A Comprehensive Guide to Blockchain Identity Verification

Understanding Blockchain Identity Verification
Blockchain technology has revolutionized how data is stored, shared, and secured. Among its many applications, identity verification stands out as a critical use case that addresses the challenges of traditional systems. Blockchain-based identity verification ensures data integrity, security, and user control, making it a preferred choice for organizations seeking advanced solutions to manage identity verification processes.
What is Blockchain Identity Verification?
Blockchain identity verification refers to the use of blockchain technology to authenticate and verify individuals’ identities securely and efficiently. Unlike traditional systems that rely on centralized databases, blockchain-based verification employs a distributed ledger where information is stored across multiple nodes.
Every piece of identity data is encrypted and linked using cryptographic methods, ensuring its immutability and transparency. For example, instead of storing sensitive information like social security numbers in a centralized database, blockchain systems tokenize this data, reducing the risk of breaches and unauthorized access.
This innovative approach is increasingly used in sectors like banking, healthcare, and e-commerce, where the need for secure and efficient identity verification is paramount.
How Blockchain Enhances Identity Verification
Blockchain technology introduces features that address long-standing issues in traditional identity verification systems:
- Decentralization:
Data is not stored in a single location but is distributed across a network of nodes. This eliminates single points of failure and enhances system resilience. - Transparency:
All transactions on a blockchain are visible to authorized participants. This transparency reduces the risk of fraud and enhances accountability. - Immutability:
Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This ensures that all identity-related information remains accurate and tamper-proof. - Security:
Advanced cryptographic techniques protect sensitive data. Even if one node is compromised, the data remains secure within the network. - Efficiency:
By automating processes through smart contracts, blockchain significantly reduces the time required for identity verification, enabling real-time authentication.
Key Components of Blockchain-Based Identity Verification

- Digital Identity (DID):
A DID is a self-sovereign identity stored on the blockchain. Users control their digital identity and decide which information to share with third parties. - Cryptographic Hashes:
Sensitive data is converted into cryptographic hashes before being stored on the blockchain. These hashes are unique and irreversible, adding an extra layer of security. - Smart Contracts:
These automated protocols execute pre-defined actions once certain conditions are met. For instance, a smart contract can verify a user’s identity instantly upon receiving the required credentials. - Distributed Ledger:
The backbone of blockchain, the distributed ledger ensures that all transactions are recorded transparently and securely across all participating nodes.
Use Cases of Blockchain Identity Verification
Blockchain identity verification is transforming various industries. Here are some notable examples:
- Financial Services:
Banks and financial institutions use blockchain to comply with Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations. By leveraging blockchain, they can verify customers’ identities faster and more securely, reducing onboarding times and operational costs. - Healthcare:
Blockchain ensures that patients’ medical records are secure and accessible only to authorized personnel. Identity verification is crucial for accessing healthcare services and maintaining the integrity of medical data. - E-commerce:
Online platforms rely on blockchain to authenticate users and prevent fraud. For instance, blockchain-based identity systems can verify a customer’s payment credentials without exposing sensitive information. - Government Services:
Governments use blockchain to issue digital IDs and streamline services like voting, tax filings, and social welfare distribution. Blockchain enhances transparency and reduces administrative inefficiencies. - Travel and Immigration:
Blockchain simplifies border control processes by enabling instant verification of passports and visas. This reduces wait times and improves security at entry points.
Benefits, Challenges, and Industry Examples
Blockchain identity verification offers numerous advantages that address the inefficiencies and vulnerabilities of traditional systems. However, the technology is not without its challenges. Understanding these aspects provides a comprehensive view of its potential in various industries.
Advantages of Blockchain Identity Verification
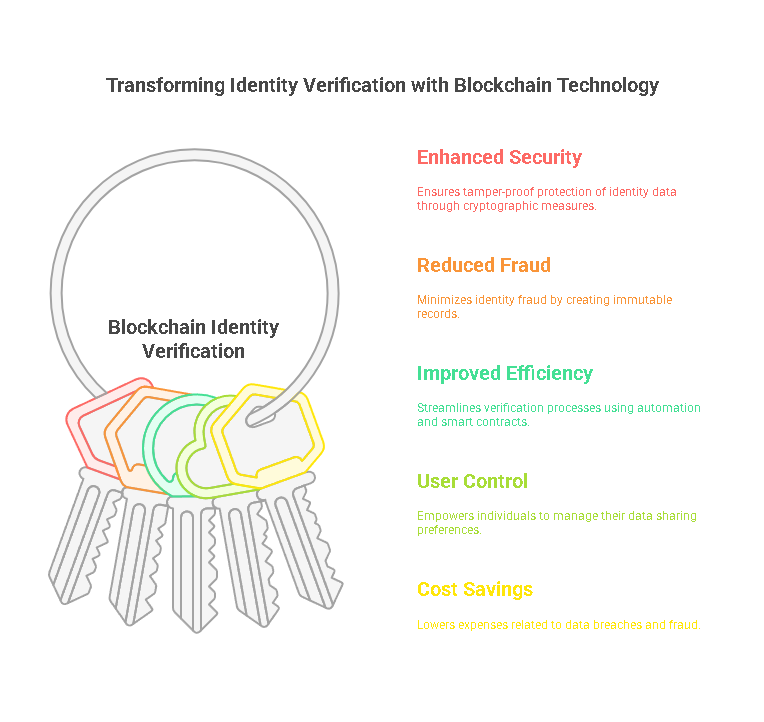
- Enhanced Security:
Blockchain technology provides unparalleled security for identity data. Its decentralized nature, combined with cryptographic hashing, ensures that information cannot be tampered with or accessed without proper authorization. - Reduced Fraud:
Identity fraud is a significant concern in traditional systems. Blockchain eliminates many vulnerabilities by creating tamper-proof records and enabling users to share only necessary information. - Improved Efficiency:
By automating identity verification processes through smart contracts, blockchain reduces the time and resources required for manual checks. This is particularly beneficial in industries with high volumes of transactions, such as banking and e-commerce. - User Control:
Blockchain-based systems give individuals control over their data through self-sovereign identities. Users can choose what information to share, with whom, and for how long, enhancing privacy and trust. - Cost Savings:
Organizations can significantly reduce costs associated with data breaches, fraud investigations, and compliance by adopting blockchain for identity verification. - Global Reach:
Blockchain operates on a decentralized network, making it accessible across borders. This is particularly valuable for multinational companies and cross-border services.
Challenges in Implementing Blockchain Identity Verification
- Scalability Issues:
Blockchain networks often face limitations in handling large volumes of data and transactions. As the number of users grows, the network may experience delays and increased costs. - Interoperability Challenges:
Different blockchain systems may not be compatible with each other. This lack of standardization can hinder the seamless exchange of information across platforms. - Regulatory Uncertainty:
The legal landscape for blockchain technology is still evolving. Organizations must navigate complex regulations that vary by jurisdiction to ensure compliance. - Data Privacy Concerns:
While blockchain enhances security, storing sensitive information on a public ledger may raise privacy concerns. Balancing transparency with confidentiality is a challenge. - High Initial Costs:
Implementing blockchain-based identity systems requires significant investment in infrastructure, training, and development, which may deter smaller organizations.
Precisehire’s Role in Blockchain Identity Verification
Precisehire is a trusted partner for organizations seeking advanced identity verification solutions. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies, Precisehire provides:
- Efficient and Secure Verification: Solutions designed to meet the unique needs of businesses across industries.
- Compliance Expertise: Ensuring adherence to regulatory standards for secure and legally compliant processes.
- Customizable Services: Tailored identity verification systems that integrate seamlessly with existing workflows.
Organizations can rely on Precisehire to simplify the adoption of blockchain-based identity verification, reducing complexity while maximizing benefits.
Data Table: Traditional vs. Blockchain Identity Verification
| Feature | Traditional Methods | Blockchain-Based Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | Centralized databases | Decentralized distributed ledgers |
| Security | Vulnerable to breaches | Enhanced with cryptographic protection |
| User Control | Limited | Full control through self-sovereign IDs |
| Transparency | Limited | High due to immutable records |
| Fraud Prevention | Reactive approach | Proactive and tamper-proof |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher operational costs | Reduced costs over time |
| Global Accessibility | Restricted by jurisdiction | Borderless and accessible globally |
Legal Aspects, FAQs, and Conclusion
As blockchain technology becomes a cornerstone of identity verification, understanding the legal framework and addressing common concerns is essential for businesses and individuals alike. This section delves into the legal considerations, frequently asked questions, and key takeaways for blockchain identity verification.
Legal Considerations for Blockchain Identity Verification
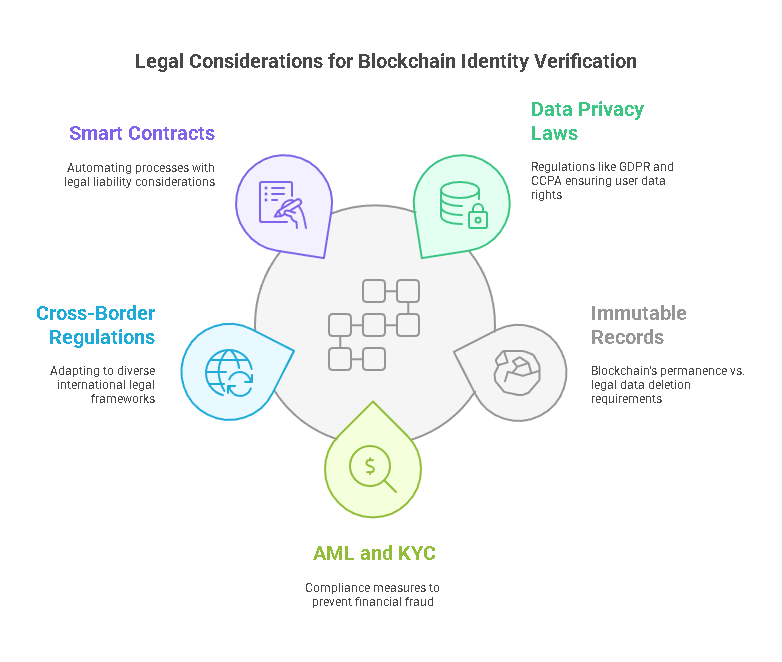
- Data Privacy Laws:
Blockchain identity verification must comply with regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. These laws emphasize user rights over their data, including access, correction, and deletion. - Immutable Records vs. Data Deletion:
A key challenge lies in reconciling blockchain’s immutability with laws requiring data deletion. Solutions like zero-knowledge proofs and off-chain storage are being explored to address this issue. - Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC):
Industries like finance must ensure blockchain-based systems meet AML and KYC requirements to prevent fraudulent activities. - Cross-Border Regulations:
Blockchain’s global reach necessitates compliance with varying international regulations. Businesses must ensure their systems are adaptable to different legal frameworks. - Smart Contracts and Liability:
Smart contracts automate processes, but questions about liability in cases of errors or disputes remain. Clear legal guidelines are needed to address these concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does blockchain technology ensure secure identity verification?
Blockchain ensures security through decentralization, cryptographic encryption, and immutable ledgers. These features make it nearly impossible to alter or hack stored data.
Is blockchain identity verification applicable for small businesses?
Yes, blockchain solutions are scalable and can be tailored to the needs of small businesses, providing cost-effective and secure identity verification.
What are the key advantages of blockchain over traditional verification methods?
Blockchain offers enhanced security, greater user control, reduced fraud, and global accessibility compared to centralized systems.
How is user data protected in blockchain identity verification systems?
User data is encrypted and stored in a decentralized manner. Only the user controls access through private keys, ensuring privacy and security.
Are there any risks associated with blockchain identity verification?
Potential risks include scalability issues, interoperability challenges, and regulatory uncertainties. However, these can be mitigated with proper planning and technology selection.
Conclusion
Blockchain identity verification is transforming the way businesses and individuals manage personal data. Its key features, including security, transparency, and decentralization, address the shortcomings of traditional identity verification systems.
As organizations adopt this technology, compliance with legal standards and addressing scalability challenges will be crucial. Partnering with trusted providers like Precisehire can streamline the transition, ensuring efficient and secure identity verification processes.
The future of identity verification lies in blockchain’s ability to empower users, enhance trust, and create a more connected, secure digital landscape. By embracing this technology, businesses can not only meet current demands but also prepare for a data-driven future.
