliva tests are gaining popularity as they are less invasive than blood tests but provide quicker results than urine tests. Saliva tests can detect methadone within a 24 to 48-hour window, which makes them useful for monitoring recent methadone use, especially in workplace or legal settings where immediate results are needed.
Why MTD Drug Screening Matters
The importance of MTD drug screening extends beyond detecting misuse—it helps ensure the integrity of treatment programs, maintains safety in workplaces, and ensures compliance in legal settings. Whether it’s confirming that an employee is drug-free, verifying that a rehabilitation patient is following their treatment regimen, or ensuring compliance with court orders, MTD drug screening plays a vital role in protecting both individuals and organizations from the consequences of methadone misuse. Furthermore, it helps to create a safer, more productive environment for everyone involved, from employees and patients to employers and legal authorities.
The Process of MTD Drug Screening: Methods, Testing, and Compliance
How MTD Drug Screening is Conducted
MTD (Methadone Drug) drug screening is typically performed through various testing methods, including urine, saliva, and blood tests. Each method offers different advantages depending on the specific needs of the test, such as how recently the substance was used, the cost, or the level of accuracy required. Below, we’ll walk through each of the sample types commonly used for MTD drug screening and explain the processes involved in collecting, analyzing, and interpreting the results.
1. Urine Drug Test for MTD Screening
Urine drug testing is the most widely used method for detecting methadone use in drug screening. It is non-invasive, easy to administer, and cost-effective, making it the preferred method in many employment settings, legal cases, and rehabilitation programs. Here is a step-by-step breakdown of the urine drug screening process:
- Sample Collection: The individual is asked to provide a urine sample. For accuracy, the sample is typically collected in a controlled environment to prevent tampering or adulteration of the specimen.
- Laboratory Analysis: The urine sample is sent to a laboratory where the concentration of methadone and other related substances (if applicable) is measured using techniques like immunoassay or gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). These methods are highly accurate and reliable for identifying methadone and its metabolites.
- Detection Window: Methadone can typically be detected in urine for up to 7 days after use, although this detection window can vary depending on the frequency of use, the individual’s metabolism, and the dose taken. In chronic users, methadone may be detectable for longer periods.
- Result Interpretation: The laboratory will provide results that indicate the presence or absence of methadone. If methadone is present in the sample, further analysis may be performed to confirm the concentration and assess whether it falls within the expected therapeutic range for prescribed methadone use.
2. Saliva Drug Test for MTD Screening
Saliva testing is another common method for drug screening, particularly in workplace settings or situations where quick results are needed. This type of test is less invasive than urine testing and can be administered on-site. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Sample Collection: The individual is asked to provide a saliva sample by swabbing the inside of their cheek or under their tongue. This method is simple, non-invasive, and can be performed in a matter of minutes.
- Laboratory Analysis: Similar to urine testing, saliva samples are sent to a laboratory where they are analyzed to detect methadone or related substances. Immunoassay techniques are often used for initial screening, followed by confirmation using more precise methods such as GC-MS if the initial result is positive.
- Detection Window: Saliva tests typically have a shorter detection window compared to urine tests. Methadone can usually be detected in saliva for up to 48 hours after use, making it ideal for identifying recent methadone ingestion.
- Result Interpretation: The laboratory will analyze the saliva sample for the presence of methadone and other substances. The results will indicate whether methadone use is present and, if detected, will provide additional details about the concentration.
3. Blood Drug Test for MTD Screening
Blood tests are the most invasive method for MTD drug screening but offer the highest level of accuracy and immediate results. This method is used when precise, real-time information about the individual’s drug use is required, such as in emergency medical situations, court-ordered testing, or for detecting very recent drug use. Here’s an overview of how blood testing works:
- Sample Collection: A blood sample is drawn from the individual by a trained professional. This procedure typically takes place at a medical facility or laboratory.
- Laboratory Analysis: The blood sample is analyzed in a laboratory to measure the concentration of methadone in the bloodstream. Blood tests can accurately identify recent methadone use, as methadone is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream.
- Detection Window: Blood tests have the shortest detection window for methadone use, typically identifying use within 24 to 48 hours after ingestion. This makes blood testing an effective method for confirming current use.
- Result Interpretation: The results will show the concentration of methadone in the blood, helping healthcare providers, employers, or legal authorities understand the extent of methadone use at the time of testing.
Key Considerations in MTD Drug Screening
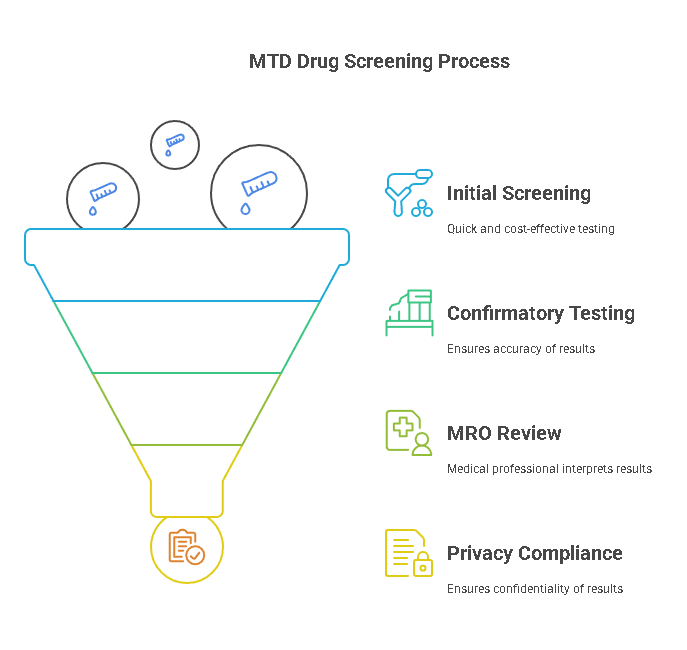
MTD drug screening is not just about detecting the presence of methadone; it’s also about ensuring accuracy, reliability, and compliance with industry standards. Here are some important factors to consider when conducting methadone drug screening:
1. Accuracy and Confirmation of Results
The accuracy of drug test results is critical to making informed decisions. Many drug tests, including MTD screening, begin with an initial screening process, followed by a confirmatory test to rule out false positives. Initial testing methods, such as immunoassays, are cost-effective but may yield false positives in some cases. If the initial test is positive for methadone, a confirmatory test, such as GC-MS, is often performed. GC-MS provides highly accurate and detailed analysis of the sample, ensuring that the results are correct and reliable.
2. Role of Medical Review Officers (MROs)
In the case of workplace drug testing, a Medical Review Officer (MRO) plays an essential role in reviewing and interpreting drug test results. MROs are licensed physicians or professionals trained in interpreting drug test results in accordance with regulatory standards. They ensure that the test results are accurate, verify whether there is a legitimate medical explanation for a positive result, and act as an intermediary between the testing facility and the employer or organization requesting the test. For example, if an employee tests positive for methadone, the MRO will review the individual’s prescription history and medical records to determine whether the methadone was used in compliance with a legitimate prescription or whether misuse has occurred.
3. Privacy and Confidentiality
The process of conducting an MTD drug test must adhere to strict privacy and confidentiality guidelines. Employers and healthcare providers are required to maintain the confidentiality of drug testing results to protect individuals’ rights to privacy. This is especially important in workplace testing, as drug test results can have a significant impact on employment status and career progression.
Similarly, healthcare providers and rehabilitation centers are legally obligated to protect the confidentiality of patients’ drug test results as part of patient care and treatment. Federal and state laws, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), require that drug testing results remain confidential and are only shared with authorized individuals or entities.
The Role of Precisehire in MTD Drug Screening
Precisehire is a trusted provider of drug screening services, offering reliable and compliant MTD drug testing solutions to employers, rehabilitation centers, healthcare providers, and legal authorities. Our platform simplifies the drug screening process by providing fast, accurate, and legally compliant drug tests that ensure the highest level of service. We work with certified laboratories and offer a range of testing options, including urine, saliva, and blood tests, to meet the unique needs of our clients.
With Precisehire, employers can confidently ensure workplace safety and compliance with drug testing regulations, while healthcare providers and rehabilitation centers can accurately monitor patient adherence to methadone treatment. We provide timely results, reliable data, and comprehensive reporting, helping decision-makers act with confidence.
Key Details of the MTD Drug Screening Process
Here is a summary of key details regarding the MTD drug screening process, including the different types of samples, timeframes for results, and costs associated with MTD testing:
| Test Type | Sample Type | Detection Window | Cost | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urine Drug Test | Urine | Up to 7 days | $30 – $60 per test | Workplace drug testing, rehabilitation monitoring |
| Saliva Drug Test | Saliva | Up to 48 hours | $25 – $50 per test | Immediate drug screening, workplace testing |
| Blood Drug Test | Blood | 24 to 48 hours | $100 – $200 per test | Medical emergencies, court-ordered testing |
Legal Aspects of MTD Drug Screening
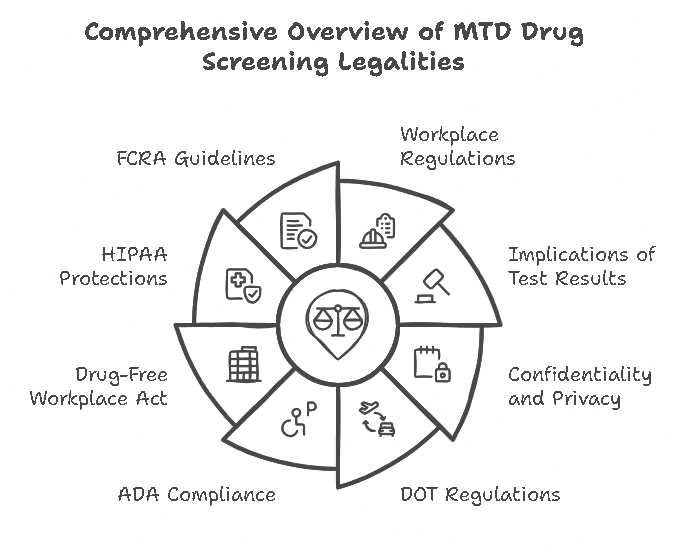
MTD (Methadone Drug) screening is not only critical for ensuring workplace safety, compliance with treatment protocols, and the integrity of legal proceedings, but it is also governed by several legal frameworks and regulations. These laws ensure that drug screening practices are carried out fairly, respect individual privacy, and do not lead to discrimination. The following sections outline the key legal aspects of MTD drug screening.
1. Regulations Governing Drug Screening in Workplaces
The U.S. federal government and individual states have established various regulations to govern drug screening, particularly in workplace environments. These regulations dictate how MTD drug tests must be conducted, what substances can be tested for, and how results should be handled. Employers must ensure compliance with these laws to avoid legal liabilities and maintain a fair and ethical drug testing process.
- Department of Transportation (DOT) Regulations: For industries regulated by the Department of Transportation, such as transportation and aviation, MTD drug screening must adhere to DOT drug testing regulations. These regulations include mandatory testing for certain substances and specific procedures for conducting and handling drug tests, including methadone.
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA): The ADA prohibits employers from discriminating against employees based on their disability status. While employers have the right to conduct drug screenings for safety reasons, they must be careful when it comes to individuals in methadone treatment programs. If an employee is in a legally prescribed methadone program, the employer cannot automatically consider them unfit for work solely due to the medication.
- Drug-Free Workplace Act: This act requires employers receiving federal funding or grants to establish a drug-free workplace policy. MTD drug screening may be part of these policies to ensure employees are not under the influence of illegal drugs or substances that impair job performance.
2. Implications of MTD Drug Screening Results
The results of an MTD drug screening can have significant consequences for various individuals, including employees, applicants, and individuals undergoing treatment. The legal implications of these results depend on the context in which the drug test was conducted.
- Employment Context: If an employee or job applicant tests positive for methadone, employers must follow specific protocols. For instance, if methadone is used legally under a prescription for opioid addiction treatment, the employer may need to allow for accommodations, such as modifying job duties or offering leave. However, if the individual is using methadone outside the prescribed guidelines, they may face disciplinary actions or termination based on company policy.
- Rehabilitation Programs: For individuals in methadone treatment programs, the test results are often used to monitor progress and ensure adherence to the prescribed treatment plan. In this context, the legal implications are focused on maintaining compliance with treatment protocols rather than punishing individuals for their use of methadone. Rehabilitation centers must ensure they handle results in a confidential manner to protect patient privacy.
- Legal Cases: In legal cases, such as court-ordered drug testing, MTD drug screening can be used as evidence in determining whether an individual has complied with probation or parole conditions, or if they are fit to stand trial. Methadone use in these contexts is often treated differently from illicit drug use, particularly when it is prescribed for addiction recovery. However, the legal system may still impose consequences for misuse or non-compliance.
3. Confidentiality and Privacy Protection
Confidentiality is a critical concern in drug testing, including MTD drug screening. Federal and state laws ensure that drug test results are handled with the highest level of privacy protection.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): For individuals undergoing drug testing as part of medical treatment or rehabilitation, their results are protected by HIPAA regulations. These rules prohibit unauthorized access to test results and ensure that any shared information is used solely for medical or treatment purposes.
- Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA): The FCRA governs how background checks, including drug screening results, can be used in employment decisions. Under this law, employers must provide clear notifications to individuals about the testing process and their rights regarding the use of their results. Employers must also obtain written consent before conducting a drug screening and follow specific procedures if they decide to take adverse action based on test results.
- State-Specific Privacy Laws: In addition to federal laws, many states have their own privacy laws that protect individuals’ rights regarding drug testing. Employers, healthcare providers, and other organizations must comply with these state-specific laws to avoid violating privacy rights.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about MTD Drug Screening
How accurate is an MTD drug test?
MTD drug tests are highly accurate, especially when confirmatory testing methods such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) are used. Initial screening tests may provide false positives or negatives, but confirmation testing ensures reliable results.
How long does it take to get results from an MTD drug test?
The time to receive results from an MTD drug test varies depending on the sample type and laboratory processing times. Urine and saliva tests typically take 1-3 business days, while blood tests may take longer due to the complexity of the analysis. Employers and organizations should plan accordingly for the processing time.
What substances does an MTD drug screening detect?
An MTD drug screening primarily detects methadone and its metabolites. It may also detect other substances related to methadone use, depending on the specific drug panel used during testing.
Can a person test positive for methadone without using it?
It is unlikely for a person to test positive for methadone unless they have used the substance. However, certain prescription medications or substances with similar chemical properties may occasionally lead to a false positive. This is why confirmatory tests are essential.
What should an employer do if an employee tests positive for methadone in an MTD drug test?
If an employee tests positive for methadone, the employer should verify whether the methadone is being used as part of a legally prescribed treatment program. If the use is legitimate, accommodations may be required. If the use is unauthorized, the employer may need to follow company policy regarding disciplinary actions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, MTD drug screening is a critical tool used to detect methadone and its metabolites in various contexts, including employment, rehabilitation, and legal proceedings. It is essential to understand the procedures, legal regulations, and implications of MTD drug tests to ensure compliance and protect both individuals and organizations.
For employers, healthcare providers, and legal professionals, it is crucial to be familiar with the legal frameworks governing drug screening and to handle test results with confidentiality and care. Ensuring the accuracy of testing, maintaining privacy, and understanding the potential consequences of test results are all fundamental to using MTD drug screening effectively.
Precisehire is committed to offering accurate and compliant drug testing services, providing organizations with the tools they need to make informed decisions while adhering to legal and ethical standards.
