A Comprehensive Guide to DHS 38 Verification of Employment

What is DHS 38 Verification of Employment?
The DHS 38 Verification of Employment form is an official document used primarily in the context of government assistance programs. It is designed to verify an individual’s employment status, job title, income, and employment history for government agencies or social service programs. When an individual applies for housing assistance, public welfare benefits, or immigration benefits, the DHS 38 form may be required to confirm that the applicant is employed and has a reliable source of income.
This form is most commonly requested in situations where eligibility for government services is based, in part, on an individual’s employment status. Whether it’s for unemployment benefits, housing programs, or social security, the DHS 38 form plays a crucial role in ensuring that the applicant meets the necessary employment and income criteria for assistance.
Why is DHS 38 Verification of Employment Important?
The DHS 38 Verification of Employment form is vital for several reasons, particularly in the context of social services and government support programs. It ensures that individuals applying for benefits are accurately reporting their employment status. This verification is crucial for maintaining the integrity of government programs and ensuring that resources are allocated to those who genuinely need assistance. Below are some of the primary reasons why this form is important:
- Accuracy of Employment Data: The form helps prevent individuals from fraudulently claiming government assistance by providing accurate and verified employment details.
- Eligibility for Benefits: The DHS 38 ensures that applicants meet the employment and income requirements for specific government programs. For example, housing programs may require proof of employment to determine rent subsidies or eligibility for assistance.
- Compliance with Regulations: By using the DHS 38 form, employers comply with government regulations related to social services, ensuring that the process remains transparent and fair.
- Prevents Misuse of Government Resources: Accurate employment verification prevents individuals from receiving benefits they may not be entitled to, ensuring government resources are reserved for those in genuine need.
How is DHS 38 Verification of Employment Used?
DHS 38 Verification of Employment is used by employers to verify an employee’s job status when they apply for government services or assistance programs. Employers are responsible for completing this form when an employee requests verification to support their application for public benefits.
Here are some common situations where the DHS 38 Verification of Employment form might be used:
- Housing Assistance: A tenant applying for rental assistance programs (such as Section 8 housing) may need to submit a DHS 38 form to demonstrate that they are employed and earning a stable income.
- Immigration Benefits: Immigrants seeking certain immigration benefits may need to submit the DHS 38 form to prove that they are employed and financially stable.
- Unemployment Benefits: Individuals who are receiving unemployment benefits may be asked to complete the form to verify their previous employment or to update their employment status as part of their ongoing claims.
Employers fill out the form to confirm the employee’s employment details, such as their position, income, and how long they’ve been employed. This form helps ensure that only eligible individuals receive public assistance, based on accurate and verifiable information.
Key Information Required in DHS 38 Verification of Employment
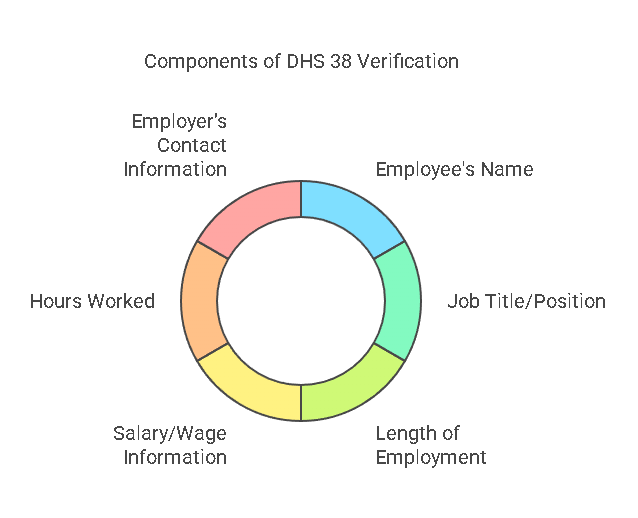
The DHS 38 Verification of Employment form requires several key pieces of information to properly verify an employee’s status. Employers are responsible for filling out these sections accurately to ensure the employee can be approved for government programs or benefits. Common information required includes:
- Employee’s Name: Full name of the individual whose employment is being verified.
- Job Title/Position: The employee’s current job title or position within the company.
- Length of Employment: The start date of the employee’s employment with the company, and sometimes the end date if the employee has recently left.
- Salary/Wage Information: The employee’s current salary or hourly wage. This is a crucial piece of information for programs that assess eligibility based on income levels.
- Hours Worked: In some cases, the number of hours worked per week or month may be required, especially for part-time employees.
- Employer’s Contact Information: The name, position, phone number, and address of the employer filling out the verification. This ensures the authenticity of the form and allows for follow-up if necessary.
The form may also request additional details or certifications depending on the specific program or government agency requiring the verification. For example, in some instances, an employee may need to provide documentation of recent pay stubs or employment contracts to complement the form.
Summary
The DHS 38 Verification of Employment form is a crucial document used by employers to confirm the employment status, income, and job history of employees applying for government assistance. By ensuring that only eligible individuals receive benefits, the DHS 38 form helps maintain the integrity of social services and prevents misuse of public resources. Employers play an important role in the verification process, providing accurate and detailed information to ensure that the applicant meets the requirements of various government programs.
Steps to Complete DHS 38 Verification of Employment
Completing the DHS 38 Verification of Employment form involves a straightforward process for both the employer and employee. Here is a step-by-step guide:
1. Setting Up the Form
To begin, employers need to obtain the DHS 38 form, which can be found on the relevant government agency’s website or provided directly by the organization requesting the verification. Ensure that the most current version of the form is being used.
2. Employer Information Section
The employer must fill out the following details in the form:
- Company Name: The official name of the employer’s business or organization.
- Employer’s Name and Title: The person filling out the form, including their job title.
- Employer’s Contact Information: The employer’s phone number, email, and mailing address for follow-up.
3. Employee Information Section
The employer will also provide the employee’s details, including:
- Employee’s Full Name: The individual whose employment is being verified.
- Job Title: The employee’s current role.
- Start Date of Employment: The date the employee began working for the employer.
- Salary or Hourly Wage: The employee’s compensation, including salary or hourly rate.
- Hours Worked per Week: For part-time employees, the number of hours they work each week.
4. Signatures
Once the form is completed, the employer will sign and date it to confirm that the information is accurate. In some cases, the employee may also be required to sign to verify the correctness of the details.
5. Submitting the Form
After signing, the employer submits the form to the relevant government agency. Depending on the requirements, the form may be submitted online, by mail, or in person.
Benefits of Using DHS 38 for Employment Verification
The DHS 38 form offers several advantages for both employers and employees:
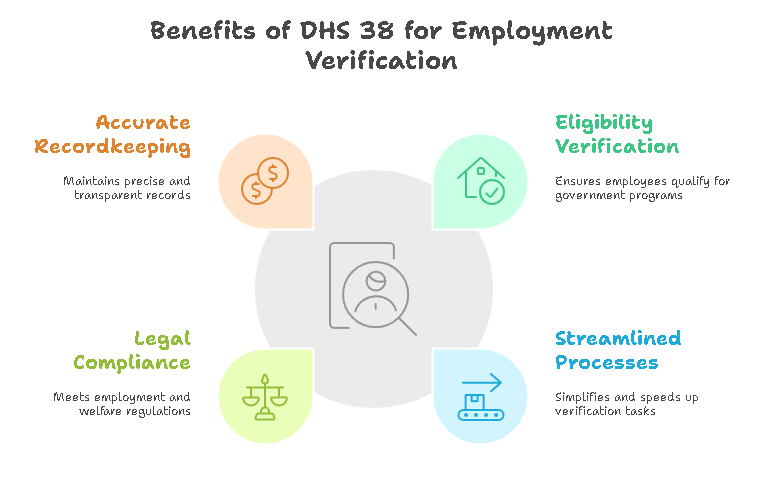
1. Ensures Eligibility for Government Programs
The DHS 38 form helps verify that employees meet the eligibility requirements for government programs, including housing benefits and unemployment assistance. It ensures that only individuals who qualify based on employment status and income can receive aid, reducing the risk of fraudulent claims.
2. Streamlines Verification Processes
The DHS 38 form simplifies the verification process for employers by providing a standard format for submitting employee information. This reduces the administrative burden of handling numerous verification requests and allows employers to quickly process requests from employees seeking government assistance.
3. Legal Compliance with Employment and Welfare Regulations
Using the DHS 38 form helps ensure that employers comply with legal requirements surrounding employment verification for welfare and social services. It provides a standardized method of reporting that meets regulatory standards, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
4. Accurate Recordkeeping and Transparency
The form allows employers to maintain accurate records of employment for each employee, which is important for audits or legal inquiries. Employees also benefit from the transparency the form provides, as it ensures that their employment details are verified correctly and reported appropriately to relevant agencies.
Precisehire
For employers seeking a more comprehensive solution for employment verification, Precisehire offers valuable services. Precisehire provides background check services and employment verification that complement the DHS 38 form, ensuring that employers can verify an employee’s full work history and meet all compliance requirements. By using Precisehire, employers can reduce the risks associated with inaccurate employee data and streamline the verification process for greater efficiency.
Data Table: Comparison of DHS 38 with Other Employment Verification Forms
Below is a data table comparing the DHS 38 form with other commonly used employment verification forms, such as the I-9 and W-2 forms:
| Form | Purpose | Key Information | Used For |
|---|---|---|---|
| DHS 38 Verification of Employment | Verifies employment status for government assistance programs | Job title, salary, hours worked, start date | Government assistance, housing programs, welfare |
| I-9 Form | Verifies eligibility to work in the U.S. | Employee’s citizenship status, work eligibility | Employment eligibility verification (U.S. only) |
| W-2 Form | Summarizes annual wages and taxes withheld for an employee | Total wages, federal tax withheld, employer’s details | Annual tax filing, income verification |
Each form serves a different purpose in verifying employment status. The DHS 38 form is specifically designed to verify employment for government assistance, whereas the I-9 and W-2 forms are used for broader employment and tax verification purposes.