Steps to Take Before a Drug Screening on Probation
What Is Probation Drug Screening?
Probation drug screening refers to the process by which individuals who are serving probation after being convicted of a crime are tested for drug use. This is a critical component of probation conditions aimed at ensuring compliance with the terms set by the court. Drug screening is designed to monitor probationers’ behavior, detect any illegal substance use, and assess their commitment to rehabilitation. The process often involves a variety of testing methods and may be administered at different intervals during the probation period, depending on the requirements of the probation officer or the court.
Drug testing for probation is essential not only for monitoring the probationer’s compliance with the law but also for promoting public safety. By detecting illicit drug use early, probation officers can intervene and provide necessary support to ensure that the probationer stays on the path to rehabilitation. Probation drug screening also helps deter drug-related crime, as individuals may be less likely to engage in illegal behavior if they know their drug use is being closely monitored.
Types of Drug Tests Used in Probation
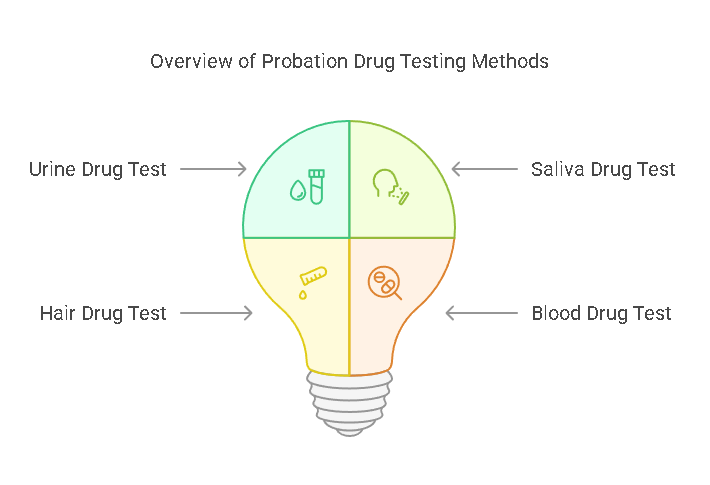
Probation drug screenings rely on various types of tests to detect substances in an individual’s system. These tests differ in terms of the substances they can detect, the length of time they can detect drug use, and their level of invasiveness. The most common types of drug tests used in probation include:
- Urine Drug Test: This is the most widely used method for probation drug screening. Urine tests are typically used to detect recent drug use, as drugs and their metabolites are usually present in urine for up to a few days. Urine tests can detect substances like marijuana, cocaine, opiates, methamphetamine, and others. Due to their non-invasive nature and cost-effectiveness, they are commonly used by probation departments.
- Saliva Drug Test: Saliva testing has become increasingly popular for probation drug screenings. It is non-invasive, easy to administer, and can detect recent drug use (usually within 24-48 hours). Saliva tests can detect many of the same substances as urine tests but may not be able to identify drug use that occurred further in the past. These tests are less invasive and can be conducted more frequently, making them a suitable choice for probation drug screening.
- Hair Drug Test: Hair follicle testing is used to detect drug use over a longer period, typically up to 90 days. This method can detect a wider range of substances and provides a more extended detection window compared to urine or saliva tests. Hair drug tests are considered less invasive but are often more expensive, which may limit their use in some probation settings.
- Blood Drug Test: Blood tests are less commonly used for routine probation drug screening but may be employed in specific cases where other tests are insufficient. Blood testing is invasive, requires a medical professional to collect the sample, and can detect drug use within a short time frame. However, it has a limited detection window compared to urine or hair tests.
Each drug test type has its advantages and limitations, and probation departments may use different testing methods depending on the specific circumstances of the probationer, such as the substances they are being monitored for or the frequency of testing required.
Importance of Probation Drug Screening for Compliance and Public Safety
Probation drug screening plays a crucial role in ensuring that individuals on probation adhere to the conditions set by the court. One of the key aspects of probation is that probationers must refrain from illegal activities, including substance abuse. Drug use is often associated with criminal behavior, and by testing probationers, authorities can identify those who are engaging in illegal drug use and take appropriate action.
The consequences of failing a drug test during probation can be severe. Depending on the terms of the probation, failing a drug test may result in an extension of the probationary period, a more stringent set of conditions, or even the revocation of probation and incarceration. For probation officers, drug testing is a vital tool for enforcing compliance with probation requirements and ensuring that probationers are making progress toward rehabilitation.
From a public safety perspective, probation drug testing helps reduce the likelihood of probationers committing further crimes. Substance abuse often contributes to criminal activity, and by monitoring and addressing drug use early, probation drug screening can reduce recidivism and promote rehabilitation. By detecting drugs in a probationer’s system, probation officers can intervene and offer support before the individual’s behavior escalates into criminal activity.
The General Process of Probation Drug Testing
Probation drug testing typically follows a standardized process, from sample collection to result interpretation. Here’s an overview of the general procedure:
- Sample Collection: The first step in probation drug screening is the collection of a sample. The sample type will depend on the drug testing method chosen by the probation department. For example, a urine sample may be collected by a trained technician or in a private, secure setting, while a saliva or blood test may be administered on-site. Hair samples are usually collected by cutting a small section of hair from the individual’s head or body.
- Laboratory Analysis: Once the sample is collected, it is sent to a laboratory for analysis. In some cases, probation departments may conduct preliminary tests in-house, but confirmatory tests are often performed by certified laboratories to ensure accuracy. The laboratory analyzes the sample for the presence of drugs and their metabolites.
- Result Interpretation: After the laboratory analysis, the results are interpreted. If drugs are detected in the sample, the probation officer will take appropriate action, which may include additional drug testing, counseling, or other interventions. Probationers are typically given the opportunity to challenge the results if they believe there has been an error.
- Follow-Up: Depending on the results of the drug test, probation officers may require additional follow-up testing or counseling. Probationers who test positive for drugs may face consequences such as extended probation or further legal action. In some cases, probation officers may refer the individual to rehabilitation programs or treatment centers.
Frequency of Drug Tests During Probation
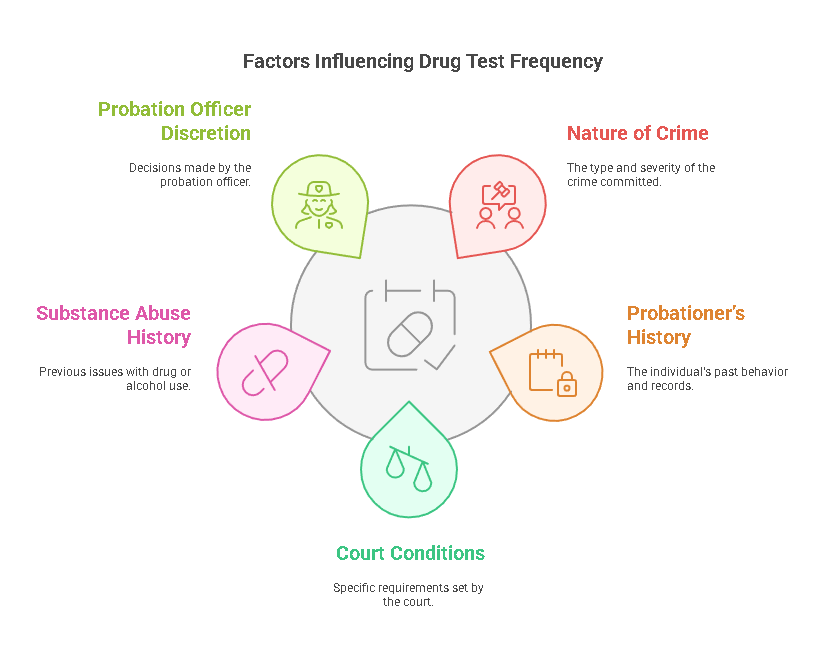
The frequency of drug tests during probation varies depending on several factors, including the nature of the crime, the probationer’s history, and the conditions set by the court. In some cases, probationers may be required to submit to drug testing on a random or periodic basis. Random drug testing helps ensure that probationers remain compliant with their probation terms and that illicit drug use is detected as early as possible.
In other cases, probationers may be required to undergo more frequent drug testing, especially if they have a history of substance abuse or if they are involved in high-risk probation cases. Probation officers have discretion in determining the frequency of testing based on the individual’s circumstances, and some individuals may be subject to daily or weekly tests.
Consequences of Failing a Drug Test During Probation
Failing a drug test during probation can have serious consequences. If a probationer tests positive for drugs, the probation officer may impose additional restrictions, such as more frequent testing, mandatory drug counseling, or even an extension of the probation period. In some cases, failing a drug test can result in the revocation of probation and the imposition of a prison sentence.
The severity of the consequences depends on the probationer’s history, the type of drugs detected, and the terms set by the court. For example, probationers who fail multiple drug tests or who are caught using drugs that were specifically prohibited in their probation terms may face harsher penalties.
Role of Probation Officers in Managing Drug Testing Requirements
Probation officers play a central role in managing and enforcing drug testing requirements. They are responsible for ensuring that probationers comply with the terms of their probation, including attending drug tests at specified times. Probation officers are also responsible for interpreting the results of drug tests and taking appropriate actions when necessary.
Additionally, probation officers often serve as a liaison between the probationer and treatment providers, referring individuals to counseling or rehabilitation programs when needed. By monitoring drug use and offering support, probation officers help probationers remain on track toward rehabilitation and reduce the risk of recidivism.
How Probation Drug Screening Is Implemented by Probation Departments
Probation drug screening is a critical aspect of the probation process, used by probation departments to ensure that individuals are abiding by the conditions set by the court. The implementation of drug screening varies depending on the department’s resources, the severity of the probationer’s offense, and the specific conditions of the probation. Generally, probation departments integrate drug testing into their daily operations to maintain compliance and safeguard the integrity of the rehabilitation process.
To begin with, probation departments typically establish protocols outlining the frequency and type of drug tests required for probationers. These protocols depend on various factors, such as the nature of the offense, the probationer’s history of drug use, and the specific requirements imposed by the court. In some cases, individuals who have a history of substance abuse may be required to submit to more frequent testing, while others may be subject to random drug screenings.
Testing may be conducted at probation offices, designated testing centers, or even remotely. Probation officers are responsible for managing the logistics of the testing process, ensuring the integrity of the sample collection, and following legal and regulatory requirements to maintain the accuracy of results.
For probationers with serious substance abuse issues, drug screening may be part of a broader rehabilitation plan, which includes counseling, treatment programs, or residential rehabilitation. Probation officers work closely with other professionals, such as counselors or healthcare providers, to ensure that probationers receive the necessary care and guidance.
Step-by-Step Process for Conducting Probation Drug Screenings
Probation drug screenings are typically performed following a structured, standardized process to ensure accuracy, reliability, and compliance with regulations. Below is a breakdown of the steps involved in conducting a probation drug screening:
- Pre-Screening Preparation: Before drug testing takes place, the probation officer must ensure that all necessary paperwork and consent forms are in order. This includes verifying the individual’s identity, ensuring that the drug test is within the scope of the probation conditions, and informing the probationer of the test’s purpose. In some cases, probationers are asked to sign a consent form acknowledging that they understand the nature of the test.
- Sample Collection: Depending on the method of drug testing being used (urine, saliva, hair, or blood), the probationer will be asked to provide a sample under controlled conditions. For urine and saliva tests, sample collection may take place in a private area to prevent tampering. In the case of hair or blood tests, samples are usually collected by a certified technician in a medical setting. The probation officer may be present to ensure that the process is carried out appropriately and securely.
- Laboratory Analysis: Once the sample has been collected, it is sent to a certified laboratory for analysis. The laboratory tests the sample for the presence of illegal drugs or their metabolites. In some cases, preliminary tests may be conducted in-house, but confirmatory testing is often required to ensure the accuracy of the results. Most laboratories follow strict protocols and use advanced technology to detect even trace amounts of drugs, ensuring the test results are reliable.
- Result Interpretation and Reporting: After the laboratory analysis, the results are sent back to the probation department. The probation officer reviews the results to determine whether the probationer is in compliance with the drug testing conditions. If the test is positive for illegal substances, the officer may initiate follow-up procedures, which could include re-testing, counseling, or taking legal action, depending on the severity of the violation.
- Post-Screening Procedures: Based on the results of the drug test, probation officers may decide to take further action. If the individual has failed the drug test, the probation officer may issue a warning, adjust the terms of probation, or, in more serious cases, recommend probation revocation or a jail sentence. Probationers may also be required to attend substance abuse counseling or rehabilitation programs to address underlying issues with drug use.
Accuracy and Reliability of Probation Drug Screening Methods
The accuracy of probation drug screening is a crucial concern for probation officers, as unreliable results can undermine the entire process. While no drug testing method is perfect, advancements in technology and scientific methods have significantly improved the reliability of drug screenings. However, challenges do remain, particularly in the form of false positives and false negatives.
- False Positives: A false positive occurs when a drug test incorrectly indicates the presence of a substance that is not actually in the probationer’s system. This can occur due to various factors, such as cross-reactivity with other substances or improper sample handling. For instance, over-the-counter medications, certain foods, and even some legal substances can cause a false positive result.
- False Negatives: A false negative happens when the drug test fails to detect a substance that is present in the probationer’s system. This can be due to errors in the testing process, insufficient sample collection, or testing methods that have a limited detection window. For example, hair tests may not detect recent drug use, and urine tests may miss certain substances depending on their metabolism rate.
Despite these challenges, probation departments can improve the accuracy and reliability of drug screening by using certified and validated testing kits, following strict testing protocols, and employing confirmatory testing for positive results. Additionally, training probation officers and testing personnel to recognize potential issues with the results can help minimize errors.
Comparing Different Drug Testing Methods
In order to better understand the pros and cons of each drug testing method used in probation drug screening, here is a comparison of common test types:
| Drug Testing Method | Accuracy | Detection Window | Cost | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urine Test | High (if properly administered) | 1-5 days (depending on the drug) | Low | Inexpensive, easy to administer | Can be affected by dilution or adulterants |
| Saliva Test | Moderate to High | 1-2 days | Moderate | Non-invasive, quick results, easy to administer | Limited detection window, not as reliable for certain drugs |
| Hair Test | High | Up to 90 days | High | Longer detection window, can detect past drug use | Expensive, cannot detect recent use |
| Blood Test | Very High | 1-2 days | Very High | Highly accurate, can detect recent use | Invasive, expensive, requires medical professional |
Each testing method has its unique strengths and weaknesses, and probation departments need to choose the right method based on the specific needs of the case.
Challenges in Probation Drug Screening and Solutions
Probation drug screening faces several challenges that can impact its effectiveness. Some of the most common challenges include:
- False Positives and False Negatives: As mentioned, false positives and false negatives can lead to inaccurate results. To minimize these errors, probation departments should use certified testing kits, implement confirmatory testing, and provide clear guidelines for probation officers on how to handle suspicious results.
- Privacy Concerns: Probationers may feel that drug testing violates their privacy, especially if the testing process is invasive or if they are required to provide frequent samples. To address these concerns, probation departments should ensure that testing procedures are done in a respectful and confidential manner and that all legal requirements regarding privacy are adhered to.
- Cost of Drug Testing: Some drug testing methods, such as hair and blood tests, can be expensive. Probation departments with limited budgets may face challenges in offering these more expensive tests. One solution is to implement a tiered approach to testing, using more cost-effective methods like urine or saliva tests as the primary screening tools and reserving more expensive tests for cases where necessary.
Precisehire’s Role in Probation Drug Screening
Precisehire offers a range of drug testing solutions that can help probation departments streamline their drug screening processes. Their services include access to certified drug testing kits, laboratory testing, and comprehensive reporting tools to ensure accuracy and compliance. By utilizing Precisehire’s solutions, probation departments can save time, reduce errors, and maintain a high level of compliance with legal requirements. Precisehire’s advanced drug screening services help probation officers make informed decisions based on accurate, timely results.