How to Perform Background Verification for Hiring

Introduction to Background Verification
In today’s fast-paced, interconnected world, trust is the cornerstone of successful relationships—whether between employers and employees, landlords and tenants, or financial institutions and borrowers. Background verification plays a pivotal role in building this trust by validating the information provided by individuals, ensuring they are reliable, qualified, and suitable for the opportunities or responsibilities they seek.
Background verification is especially critical in employment screening, where hiring the wrong candidate can lead to financial loss, reputational damage, or even legal complications. By conducting a thorough verification process, organizations can reduce risks and make well-informed decisions.
What is Background Verification?
At its core, background verification is the process of confirming the authenticity and accuracy of an individual’s personal, professional, and educational details. It involves a systematic examination of claims made by an individual—whether on a resume, in an application form, or during an interview—and cross-referencing these claims with official records or trusted sources.
Key Differences Between Background Verification and Background Checks
Though often used interchangeably, background verification and background checks differ in scope:
| Aspect | Background Verification | Background Check |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Validates the information provided by an individual. | Discovers additional or hidden information. |
| Scope | Focused on verifying specific details (e.g., education, employment). | Broader, including criminal records and credit history. |
| Process | Confirmatory in nature. | Investigative in nature. |
Why Background Verification is Important
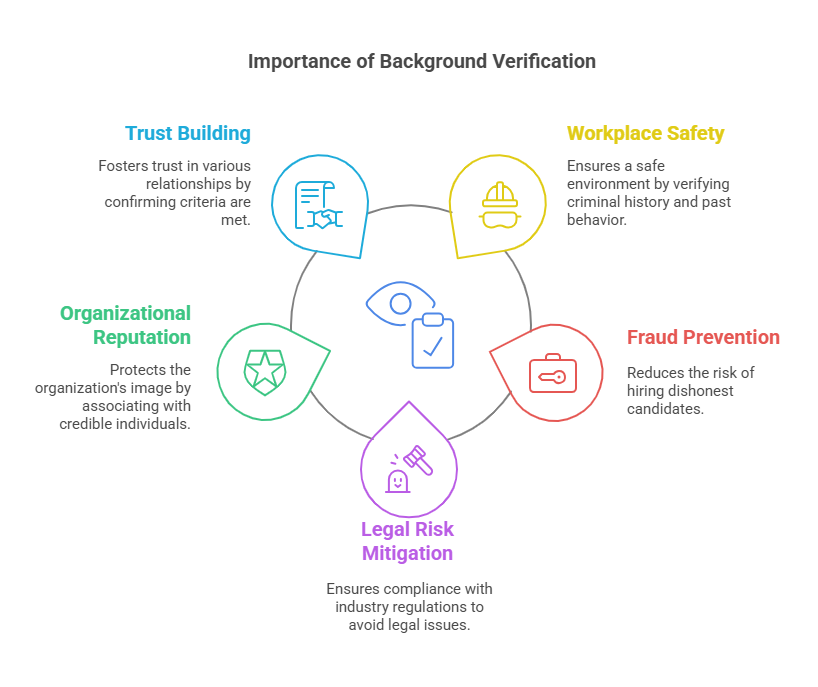
Background verification is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. The following reasons illustrate its critical role across industries:
1. Ensuring Workplace Safety
Employers have a responsibility to provide a safe working environment for their employees. Verifying criminal history, past behavior, and employment records ensures that new hires do not pose a safety risk to others.
2. Preventing Fraud and Theft
Fraudulent claims about qualifications or experience can lead to underqualified hires, causing financial or operational setbacks. Thorough background verification minimizes the chances of hiring dishonest candidates.
3. Mitigating Legal Risks
Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, have strict legal requirements for employee background verification. Non-compliance with these regulations can lead to fines, lawsuits, and reputational damage.
4. Protecting Organizational Reputation
Employing an individual who later proves untrustworthy can tarnish an organization’s reputation. Background verification ensures that only credible individuals are associated with the organization.
5. Building Trust
Whether it’s a landlord renting a property or a financial institution approving a loan, background verification fosters mutual trust by confirming that individuals meet the required criteria.
What Does Background Verification Involve?
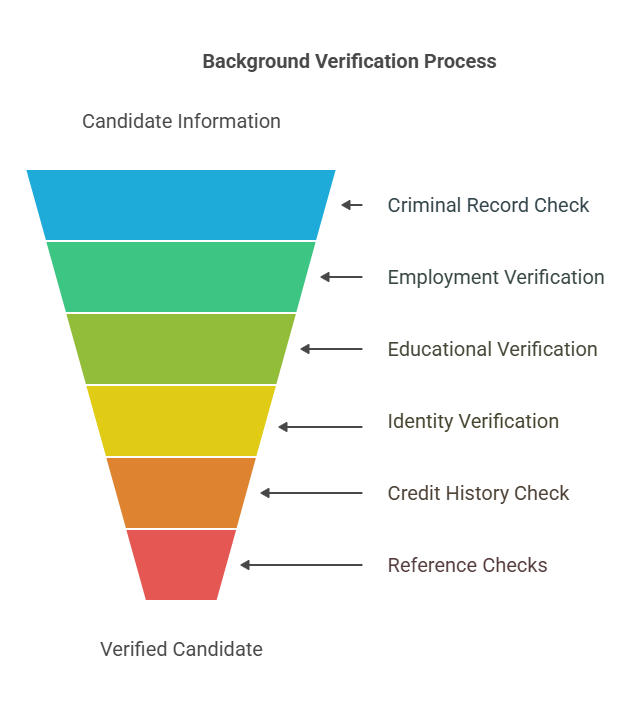
Background verification encompasses a variety of checks, each designed to address specific concerns or requirements. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
1. Criminal Record Check
This involves reviewing national and local databases to identify any criminal history, such as arrests, convictions, or court proceedings. Criminal record checks are particularly important for roles involving high security or access to sensitive data.
- Industries: Finance, healthcare, childcare, security services.
- Key Insights: Identifies risks related to safety, theft, or fraud.
2. Employment History Verification
Employment verification confirms the accuracy of past job titles, responsibilities, tenure, and reasons for leaving. This step helps ensure that candidates have the experience necessary for the role.
- Industries: Corporate, IT, education, logistics.
- Key Insights: Prevents resume fraud and validates work experience.
3. Educational Qualification Verification
This process confirms the authenticity of academic credentials, degrees, and certifications. Institutions are contacted directly to verify claims made by the individual.
- Industries: Healthcare, engineering, education, research.
- Key Insights: Validates expertise and knowledge for specialized roles.
4. Identity Verification
Identity verification ensures that the individual’s personal information (e.g., name, date of birth, social security number) matches official records. This prevents identity fraud and impersonation.
- Industries: All industries.
- Key Insights: Prevents identity theft and impersonation risks.
5. Credit History Check
Credit checks evaluate an individual’s financial behavior, highlighting any patterns of unpaid debt, defaults, or bankruptcies. These are often required for positions involving financial responsibilities.
- Industries: Banking, finance, real estate, upper management.
- Key Insights: Assesses financial responsibility and reliability.
6. Reference Checks
Reference checks involve contacting personal or professional references provided by the candidate. These checks help verify the individual’s character, work ethic, and performance in previous roles.
- Industries: All industries.
- Key Insights: Offers firsthand insights into a candidate’s behavior and performance.
7. Driving Record Checks
For roles involving transportation, such as delivery drivers or commercial vehicle operators, driving record checks are conducted to ensure safety and compliance with licensing regulations.
- Industries: Logistics, transportation, courier services.
- Key Insights: Ensures safe driving habits and legal compliance.
Benefits of Background Verification for Organizations
1. Enhanced Hiring Accuracy
By verifying details such as qualifications, employment history, and references, organizations can ensure they hire candidates who genuinely meet the requirements of the role.
2. Reduced Turnover Costs
Hiring mistakes are expensive. Background verification helps avoid these errors, leading to higher employee retention and lower recruitment costs.
3. Better Decision-Making
Comprehensive background verification provides employers with accurate, reliable data to make well-informed decisions.
4. Industry Compliance
For industries like healthcare, finance, or transportation, compliance with legal and regulatory requirements is mandatory. Background verification ensures adherence to these standards.
Types of Background Verification and the Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Each type of background verification serves a unique purpose. Below is a detailed breakdown of the most common verifications:
1. Criminal Record Checks
Criminal record checks assess whether an individual has been involved in any criminal activities, including arrests, convictions, or pending cases.
- Importance: Protects organizations from hiring individuals with a history of theft, fraud, or violence.
- Sources: National and local criminal databases, court records, and law enforcement agencies.
- Best For: High-security industries such as finance, healthcare, childcare, and government.
2. Employment Verification
Employment verification confirms the accuracy of an individual’s work history, including job titles, responsibilities, tenure, and reasons for leaving.
- Importance: Ensures the candidate has the claimed experience and skills, reducing resume fraud.
- Sources: Direct contact with previous employers, official employment records, and third-party verification agencies.
- Best For: Corporate jobs, leadership roles, and industries requiring specialized experience.
3. Educational Qualification Verification
Educational verification involves confirming degrees, certifications, and academic records to validate a candidate’s qualifications.
- Importance: Ensures the individual meets the educational requirements for the role, especially in technical or specialized fields.
- Sources: Direct contact with educational institutions and records databases.
- Best For: Healthcare, engineering, teaching, and research positions.
4. Identity Verification
This type of verification ensures that the individual’s identity matches official records, including their name, date of birth, and government-issued identification (e.g., Social Security Number, passport, or driver’s license).
- Importance: Prevents identity theft, impersonation, and fraudulent activities.
- Sources: Government databases and identity verification software.
- Best For: All industries and roles requiring trust and accountability.
5. Credit History Checks
Credit checks evaluate an individual’s financial history, including payment patterns, outstanding debts, and bankruptcies.
- Importance: Assesses financial responsibility, especially for roles involving access to funds or sensitive financial information.
- Sources: Credit bureaus and financial institutions.
- Best For: Banking, finance, and upper management positions.
6. Reference Checks
Reference checks involve contacting the candidate’s provided personal or professional references to gain insight into their character, skills, and past performance.
- Importance: Offers a first-hand perspective on the candidate’s behavior and capabilities.
- Sources: Direct communication with references (supervisors, colleagues, etc.).
- Best For: All roles where character assessment is essential.
7. Driving Records
Driving record checks verify whether the individual holds a valid license and assess their history of traffic violations or accidents.
- Importance: Ensures the safety and reliability of candidates in driving-related roles.
- Sources: Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) and transportation authorities.
- Best For: Logistics, transportation, and courier services.
8. Drug Testing and Medical History
Some employers require drug testing to ensure that candidates adhere to workplace safety and health standards.
- Importance: Minimizes safety risks and ensures compliance with industry-specific regulations.
- Sources: Licensed medical testing facilities.
- Best For: Healthcare, construction, and roles requiring heavy machinery operation.
How Background Verification Works: Step-by-Step Process
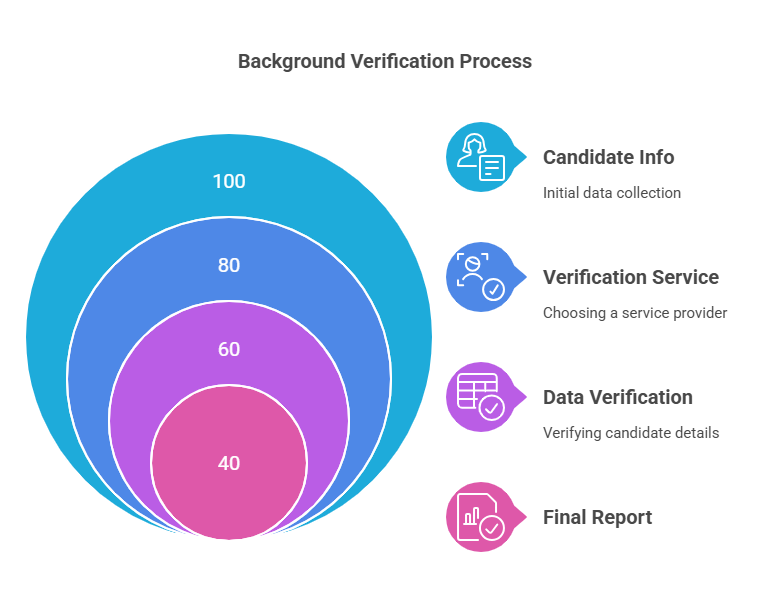
Understanding how the background verification process works can help organizations and individuals navigate it effectively. Below is a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Gathering Candidate Information
The first step is collecting the necessary information from the individual, such as:
- Full name, date of birth, and Social Security Number.
- Employment and education history.
- References and contact information.
- Consent form for background verification.
Step 2: Choosing a Verification Service
Organizations often partner with third-party background verification providers to ensure a thorough and legally compliant process. Factors to consider when selecting a provider include:
- Experience and expertise.
- Compliance with laws such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA).
- Turnaround time and accuracy.
- Range of services offered.
Step 3: Data Collection and Verification
Once a provider is chosen, the actual verification process begins. This involves:
- Cross-referencing information provided by the candidate.
- Contacting relevant authorities such as educational institutions, previous employers, and government agencies.
- Accessing public records like criminal databases and credit reports.
Step 4: Reporting and Final Results
After gathering and verifying data, the provider compiles a detailed report. This report includes:
- Verified details (e.g., education, employment).
- Any discrepancies or red flags (e.g., criminal history, false claims).
- Recommendations or insights for decision-making.
Organizations then review the report and decide whether to proceed with the candidate, request clarification, or take other actions.
Precise Hire’s Role in Background Verification
Precise Hire is a leading background verification provider that offers tailored solutions to meet the unique needs of employers across various industries. Here’s how Precise Hire stands out:
- Comprehensive Services: Criminal record checks, employment and education verification, reference checks, and more.
- Compliance: Ensures adherence to FCRA, GDPR, and other regulations.
- Fast Turnaround Time: Delivers accurate results quickly, helping employers make timely decisions.
- Customizable Solutions: Offers services tailored to specific industries and roles.
With Precise Hire, employers can conduct thorough background verifications while maintaining compliance and efficiency.
Challenges in Background Verification
Despite its importance, background verification can present certain challenges:
- Delays in Data Retrieval
Some institutions, like universities or government agencies, may take time to respond to verification requests. - Inaccurate or Outdated Records
Errors in databases can lead to discrepancies, requiring additional time to resolve. - Candidate Consent Issues
Candidates may hesitate to provide consent for certain verifications, especially those involving financial or criminal records. - Legal and Compliance Concerns
Organizations must ensure that their verification practices align with laws like the FCRA and Ban-the-Box regulations to avoid legal issues.
Legal Aspects of Background Verification
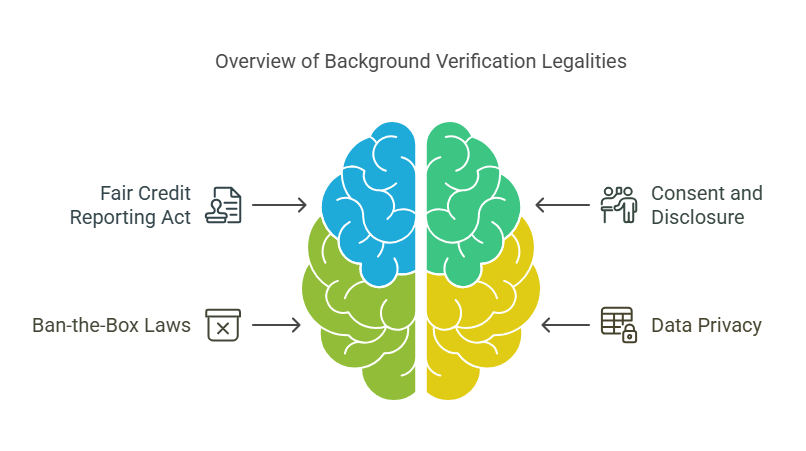
1. Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is a key piece of legislation that governs how background checks should be conducted, especially when it comes to criminal records, credit reports, and employment history checks. Here’s how the FCRA affects background verification:
- Candidate Consent: The FCRA mandates that employers or organizations obtain explicit consent from candidates before conducting background checks, especially when using a third-party provider.
- Notification of Adverse Actions: If the results of a background verification negatively affect a hiring decision (e.g., a criminal record or negative credit history), the FCRA requires the employer to notify the candidate.
- Accuracy of Information: Organizations must ensure that the data they use for background verification is accurate and up-to-date. Mistakes or outdated information can lead to legal repercussions.
Employers and verification agencies must be careful not to misuse the information gathered or act on incomplete or inaccurate data.
2. Consent and Disclosure
In addition to the FCRA, another crucial aspect of legal background verification is candidate consent and disclosure:
- Obtaining Consent: Before starting a background verification process, it is essential to get the candidate’s written consent. The process should be transparent, and candidates should be informed of what information will be checked.
- Clear Disclosure: Employers must inform candidates of the potential for background checks and provide them with a clear explanation of the types of checks being conducted (e.g., criminal, education, or employment).
Failure to obtain proper consent or disclose the nature of the background check can result in lawsuits and legal penalties for non-compliance.
3. Ban-the-Box Laws
Many states and localities have enacted Ban-the-Box laws, which restrict the ability of employers to ask about criminal history early in the hiring process. These laws were created to ensure fairer treatment for candidates with past convictions. Here’s how Ban-the-Box laws impact background verification:
- Timing of Questions: Employers cannot inquire about criminal history until later in the hiring process (typically after an interview or conditional job offer).
- Impact on Background Verification: These laws don’t prevent employers from conducting criminal background checks; rather, they limit when the inquiry can be made. This prevents discrimination based on past offenses before an applicant’s qualifications are assessed.
It is important for employers to stay up-to-date with Ban-the-Box laws in their jurisdiction to ensure that they comply with state-specific regulations.
4. Data Privacy
With sensitive personal information being collected during background verifications, data privacy is a critical concern. Ensuring that the data collected during verification is stored securely and accessed only by authorized personnel is vital for compliance with privacy laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and other local data protection regulations.
- Confidentiality: Background verification providers must safeguard personal data to prevent unauthorized access or breaches.
- Data Retention: Personal data should not be retained longer than necessary. Employers and verification agencies must have policies in place to safely dispose of data when it is no longer required.
- Data Access Control: Employers should ensure that only relevant personnel have access to the verification data and that it is stored securely.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some commonly asked questions regarding background verification:
What’s the difference between a background check and background verification?
While the terms "background check" and "background verification" are often used interchangeably, there is a subtle difference:
- Background Check: A broader term that encompasses all types of screenings, such as criminal history, credit report, and drug testing.
- Background Verification: Focuses more on confirming the accuracy of the information provided by an individual, such as their employment history, educational qualifications, and identity.
In short, verification ensures that the claims made by the candidate are truthful and accurate.
How long does background verification take?
The time it takes to complete a background verification depends on various factors, including the type of verification and the cooperation of the sources being contacted. Typically:
- Basic checks (e.g., criminal history) can take a few days.
- Comprehensive checks (e.g., employment and educational verifications) may take a week or more due to the time required to obtain official records and confirmations.
Using a reputable background verification service provider can expedite the process, but delays can occur depending on the responsiveness of third-party organizations.
Can an employer deny employment based on background verification results?
Yes, employers can deny employment based on the results of a background verification if they find information that is relevant to the role and poses a potential risk. However, they must:
- Provide the candidate with a notice of adverse action (if the results were unfavorable).
- Allow the candidate an opportunity to dispute any inaccuracies before a final decision is made.
Employers should ensure that the background verification results are directly relevant to the job position to avoid discrimination claims.
Do I have to give consent for background verification?
Yes, under the FCRA and other legal regulations, candidates must give explicit written consent before background verifications can be conducted. This consent must be informed, meaning that the candidate knows what checks will be performed and how the results may impact their application.
Employers must also disclose the nature of the verification process in a clear and transparent manner.
What can employers do if a background verification reveals inaccurate information?
If inaccurate information is found during the background verification process, the employer should:
- Notify the candidate and allow them to clarify the discrepancies or provide corrected information.
- Work with the verification service to resolve the issue and obtain the correct data.
- Avoid taking adverse action based solely on incorrect or incomplete information.
Employers must take steps to ensure that decisions are based on verified, accurate, and relevant data.
What’s the difference between a background check and background verification?
While the terms "background check" and "background verification" are often used interchangeably, there is a subtle difference:
- Background Check: A broader term that encompasses all types of screenings, such as criminal history, credit report, and drug testing.
- Background Verification: Focuses more on confirming the accuracy of the information provided by an individual, such as their employment history, educational qualifications, and identity.
In short, verification ensures that the claims made by the candidate are truthful and accurate.
How long does background verification take?
The time it takes to complete a background verification depends on various factors, including the type of verification and the cooperation of the sources being contacted. Typically:
- Basic checks (e.g., criminal history) can take a few days.
- Comprehensive checks (e.g., employment and educational verifications) may take a week or more due to the time required to obtain official records and confirmations.
Using a reputable background verification service provider can expedite the process, but delays can occur depending on the responsiveness of third-party organizations.
Can an employer deny employment based on background verification results?
Yes, employers can deny employment based on the results of a background verification if they find information that is relevant to the role and poses a potential risk. However, they must:
- Provide the candidate with a notice of adverse action (if the results were unfavorable).
- Allow the candidate an opportunity to dispute any inaccuracies before a final decision is made.
Employers should ensure that the background verification results are directly relevant to the job position to avoid discrimination claims.
Do I have to give consent for background verification?
Yes, under the FCRA and other legal regulations, candidates must give explicit written consent before background verifications can be conducted. This consent must be informed, meaning that the candidate knows what checks will be performed and how the results may impact their application.
Employers must also disclose the nature of the verification process in a clear and transparent manner.
What can employers do if a background verification reveals inaccurate information?
If inaccurate information is found during the background verification process, the employer should:
- Notify the candidate and allow them to clarify the discrepancies or provide corrected information.
- Work with the verification service to resolve the issue and obtain the correct data.
- Avoid taking adverse action based solely on incorrect or incomplete information.
Employers must take steps to ensure that decisions are based on verified, accurate, and relevant data.
Key Takeaways
Background verification is an essential tool for ensuring safety, trust, and compliance in various sectors, including employment, finance, and housing. Here are the key takeaways:
- Legality and Compliance: Adhering to laws such as the FCRA, Ban-the-Box, and data privacy regulations is crucial to ensure legal and ethical background verifications.
- Transparency and Consent: Always obtain clear consent from candidates and disclose the details of the checks being conducted.
- Accuracy is Essential: It is important to ensure that background verifications are accurate and up-to-date, as errors can lead to legal consequences.
- Protecting Data: Personal information must be handled with the utmost care to comply with data protection laws and ensure privacy.
- Using a Reliable Service: Partnering with trusted background verification service providers like Precise Hire ensures accurate, compliant, and efficient screening processes.
Conclusion
Background verification is a critical process that helps employers and organizations assess the trustworthiness of candidates and employees. By understanding the legal aspects, addressing common concerns, and following best practices, organizations can conduct thorough verifications while ensuring compliance with regulations. With the right processes in place, background verification protects both individuals and businesses, ensuring a safer and more reliable environment for everyone involved.
