The Complete Guide to Unemployment Identity Verification

Unemployment Identity Verification: Why It’s Crucial for Fair and Effective Unemployment Systems
Unemployment identity verification is a cornerstone of modern systems managing unemployment benefits. As more people access benefits online, the need for accurate and secure verification has grown exponentially. This article explores the critical role of unemployment identity verification, its necessity in today’s landscape, and the challenges organizations face in implementing it effectively.
What Is Unemployment Identity Verification?
Unemployment identity verification is the process of confirming an applicant’s identity when they apply for unemployment benefits. It acts as a safeguard to ensure that only eligible individuals receive benefits and to prevent fraud. This verification process typically involves validating an individual’s personal details, such as name, Social Security number, and employment history, using various tools and technologies.
In today’s increasingly digital world, traditional methods of verification, like in-person document submission, are being replaced by advanced systems that include:
- Biometric Authentication: Fingerprint scans, facial recognition, or voice verification to confirm identity.
- Document Verification: Uploading and validating government-issued IDs like passports or driver’s licenses.
- Cross-referencing Databases: Matching applicant data against government, financial, or employment records to verify accuracy.
These methods make unemployment identity verification faster, more reliable, and less prone to human error.
Why Is Unemployment Identity Verification Necessary?
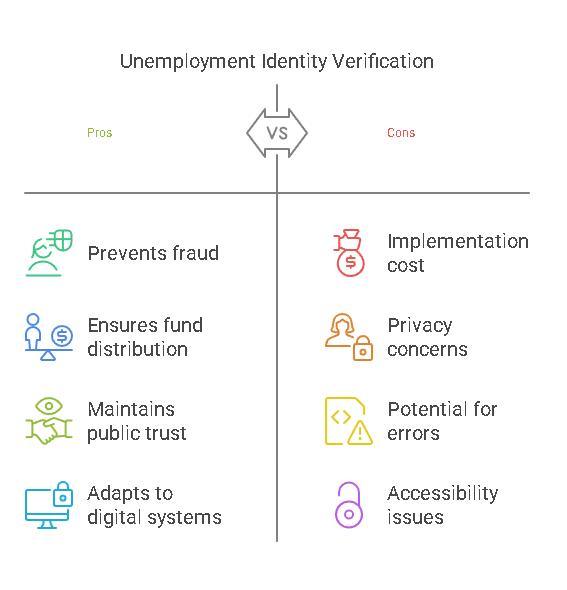
The necessity for unemployment identity verification arises from the need to ensure fairness, prevent fraud, and maintain trust in unemployment systems. Below are the key reasons why it plays a pivotal role:
1. Preventing Fraud and Abuse
Fraudulent unemployment claims have become a significant concern, especially during crises like economic recessions or pandemics. Fraudsters exploit gaps in verification processes to file claims using stolen or fake identities, diverting funds meant for genuine applicants.
For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, U.S. states reported billions of dollars lost to unemployment fraud due to inadequate verification measures. Robust identity verification helps mitigate these risks by detecting and blocking fraudulent applications.
2. Ensuring Proper Distribution of Benefits
Governments allocate limited funds for unemployment programs. Ensuring these funds reach deserving individuals is crucial to maintaining the integrity of these systems. Unemployment identity verification minimizes errors, ensuring benefits go to those who need them most.
3. Maintaining Public Trust
Public trust in unemployment systems is vital for their success. When benefits are distributed accurately and securely, it fosters confidence among citizens. Conversely, reports of fraud or mismanagement can erode trust and create skepticism about the effectiveness of unemployment programs.
4. Adapting to Digital Transformation
The shift toward online unemployment systems has made identity verification more important than ever. Unlike in-person verification, where applicants present physical documents, online systems must rely on digital tools to authenticate identities. This transition requires robust mechanisms to prevent cyber fraud while ensuring accessibility.
The Consequences of Inadequate Verification
Failing to implement effective unemployment identity verification measures can lead to severe repercussions:
1. Increase in Fraudulent Claims
Inadequate verification allows bad actors to file fraudulent claims, depleting resources and delaying payments for legitimate applicants.
2. Delayed Benefits for Genuine Applicants
Errors in verification systems can flag legitimate claims as suspicious, leading to unnecessary delays in benefit distribution. This can place financial strain on individuals who are already struggling due to job loss.
3. Legal and Financial Implications for Governments
Unaddressed fraud and mismanagement in unemployment systems can lead to lawsuits, audits, and a loss of public confidence. Governments may also face challenges in securing additional funding for future unemployment programs.
4. Administrative Overhead
When verification processes are flawed, agencies spend more time and resources correcting errors, investigating fraud, and resolving disputes. This increases the overall cost of administering unemployment benefits.
Common Challenges in Unemployment Identity Verification
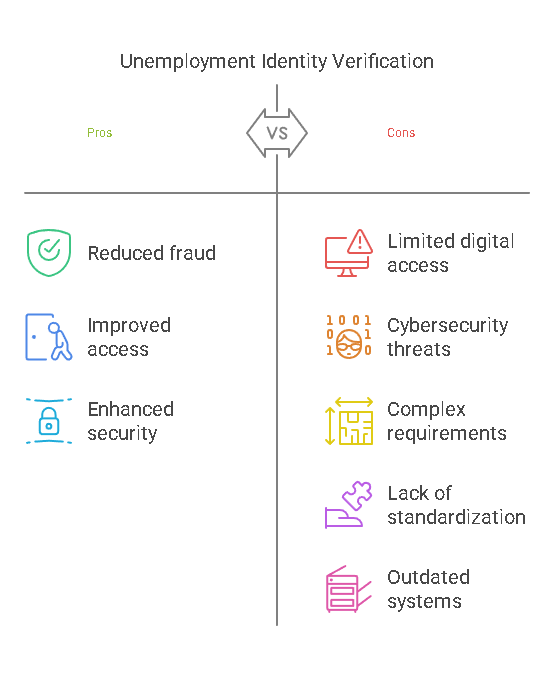
While unemployment identity verification is essential, it is not without challenges. Below are some of the common hurdles faced by governments and organizations:
1. Limited Access to Digital Tools
Not all applicants have access to the internet, smartphones, or computers required for online verification processes. This digital divide can exclude vulnerable populations, such as low-income individuals or senior citizens, from accessing unemployment benefits.
2. Identity Theft and Cybersecurity Threats
As systems move online, they become targets for cybercriminals. Data breaches can expose sensitive information, which fraudsters use to impersonate individuals and file fake claims. Strengthening cybersecurity measures is vital to address this challenge.
3. Complex Verification Requirements
Many verification systems require multiple steps, such as uploading documents, answering security questions, or completing biometric scans. While these measures enhance security, they can also make the process cumbersome for applicants, leading to frustration and errors.
4. Lack of Standardization Across States and Agencies
In countries like the United States, unemployment systems vary by state. This lack of uniformity in verification requirements and tools can create inefficiencies, making it harder to detect fraud and resolve disputes.
5. Dependence on Outdated Systems
Some unemployment agencies still rely on legacy systems that lack the capabilities to handle modern identity verification requirements. These outdated systems are not only inefficient but also more vulnerable to fraud and errors.
Why Addressing These Challenges Is Crucial
Overcoming these challenges is critical to ensuring that unemployment benefits are distributed efficiently and equitably. Policymakers, government agencies, and service providers must work together to implement robust identity verification solutions that balance security with accessibility.
We will delve into the step-by-step process of unemployment identity verification, explore the tools and technologies used, and discuss how companies like Precise Hire are innovating to provide effective solutions.
The Process and Tools for Unemployment Identity Verification
Unemployment identity verification involves a structured process that ensures only eligible applicants receive benefits. As fraudulent claims and cybersecurity threats continue to rise, government agencies and organizations have adopted advanced tools and techniques to streamline the verification process. In this section, we’ll explore the step-by-step process, discuss the technologies employed, and highlight solutions offered by companies like Precise Hire.
The Step-by-Step Process of Unemployment Identity Verification
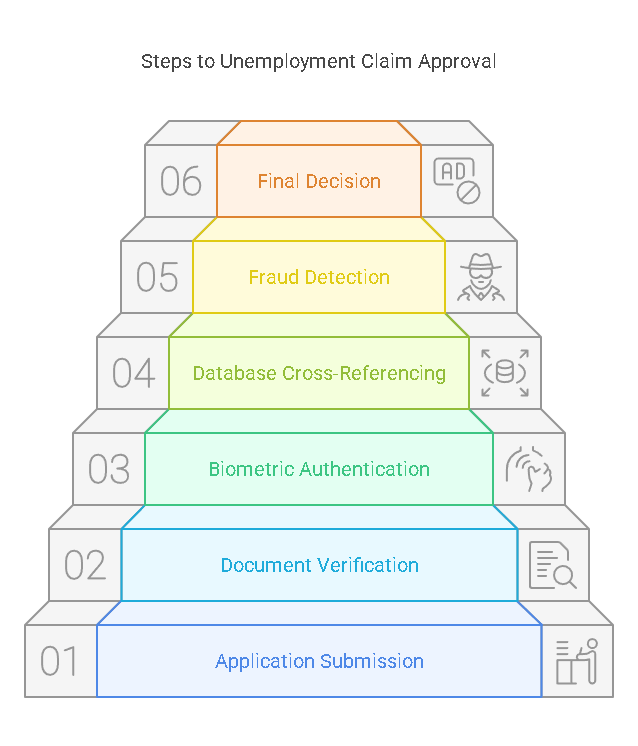
Effective unemployment identity verification typically involves several key steps:
1. Application Submission
The process begins when an applicant submits their unemployment claim. This step requires providing basic personal information, such as:
- Full name
- Social Security number or national identification number
- Date of birth
- Employment history
Applicants may also be asked to upload supporting documents, such as pay stubs, tax returns, or termination letters.
2. Identity Document Verification
Once the application is submitted, the system verifies the authenticity of identity documents. This can include:
- Checking the document’s format and expiration date.
- Verifying the document against official databases, such as DMV or passport records.
Advanced tools can scan for signs of forgery, such as mismatched fonts, altered photos, or tampered barcodes.
3. Biometric Authentication
Many modern systems incorporate biometric data to enhance security. Common methods include:
- Facial Recognition: Applicants upload a selfie, which is matched against their ID photo.
- Fingerprint Scans: Collected via mobile apps or kiosks.
- Voice Recognition: Used for phone-based verification.
These techniques add an extra layer of security, making it harder for fraudsters to impersonate legitimate applicants.
4. Cross-Referencing Databases
The verification system cross-references applicant information with external databases, including:
- Tax records
- Social Security Administration data
- Employment history databases
- Financial institutions
This ensures that the applicant’s claims are consistent with their official records.
5. Fraud Detection and Risk Assessment
Automated systems analyze application data to detect red flags, such as:
- Multiple claims from the same IP address.
- Mismatched employment details.
- Suspicious patterns in biometric data.
High-risk applications may be flagged for manual review by trained personnel.
6. Final Approval or Denial
Once the verification process is complete, the system either approves or denies the claim. Applicants are notified of the decision, and those denied are typically given the option to appeal or provide additional information.
Modern Tools and Technologies for Identity Verification
To combat sophisticated fraud schemes, organizations have turned to cutting-edge tools and technologies. Below are some of the most commonly used solutions:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data to detect anomalies and predict fraudulent behavior. Machine learning algorithms continuously improve by learning from past cases, making fraud detection more accurate over time.
2. Document Verification Software
These tools use optical character recognition (OCR) to read and verify information on identity documents. Some advanced systems can detect tampered documents by analyzing pixel-level discrepancies.
3. Biometric Technology
Biometric authentication tools, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanners, offer a highly secure method of identity verification. These systems are often integrated into mobile apps, allowing applicants to verify their identity from anywhere.
4. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds another layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple channels, such as:
- Passwords or PINs
- One-time codes sent via SMS or email
- Biometric data
5. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain provides a decentralized and tamper-proof way to store identity data. By leveraging blockchain, unemployment agencies can securely share data across platforms while ensuring transparency and immutability.
How Precise Hire Enhances the Verification Process
At Precise Hire, we specialize in providing tailored identity verification solutions to streamline unemployment claims. Our services integrate state-of-the-art technology to offer:
- Seamless Document Verification:
Our platform uses AI-driven tools to verify identity documents with speed and accuracy. - Biometric Authentication:
We offer facial recognition and fingerprint scanning services that ensure secure and user-friendly verification. - Fraud Detection Algorithms:
Our fraud detection tools use machine learning to identify high-risk applications, minimizing errors and delays. - 24/7 Support:
Applicants and administrators can access round-the-clock assistance for troubleshooting and guidance.
Benefits of Partnering with Precise Hire
- Faster claim processing.
- Reduced fraud and error rates.
- Enhanced applicant satisfaction through a streamlined experience.
Best Practices for Unemployment Identity Verification
To ensure efficient and secure verification, organizations should follow these best practices:
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Adopt Advanced Technologies | Use AI, biometrics, and blockchain to enhance security and accuracy. |
| Provide Clear Instructions | Ensure applicants understand the process and requirements for verification. |
| Focus on Accessibility | Design systems that accommodate users with limited access to technology. |
| Regularly Update Systems | Upgrade software and tools to keep pace with evolving fraud tactics. |
| Ensure Compliance | Adhere to legal and regulatory standards to avoid penalties and lawsuits. |
In this section, we’ve examined the step-by-step process and tools used for unemployment identity verification, highlighting how companies like Precise Hire contribute to a secure and efficient system.
Legal Aspects, FAQs, and Conclusion
Unemployment identity verification not only involves advanced tools and processes but also operates within a framework of legal and regulatory requirements. Ensuring compliance with these laws is essential for protecting both applicants and organizations. In this final section, we’ll explore the legal aspects of unemployment identity verification, answer frequently asked questions, and summarize key takeaways.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects of Unemployment Identity Verification
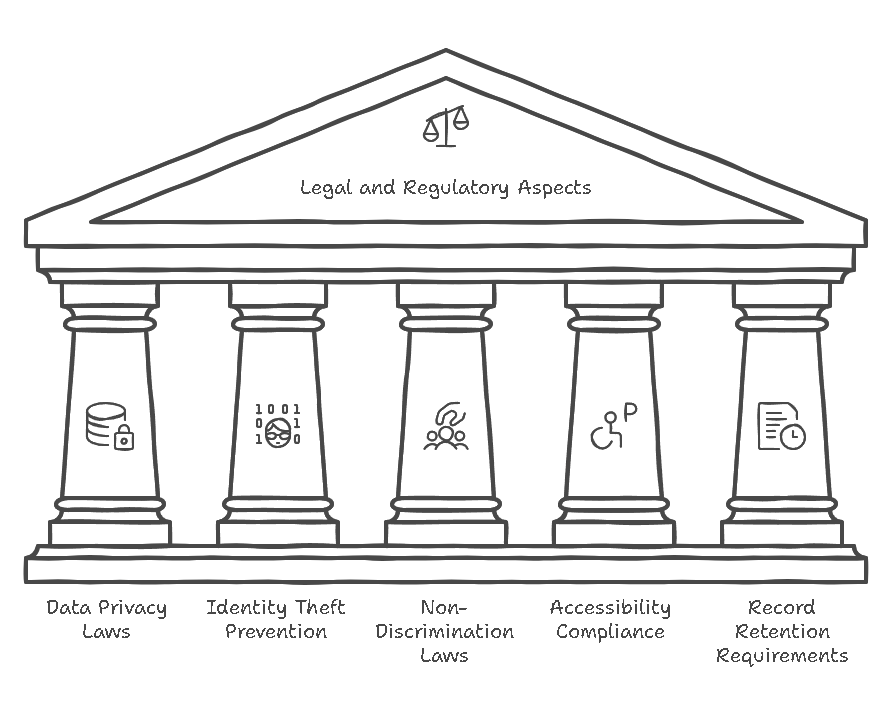
Unemployment identity verification processes are subject to various laws and regulations that govern how personal data is collected, stored, and used. Below are some of the critical legal considerations:
1. Data Privacy Laws
Organizations handling unemployment claims must comply with data privacy regulations such as:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Applies to entities processing the personal data of EU citizens, ensuring transparency and user control.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): Gives California residents rights over their personal information, including the right to know, delete, and opt-out of data collection.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): May apply when unemployment claims involve health-related information, ensuring confidentiality.
2. Identity Theft Prevention
Agencies must implement measures to protect against identity theft, such as secure data storage, encryption, and regular system audits. Failure to do so can result in legal penalties and reputational damage.
3. Non-Discrimination Laws
Verification systems must be designed to avoid bias. For example, biometric tools should account for variations in skin tones, ages, and other demographic factors to ensure fair treatment for all applicants.
4. Accessibility Compliance
Under laws such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), verification processes must be accessible to individuals with disabilities. This includes offering alternative verification methods and providing user-friendly interfaces.
5. Record Retention Requirements
Governments and organizations must adhere to regulations regarding how long unemployment claim data is retained. These rules vary by jurisdiction and aim to balance accountability with privacy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are five commonly asked questions about unemployment identity verification, along with detailed answers:
Why was my unemployment claim flagged for identity verification?
Your claim may have been flagged due to discrepancies in your submitted information or potential red flags detected by automated systems. For example:
- Mismatched data between your application and official records.
- Multiple claims from the same IP address or physical location.
- Unusual patterns in your employment history.
In such cases, additional documentation or manual verification may be required.
What documents are typically required for unemployment identity verification?
The required documents can vary depending on the state or country but often include:
- A government-issued ID (passport, driver’s license, etc.).
- Social Security card or equivalent.
- Proof of employment, such as pay stubs or a letter of termination.
- Tax documents like W-2 forms.
Applicants should ensure their documents are clear, up-to-date, and free of errors.
How does biometric authentication improve the verification process?
Biometric authentication uses unique physical or behavioral traits, such as facial recognition or fingerprints, to verify identity. Benefits include:
- Increased Security: Harder to forge than traditional documents.
- Speed and Convenience: Reduces the need for manual checks, enabling faster approvals.
- Accessibility: Mobile-based biometrics allow applicants to verify their identity remotely.
However, biometric tools must adhere to privacy laws and ensure data is stored securely.
Can I appeal if my unemployment claim is denied due to identity verification issues?
Yes, most unemployment systems allow applicants to appeal denied claims. The process typically involves:
- Providing additional documentation to confirm your identity.
- Submitting a written appeal explaining the situation.
- Contacting the relevant unemployment office for assistance.
Applicants should act promptly, as appeal deadlines can vary by jurisdiction.
What role does technology play in preventing unemployment fraud?
Technology plays a central role in detecting and preventing unemployment fraud by:
- Automating Data Analysis: AI systems identify patterns and anomalies that indicate fraud.
- Cross-Referencing Databases: Tools verify applicant information against official records.
- Enhancing Security: Biometric authentication and multi-factor verification reduce the risk of identity theft.
These innovations ensure benefits are distributed fairly while protecting public funds.
Conclusion
Unemployment identity verification is a vital process that ensures the integrity, fairness, and efficiency of unemployment benefits systems. With the rise of online applications and sophisticated fraud schemes, the need for secure and advanced verification methods has never been greater.
By adopting modern tools such as biometric authentication, AI-powered fraud detection, and blockchain technology, organizations can enhance security while providing a seamless experience for applicants. Additionally, compliance with legal and regulatory standards is crucial for protecting sensitive data and maintaining public trust.
Companies like Precise Hire play a critical role in this landscape, offering innovative solutions that address the challenges of unemployment identity verification. By prioritizing both security and accessibility, we can build a system that supports those in need while safeguarding resources for future generations.
