Key Factors in Universal Background Screening

Introduction & Overview of Universal Background Screening
Background screening is a critical part of the hiring and vetting process for many businesses. As the need for comprehensive and reliable checks increases, universal background screening has emerged as a solution that caters to various industries and hiring requirements. In this first part of our article, we will introduce universal background screening, explore its significance across multiple industries, and outline the types of information that are typically covered in such a screening process.
What is Universal Background Screening?
Universal background screening refers to the process of collecting and evaluating a broad spectrum of information to assess the suitability of individuals for a given role, partnership, or position. Unlike more specialized background checks that might only look at specific areas like criminal history or credit reports, universal background screening offers a more holistic view of a person’s background.
The term “universal” in this context emphasizes the versatility and wide application of these checks. Universal background screening is designed to provide employers and organizations with a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s past, which can help in making informed decisions about employment, tenancy, partnerships, and other professional relationships.
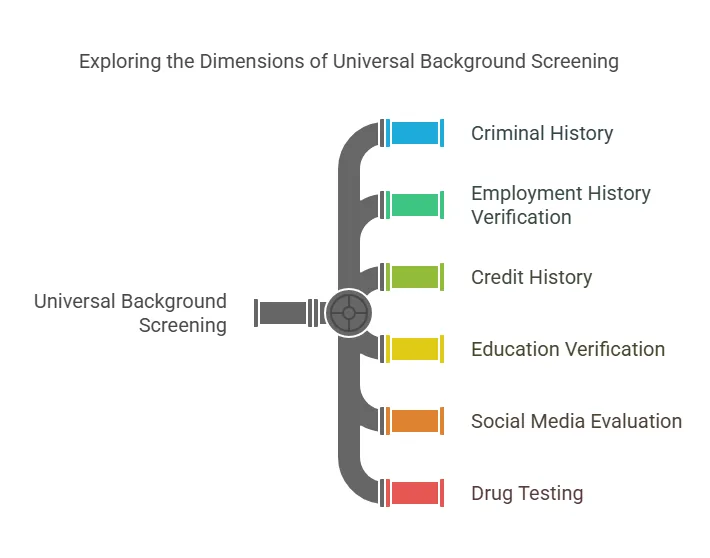
Universal background screening typically covers various checks such as:
- Criminal history
- Employment history verification
- Credit history (where applicable)
- Education verification
- Social media and online presence evaluation
- Drug testing (in some cases)
- Driving records (for positions requiring a vehicle)
- Professional licensing verification
This comprehensive approach ensures that employers and other organizations are assessing all aspects of a candidate’s background, which helps mitigate risks related to fraud, criminal activity, financial mismanagement, and other concerns.
How Does Universal Background Screening Differ from Other Background Check Services?
Universal background screening stands apart from traditional background checks by offering a broader scope of verification. While standard background checks might focus on one or two areas of a person’s history, universal background screening ensures that a wide range of information is considered in the assessment. Here’s how it compares to other types of background checks:
- Standard Background Check: A standard background check may only include criminal history, employment verification, and possibly a credit report. It is more limited in scope and typically used for general hiring purposes.
- Universal Background Check: A universal background screening service covers a wider range of information, offering insights into criminal records, credit history, past employment, educational background, and even social media activity. This makes it more suitable for organizations that need a well-rounded picture of a candidate.
- Specialized Background Check: These checks are designed for specific industries or roles. For example, healthcare background checks may focus on verifying professional certifications, while financial services background checks may give more weight to credit history and financial standing. Universal background screening, on the other hand, is not industry-specific and is applicable across various sectors.
While specialized background checks may provide in-depth verification in one area, universal background screening offers a more comprehensive approach to employee evaluation, making it suitable for companies that require a thorough review of a candidate’s qualifications and character.
Importance of Universal Background Screening Across Various Industries
Universal background screening plays a critical role in ensuring that organizations hire individuals who are trustworthy, reliable, and suitable for the job at hand. The necessity of background screening is not confined to a specific industry—virtually every sector can benefit from conducting thorough screenings to minimize risk and ensure organizational integrity.
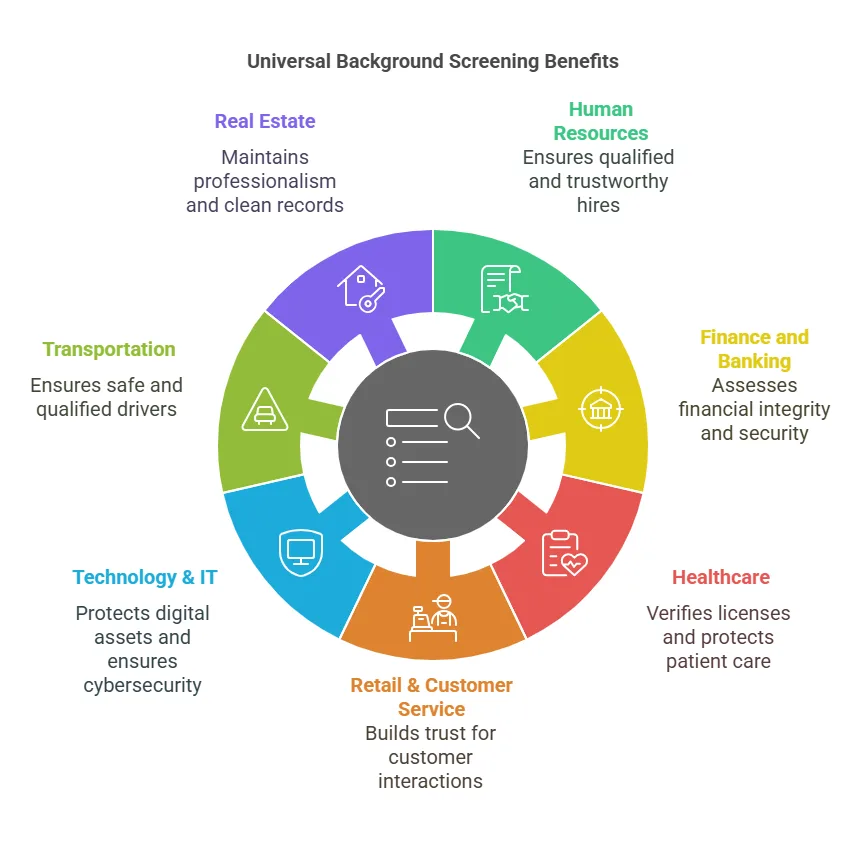
- Human Resources & Recruitment: In HR, universal background screening is fundamental for verifying the credentials of potential employees. Employers are responsible for ensuring that their hires have the necessary qualifications and that they don’t pose any security or financial risks to the company.
- Finance and Banking: In industries like finance and banking, companies need to ensure that potential employees have a strong financial standing and no criminal history that could jeopardize their ability to handle sensitive data and transactions. Universal background checks help assess creditworthiness, employment history, and other critical factors.
- Healthcare: Healthcare organizations rely on universal background screening to ensure that candidates do not have a history of criminal behavior or fraudulent activity, which could be detrimental to patient care. Additionally, verifying professional licenses, education, and employment history is essential to maintaining high standards of healthcare service delivery.
- Retail & Customer Service: In customer-facing industries, universal background screening is important for ensuring that candidates are trustworthy and reliable, particularly when handling cash, managing inventory, or accessing sensitive customer information.
- Technology & IT: Tech companies often use universal background screening to evaluate candidates’ cybersecurity skills, technical expertise, and criminal history. Protecting digital assets and maintaining secure cloud systems requires hiring candidates who have the right skills and a clean record.
- Transportation: In transportation and logistics, organizations use universal background screening to verify driving records, criminal history, and employment history to ensure that drivers are qualified and safe to operate vehicles.
- Real Estate: For real estate agencies, background screening helps ensure that agents, property managers, and contractors have a clean criminal record and a history of professionalism. It also helps verify past employment and education in the real estate field.
What Type of Information is Typically Covered in Universal Background Screening?
When conducting a universal background check, a wide range of information is evaluated to assess a candidate’s qualifications, reliability, and integrity. Here are the key components typically included in a universal background check:
- Criminal History Check: This is one of the most common components of a universal background check. It involves checking local, state, and national criminal databases to assess whether the candidate has any felony or misdemeanor convictions that could pose a risk to the organization. This check helps identify red flags such as history of violence, fraud, theft, or other serious criminal activities.
- Employment History Verification: Verifying the accuracy of a candidate’s employment history is a crucial part of universal background screening. Employers check the dates of previous employment, job titles, and reasons for leaving. This process helps ensure that candidates have the experience they claim to have and that they didn’t leave previous jobs under unfavorable circumstances.
- Credit History Check: This component is typically included in background checks for positions that involve managing financial resources or accessing sensitive financial data. The credit report assesses the candidate’s financial responsibility, revealing issues such as bankruptcies, unpaid debts, or history of financial mismanagement.
- Educational Background Verification: Universal background screening includes verifying the educational credentials claimed by the candidate, including degrees earned, institutions attended, and dates of attendance. This check ensures that the candidate has the qualifications they claim and helps prevent fraudulent claims.
- Social Media and Online Presence Review: Many companies conduct a review of a candidate’s social media accounts and other online activity to assess their character and professionalism. This can include checking public social media profiles, blogs, or any online content that could influence the hiring decision.
- Professional Licensing and Certification Verification: For certain roles, particularly in healthcare, finance, and law, verifying professional licenses and certifications is a crucial part of universal background screening. This ensures that the candidate is properly credentialed and in good standing with the relevant governing bodies.
- Drug Testing: Some organizations include drug testing as part of the background check process, particularly for roles in safety-sensitive industries such as transportation, healthcare, or manufacturing.
- Driving Record Check: For roles that involve operating a vehicle, a driving record check is an essential part of the universal background screening process. This checks for any history of traffic violations, accidents, or DUI convictions.
How Universal Background Screening Works: Step-by-Step Guide
Conducting a universal background screening involves several key steps, each designed to gather critical information about a candidate’s past. This process ensures that employers and organizations make well-informed decisions about who they hire, partner with, or do business with. Here’s a step-by-step guide to how the process typically works:
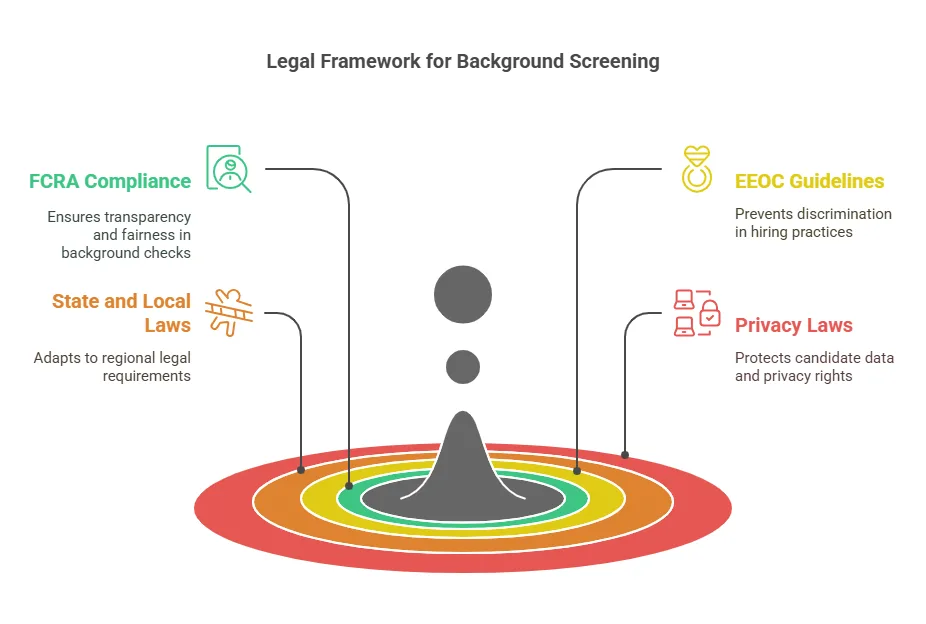
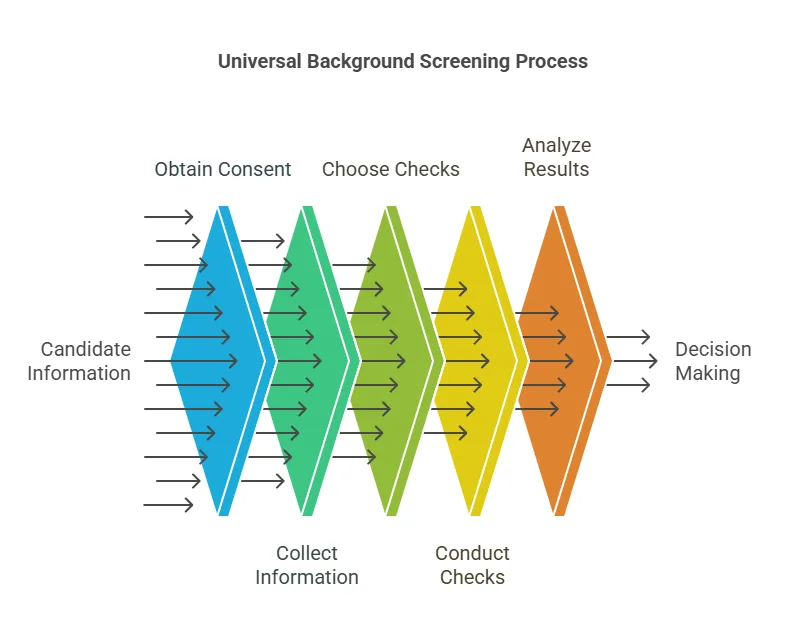
- Candidate Consent and Authorization Before any background check is conducted, the candidate must give their explicit consent to the process. Under laws such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), employers are required to obtain written permission before conducting a background check. This ensures that the candidate is aware of the screening and agrees to the collection of their information. Failure to obtain consent can result in legal repercussions.
- Collecting Basic Information After obtaining consent, the employer or organization collects the necessary information to initiate the background check. This typically includes the candidate’s full name, date of birth, social security number (in some cases), address history, and contact information. These details help verify the identity of the individual and ensure that the background check is accurate.
- Choosing the Type of Checks The next step is to determine which specific background checks need to be performed. Universal background screening usually includes a combination of the following checks:
- Criminal record check: Verifies whether the candidate has any criminal history.
- Employment history verification: Confirms past jobs, roles, and dates of employment.
- Credit history check: Assesses the candidate’s financial behavior, typically for roles that involve financial responsibilities.
- Educational verification: Confirms the authenticity of claimed educational qualifications.
- Professional license verification: Ensures the candidate holds valid licenses for specific fields, such as healthcare, legal, or financial services.
- Driving record check: For positions that require driving, this check ensures the candidate has a clean driving history.
- Conducting the Background Checks With the candidate’s consent and the necessary information at hand, the background check process begins. Depending on the type of information being verified, the process may involve accessing various public and private databases, contacting previous employers, or verifying educational institutions. For example, criminal history checks might involve accessing national, state, and county-level criminal databases, while employment history checks could require reaching out to previous employers directly.
- Analyzing the Results After gathering the necessary information, the background screening company or employer analyzes the results. This is the stage where any red flags are identified—whether it’s a criminal record, discrepancies in employment history, or financial problems in the candidate’s past. Employers typically review these findings carefully to ensure they align with the requirements of the role.
- Providing the Report Once the background check is complete, the results are compiled into a comprehensive report, which is shared with the employer or organization requesting the check. This report will include detailed information about the candidate’s criminal history, employment history, financial standing, and any other relevant data. In some cases, the report may also include a summary or recommendations based on the findings.
- Making the Decision Based on the background screening report, the employer or organization decides whether to proceed with the candidate’s application. If the candidate is cleared, they may proceed to the next stage of the hiring process. If any red flags are identified, the employer may choose to either move forward with caution or reject the candidate. Employers are advised to ensure compliance with all applicable laws, such as the EEOC guidelines and FCRA, when making decisions based on background check results.
Key Components of Universal Background Screening
Universal background screening covers a broad range of components, each of which provides valuable insights into a candidate’s background and suitability for the role. Below are the key elements of a typical universal background check:
- Criminal Record Check One of the most critical aspects of background screening, criminal record checks help determine if a candidate has any criminal convictions that might affect their ability to perform the job or pose a risk to the organization. This check can include:
- Felony and misdemeanor convictions
- Pending charges or ongoing investigations
- Arrest records (depending on jurisdiction)
A criminal record check is particularly important for roles involving trust, security, or access to sensitive information, such as positions in healthcare, finance, or law enforcement.
- Employment History Verification Verifying past employment is essential for confirming the qualifications and experience of a candidate. This check typically involves:
- Verifying the job title, dates of employment, and responsibilities.
- Contacting previous employers to verify the information.
- Checking if the candidate left on good terms or if there were any disciplinary issues.
Employers use this verification to ensure that the candidate has the relevant experience for the role and has a track record of reliability and professionalism.
- Credit History Check A credit report provides a snapshot of a candidate’s financial history. It typically includes:
- Credit score
- Outstanding debts and liabilities
- Bankruptcy history
- Payment history and debt-to-income ratio
A credit history check is particularly important for positions that require handling financial transactions or sensitive financial information, such as in banking, finance, or management roles.
- Educational Verification Verifying a candidate’s educational background is an essential part of universal background screening. This may involve:
- Confirming the degrees or diplomas claimed by the candidate.
- Verifying the institutions attended and dates of attendance.
- Checking for any honors or academic achievements.
Educational verification ensures that candidates possess the necessary qualifications for the job and helps prevent cases of resume fraud.
- Social Media & Online Presence Review Many employers now include social media and online presence evaluations as part of universal background screening. This check helps to assess the candidate’s professionalism and character by reviewing their public social media profiles, blog posts, and online content. The review typically focuses on:
- Inappropriate or offensive behavior.
- Professionalism in interactions and postings.
- Alignment with company values and culture.
- Professional License Verification For roles in regulated industries such as healthcare, law, finance, or real estate, verifying a candidate’s professional licenses is critical. This process involves checking with the appropriate licensing bodies to ensure that the candidate holds valid, up-to-date licenses or certifications required for the role.
- Drug Testing In some industries, drug testing is an essential part of the background screening process. This check helps ensure that candidates do not have a history of substance abuse that could affect their job performance, safety, or well-being. Drug testing is especially common in safety-sensitive industries like transportation, healthcare, and manufacturing.
- Driving Record Check For positions that involve driving, such as truck drivers, delivery personnel, or field service technicians, a driving record check is a key component of the background screening process. This check verifies:
- Traffic violations
- DUI or DWI convictions
- Accident history
- License suspension or revocation
Benefits of Universal Background Screening
- Improved Hiring Decisions Universal background screening helps employers make more informed decisions by providing a comprehensive view of a candidate’s qualifications, experience, and past behavior. This reduces the risk of hiring individuals who may pose a security risk, have a history of dishonesty, or lack the necessary skills for the role.
- Mitigation of Legal Risks By thoroughly screening candidates, employers can avoid hiring individuals with criminal backgrounds that could lead to legal issues. Universal background screening helps ensure that candidates meet legal and regulatory requirements for specific roles, such as those in finance, healthcare, or transportation.
- Protection of Company Reputation Hiring individuals with questionable backgrounds can damage an organization’s reputation. Universal background screening helps ensure that employees and contractors represent the company’s values and uphold its reputation in the industry.
- Enhanced Workplace Safety Verifying criminal histories and checking for drug use or driving offenses helps reduce the risk of workplace incidents and accidents. Employees with clean records are less likely to engage in unsafe or disruptive behaviors.
- Increased Employee Retention When organizations make the right hiring decisions, they are more likely to retain employees who are a good fit for the role and company culture. Thorough background checks help ensure that employees are capable, qualified, and aligned with the company’s goals and values.
Precise Hire’s Background Screening Services
At Precise Hire, we understand the importance of conducting thorough, compliant, and efficient background checks for your organization. Our comprehensive universal background screening services are designed to meet the unique needs of businesses across industries. We offer a wide range of checks, including criminal records, credit history, employment verification, and professional licensing, to ensure that your hiring decisions are informed and risk-free.