A Comprehensive Guide to Identity Verification for Digital Onboarding

Introduction to Digital Onboarding and Identity Verification
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses across various sectors are transitioning to digital-first strategies. One of the key aspects of this transformation is the process of digital onboarding, which is becoming increasingly crucial for industries such as financial services, human resources, e-commerce, Identity Verification and more. This shift towards online systems and interactions has changed the way organizations engage with users and employees from the very first point of contact.
What is Digital Onboarding?
Digital onboarding refers to the process through which a new user or employee is brought into a system or organization using digital platforms. The objective is to gather the necessary information, set up accounts, or initiate employment, all online. This process replaces traditional in-person methods, making it faster, more efficient, and accessible. Digital onboarding typically involves several stages, including collecting personal information, verifying that information, completing necessary forms, and setting up user access to various services or tools.
The growing adoption of digital onboarding is driven by the increasing need for efficiency, especially in industries that deal with large volumes of customers or new hires. By eliminating the need for physical paperwork, in-person meetings, and manual processing, businesses can save time and reduce administrative costs while improving the overall experience for users.
What is Identity Verification in Digital Onboarding?
Identity verification is the process of confirming that the person filling out the digital onboarding forms is who they say they are. It is an essential component of digital onboarding, as it helps ensure that businesses and organizations are engaging with legitimate individuals and not fraudsters or impostors. Identity verification is particularly important when dealing with sensitive activities such as opening a bank account, applying for a loan, hiring employees, or purchasing goods online.
Identity verification is not only about ensuring a secure process but also about complying with regulatory standards in many industries. For example, financial institutions are required by law to follow Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations, which mandate that businesses verify the identity of individuals they engage with. This also helps organizations meet Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance and other legal requirements.
Why is Identity Verification Crucial in Digital Onboarding?
The digital nature of onboarding processes makes it more susceptible to various forms of fraud. Since users or employees are not physically present to interact with organizations, there are numerous ways in which individuals can falsify their identities. Identity verification reduces these risks, ensuring that businesses are not only protecting their assets but also providing a secure environment for users.
For businesses, identity verification allows them to:
- Prevent fraud and identity theft
- Ensure compliance with legal requirements (e.g., KYC, AML)
- Protect customer or employee data from unauthorized access
- Streamline operations by automating the verification process
- Provide a smoother and faster onboarding experience for legitimate users
For users, identity verification offers a secure and reliable process for engaging with services or employers, giving them confidence that their personal information will be safeguarded.
Methods of Identity Verification in Digital Onboarding
To ensure accuracy and prevent fraud, businesses utilize several methods of identity verification during the digital onboarding process. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses, depending on the level of security and convenience required by the business or the industry.
- Document Verification Document verification is one of the most common methods used for identity verification. It involves users submitting a digital copy of a government-issued ID (e.g., passport, driver’s license, or national ID card), which is then cross-referenced with public databases or checked against internal systems for authenticity. This method helps businesses confirm that the individual matches the identity on the document provided. Advanced algorithms are used to detect forged or tampered documents by analyzing features such as holograms, barcodes, and watermarks.
- Biometric Verification Biometric verification is a more advanced form of identity verification that relies on unique biological traits of the individual. Two of the most commonly used biometric methods are facial recognition and fingerprint scanning. With facial recognition, users are required to take a selfie, which is then compared with the image on their official documents. Biometric verification offers a higher level of security compared to document verification, as it is much more difficult for someone to replicate facial features or fingerprints.
- Knowledge-Based Authentication (KBA) Knowledge-based authentication is a method that requires users to answer security questions based on their personal information. These questions are typically drawn from public or private databases (e.g., credit report data or previous addresses). The user must answer correctly to prove their identity. While this method is commonly used in combination with other forms of verification, it can be less secure, as personal information may be accessible through data breaches or social engineering attacks.
Why Identity Verification is Critical in a Digital-First Environment
As more businesses embrace digital-first strategies, the importance of identity verification only continues to grow. In today’s online world, where interactions often occur without face-to-face contact, ensuring that the right individuals are accessing services or joining organizations has become a key concern. Digital identity verification helps organizations meet these challenges by providing an efficient and secure way to confirm users’ identities.
The growth of digital onboarding aligns with the rise of remote work, online banking, e-commerce, and the gig economy, where people are increasingly conducting business and applying for jobs remotely. In these scenarios, users expect the same level of security and ease of use as they would in an in-person interaction. This is where identity verification plays a crucial role, ensuring the process is seamless and trustworthy.
For businesses, digital onboarding presents an opportunity to attract a global audience, reduce operational costs, and improve customer or employee satisfaction. However, to fully leverage these benefits, it is crucial that the identity verification process is both secure and efficient.
How Identity Verification Works for Digital Onboarding
Now that we have discussed the importance of digital onboarding and identity verification, let’s delve deeper into the step-by-step process of how identity verification works during digital onboarding. The process involves several stages and technologies to ensure the legitimacy and security of new users or employees.
Step-by-Step Process of Identity Verification in Digital Onboarding
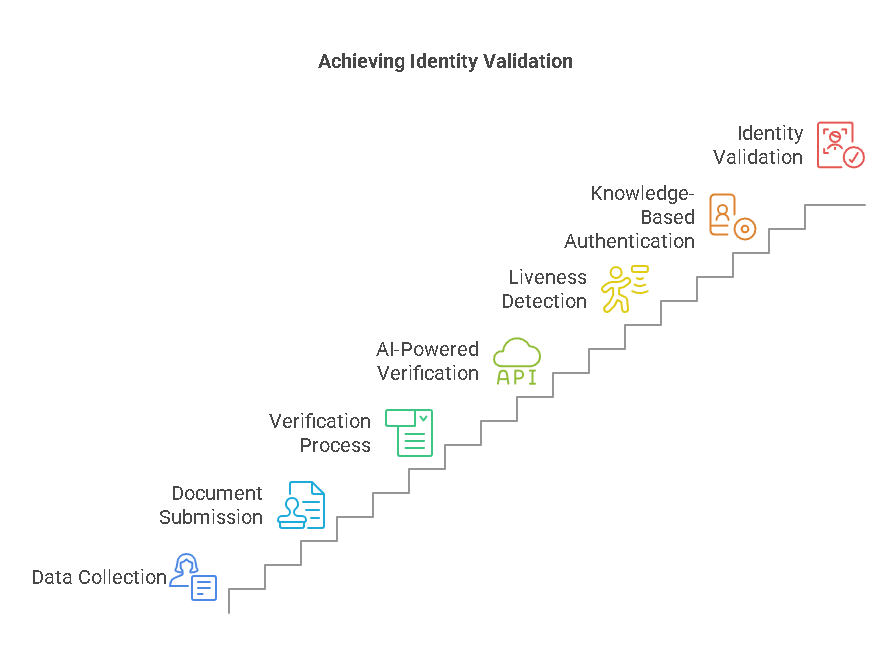
- Data Collection The first step in the identity verification process involves collecting data from the individual during the onboarding process. This data typically includes personal information such as the individual’s full name, date of birth, address, and contact information. This data may be entered manually by the individual or pulled from existing databases, depending on the platform being used for onboarding.
- Document Submission In the case of document verification, the individual will be required to upload digital copies of official documents, such as a government-issued ID, passport, or driver’s license. This step ensures that the person’s identity can be cross-referenced against databases to confirm their legitimacy. The document is typically scanned or photographed and submitted via the digital platform.
- Verification Process After document submission, advanced algorithms and technologies are employed to verify the authenticity of the documents provided. This can involve:
- Checking for security features on the documents, such as holograms, watermarks, or QR codes.
- Comparing the provided image to the individual’s photo to ensure they match.
- Cross-referencing the document’s information with official databases, such as government-issued records or financial data.
In the case of biometric verification, users are prompted to take a selfie or submit a fingerprint scan, which is then compared with the document image or biometric template stored in secure databases.
- AI-Powered Verification Algorithms Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) play a significant role in verifying documents and biometric data. AI algorithms are designed to identify discrepancies in documents and facial recognition software helps verify that the user submitting the information is real and not using altered images. These advanced technologies make the verification process faster, more reliable, and more accurate.
- Liveness Detection One of the most critical technologies used in digital onboarding is liveness detection. This technology ensures that the individual attempting to verify their identity is a real person and not a static image or video being used to bypass the system. Liveness detection analyzes factors such as eye movement, blinking, or other real-time physical movements to confirm that the individual is present and not a recorded image. This technology helps prevent fraud attempts where individuals might try to use a photo or video to impersonate someone else.
- Knowledge-Based Authentication (KBA) In addition to document and biometric verification, some systems may require knowledge-based authentication (KBA). KBA relies on information that only the individual should know, such as previous addresses, loan history, or details from public records. If the user answers the questions correctly, it confirms their identity. This step is typically used in conjunction with document or biometric verification to provide multiple layers of security.
- Identity Validation and Approval After the verification process is complete, the system assesses whether all the necessary checks have been met. If the identity is validated successfully, the individual can proceed with completing their onboarding process, gaining access to accounts, services, or employment. If discrepancies are found, the system may prompt the individual to submit additional documents or undergo further verification steps.
Technologies Behind Identity Verification for Digital Onboarding
Several advanced technologies and methods are employed in digital onboarding and identity verification to make the process efficient, secure, and user-friendly.
- AI-Powered Algorithms Artificial intelligence plays a key role in verifying identity documents and biometric data. AI algorithms can analyze documents for authenticity, detect forgeries, and even compare facial features in biometric verification. These algorithms make the process more accurate and faster than manual checks, improving efficiency and reducing human error.
- Machine Learning Models Machine learning is used to improve the accuracy of identity verification systems. These models can learn and adapt based on the data they analyze, improving their ability to detect fraud over time. Machine learning enhances the system’s ability to recognize patterns in biometric data and detect potential fraud attempts, making the entire process more secure.
- Liveness Detection Technology Liveness detection ensures that the individual undergoing identity verification is physically present and engaged in the process. By analyzing small movements like blinking or facial expressions, the system can confirm that the individual is not using a static image or video to impersonate someone else. This technology is especially important in biometric identity verification methods, such as facial recognition, to ensure the system is not being bypassed.
- Biometric Verification Biometric verification is one of the most secure methods used in digital onboarding. It uses unique biological traits such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice recognition to verify an individual’s identity. Biometric data is highly secure and difficult to replicate, making it an ideal method for ensuring the legitimacy of users during the onboarding process.
Challenges in Digital Identity Verification
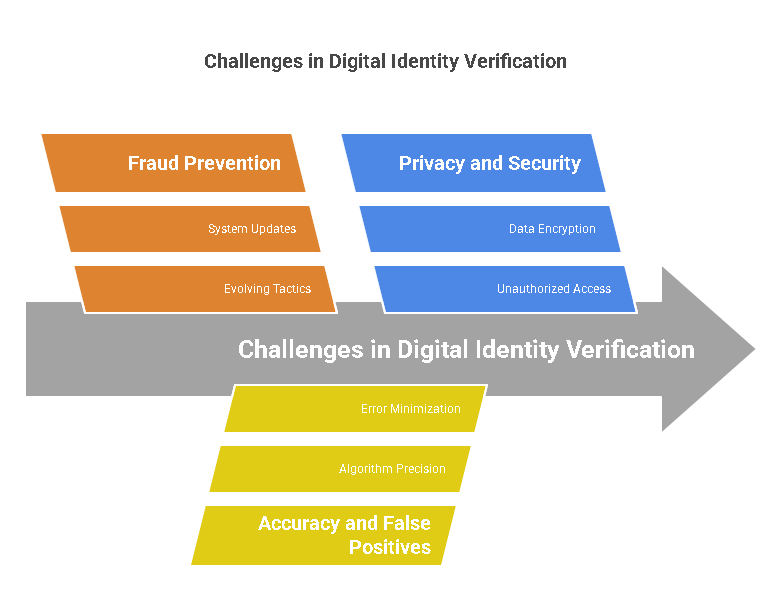
While digital identity verification is a powerful tool in ensuring security, there are several challenges that businesses face when implementing this technology. Some of the key challenges include:
- Fraud Prevention One of the biggest concerns in digital identity verification is preventing fraud. Fraudsters are continuously developing new tactics to bypass verification systems, such as using photos, videos, or stolen identity information. To mitigate this risk, businesses must continuously update their verification systems to stay ahead of new fraud methods.
- Accuracy and False Positives Maintaining high accuracy in digital identity verification is crucial. False positives (incorrectly identifying a legitimate user as fraudulent) and false negatives (failing to detect a fraudster) can lead to security risks or unnecessary delays. Businesses must ensure that their identity verification systems use advanced algorithms that minimize these errors.
- Maintaining Privacy and Security Privacy concerns are another challenge in digital identity verification. Users must trust that their personal data, especially biometric data, is being handled securely and not exposed to unauthorized parties. To address this, businesses must implement strong encryption and data protection protocols to safeguard user information.
How Precisehire Supports Businesses with Identity Verification Solutions
Precisehire offers a comprehensive suite of services to help businesses streamline their digital onboarding processes while ensuring secure and compliant identity verification. With a focus on reducing fraud and improving accuracy, Precisehire supports businesses by:
- Implementing AI-powered identity verification systems
- Utilizing biometric authentication methods, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning
- Offering KYC and AML compliance solutions for financial institutions
- Providing liveness detection to prevent fraud
- Ensuring compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA
By leveraging Precisehire’s services, businesses can enhance their security, reduce fraud, and offer a smoother onboarding experience for users.
Data Table: Comparison of Identity Verification Methods
| Verification Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Document Verification | Simple, low-cost, widely accepted | Can be bypassed with forged documents |
| Biometric Verification | High security, hard to replicate, user-friendly | Requires specialized technology, privacy concerns |
| Knowledge-Based Authentication (KBA) | Low-cost, easy to implement | Vulnerable to data breaches, less secure |
Legal Aspects of Digital Identity Verification
Digital onboarding and identity verification are governed by several laws and regulations that aim to protect the privacy of individuals and ensure that businesses comply with security standards. Some of the key legal frameworks that apply include:
Data Protection Laws
When conducting digital identity verification, businesses must comply with data protection laws that regulate how personal data is collected, stored, and used. Some of the most significant data protection laws include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This regulation is a key piece of legislation in the European Union that governs how businesses handle personal data. It mandates that businesses ensure the security of personal information, obtain consent from users, and provide transparency on data collection practices.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): The CCPA is similar to GDPR but applies to businesses in California, USA. It gives California residents greater control over their personal data, including the right to request the deletion of their data and to opt-out of the sale of their personal information.
Both laws require businesses to adopt stringent security measures during digital onboarding, particularly when collecting sensitive data such as biometric information.
Know Your Customer (KYC) Regulations
KYC regulations are particularly relevant in industries such as banking, fintech, and insurance. These regulations require businesses to verify the identity of their customers to prevent fraud, money laundering, and terrorist financing.
- Financial Institutions: Banks and financial service providers are obligated to conduct KYC checks to verify the identity of their customers. Digital onboarding platforms in these sectors must comply with KYC standards to ensure that customers are who they claim to be.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML): AML regulations work hand in hand with KYC rules to prevent money laundering and other illicit financial activities. Businesses in sectors like banking and insurance must adhere to both KYC and AML standards during the onboarding process.
Regulations on Biometric Data
Since biometric data (such as facial recognition and fingerprint scans) is highly sensitive, it is subject to stricter regulations than other forms of personal data. In many jurisdictions, businesses are required to obtain explicit consent from users before collecting biometric data and must adhere to robust security measures to protect this data.
- Biometric Information Privacy Act (BIPA): In the United States, Illinois has implemented BIPA, which requires companies to obtain written consent from individuals before collecting biometric data. Businesses must also disclose how the data will be used, stored, and protected.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with these legal regulations can result in significant penalties and reputational damage for businesses. Non-compliance with data protection laws, KYC requirements, or biometric data regulations can lead to fines, lawsuits, or even loss of business licenses. For instance:
- Under the GDPR, companies can face fines of up to 4% of their annual global turnover or €20 million (whichever is greater) for violations.
- Violations of the CCPA can lead to fines of up to $7,500 per violation.
- KYC and AML non-compliance in the financial industry can result in hefty fines and legal action, as seen in several high-profile cases involving money laundering.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some common questions related to digital onboarding and identity verification:
What is the role of identity verification in preventing fraud during onboarding?
Identity verification is essential in preventing fraud during onboarding by ensuring that the person completing the process is who they claim to be. By verifying documents, using biometric authentication, and employing AI-powered algorithms, businesses can effectively reduce the risk of identity theft and fraudulent activities.
How do businesses ensure the accuracy of identity verification in digital onboarding?
Businesses use advanced technologies, such as AI, machine learning, and liveness detection, to ensure the accuracy of identity verification. These technologies can compare documents against official databases, detect discrepancies in biometric data, and verify that the individual is physically present during the verification process.
Can digital identity verification be bypassed or hacked?
While no system is entirely foolproof, digital identity verification technologies such as biometric authentication and liveness detection make it extremely difficult for fraudsters to bypass the system. The use of AI-powered algorithms and machine learning models also helps in detecting fraudulent attempts more effectively.
Is biometric data secure during digital onboarding?
Biometric data is highly secure due to its unique nature. However, businesses must ensure they are following strict security protocols, including data encryption, secure storage, and compliance with privacy laws, to protect biometric information from unauthorized access.
How does digital identity verification comply with global data privacy laws?
Digital identity verification platforms comply with global data privacy laws by implementing secure data handling practices, obtaining user consent for data collection, and ensuring transparency in how personal data is used. Compliance with regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and BIPA ensures that businesses protect user privacy while conducting secure identity verification.
Conclusion
In conclusion, digital onboarding and identity verification play a vital role in ensuring the security, efficiency, and compliance of onboarding processes across various industries. As businesses increasingly adopt digital platforms to onboard new users or employees, identity verification becomes a crucial step in preventing fraud, ensuring compliance with regulations, and protecting sensitive personal information.
By leveraging advanced technologies like AI, biometric verification, and liveness detection, businesses can streamline their onboarding processes while enhancing security and user experience. However, businesses must also remain vigilant in ensuring they comply with legal requirements, such as GDPR, CCPA, KYC, and AML regulations, to avoid penalties and protect their reputation.
For companies looking to enhance their digital onboarding process, partnering with a trusted provider like Precisehire can help businesses navigate the complexities of identity verification, reduce fraud, and ensure compliance with data privacy and security laws. By using reliable identity verification solutions, businesses can provide a seamless and secure onboarding experience for users while staying ahead of emerging threats in the digital space.
