Bup Drug Screening Explained: How It Works, Why It Matters, and Legal Implications

Understanding Bup Drug Screening
Drug testing plays a crucial role in various industries and medical practices, particularly when it comes to monitoring the use of specific substances like buprenorphine. Bup drug screening refers to the testing for buprenorphine and its metabolites in the body. This article delves into the process, purpose, and importance of Bup drug screening, as well as the different types of tests available and how they work.
What Is Bup Drug Screening?
Bup drug screening is a testing process used to detect the presence of buprenorphine in a person’s system. Buprenorphine is a medication commonly used in the treatment of opioid addiction and pain management. It is a partial agonist that helps alleviate withdrawal symptoms and cravings in individuals who are dependent on opioids. However, because buprenorphine can also be misused or abused, drug screenings are often employed to ensure it is being used appropriately and to detect any signs of misuse or diversion.
The term “Bup” is commonly used as shorthand for buprenorphine in the context of drug testing. These screenings are widely used in various settings, including medical treatment programs, employment, and law enforcement, to verify adherence to treatment regimens or to identify abuse.
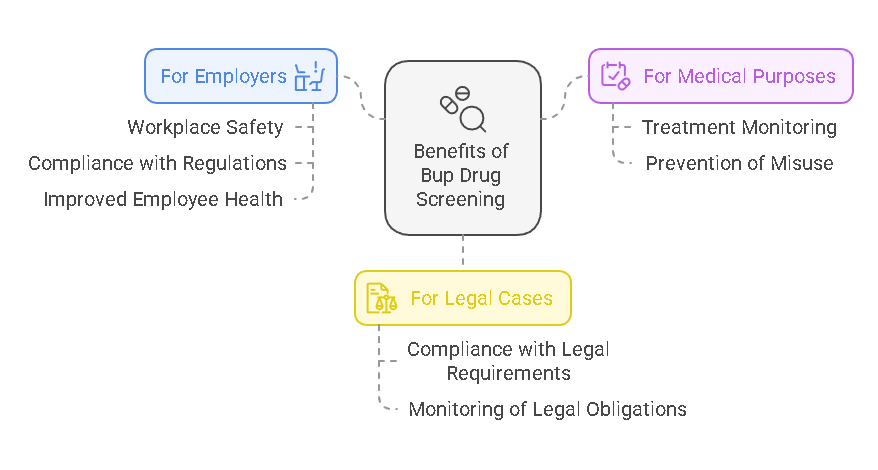
Why Is Bup Drug Screening Important?
Bup drug screening plays a critical role in several areas:
- Substance Abuse Treatment
One of the primary uses of Bup drug screening is in addiction treatment programs, where buprenorphine is prescribed to help manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Regular drug screenings help ensure that the patient is adhering to their prescribed treatment plan and not abusing the drug. - Employment
Many employers, particularly in safety-sensitive industries (such as transportation or construction), require drug screenings to ensure that employees are not under the influence of substances that could impair their ability to perform their duties. Bup drug screening may be part of a larger drug testing policy to ensure workplace safety and compliance. - Law Enforcement and Legal Proceedings
In legal contexts, Bup drug screening can be crucial for individuals on probation or parole, or involved in custody disputes. These tests can help confirm whether someone is abiding by court orders or conditions of release. They can also be used in situations where a person is suspected of abusing their prescription medications. - Medical Monitoring
Healthcare providers use Bup drug testing to monitor patients who are prescribed buprenorphine to ensure they are following their treatment protocol. It can also help identify any potential misuse or diversion of the drug.
By ensuring compliance with prescribed use, Bup drug screening helps prevent abuse and ensures safety in both medical and professional environments.
What Does Bup Drug Screening Detect?
Bup drug screening primarily detects buprenorphine, but it can also identify its metabolites in the body. When buprenorphine is ingested, it is metabolized by the liver and converted into various metabolites, such as norbuprenorphine. These metabolites are then excreted in the urine, blood, or saliva, making them detectable through drug tests.
Here are the key substances that Bup drug screening typically detects:
- Buprenorphine: The parent drug that is directly prescribed for opioid addiction and pain management.
- Norbuprenorphine: A major metabolite of buprenorphine, which is also tested for in drug screening, as it can remain in the body longer than the parent drug.
The presence of either buprenorphine or its metabolites can indicate recent use or ongoing consumption, and the test results can be used to determine if the individual is adhering to their treatment regimen or abusing the drug.
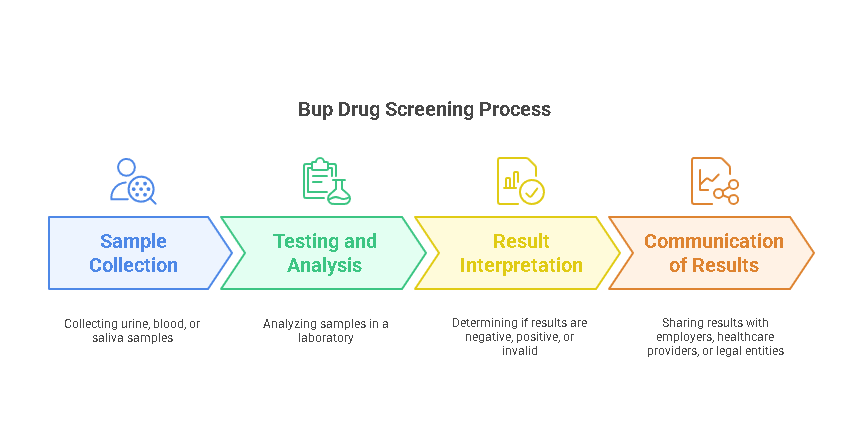
How Does Bup Drug Screening Work?
Bup drug screening typically involves the collection of biological samples, which are then tested for the presence of buprenorphine or its metabolites. There are several types of tests commonly used for this purpose, each with its own procedure, advantages, and limitations.
Types of Bup Drug Tests
- Urine Drug Testing
- How It Works: Urine tests are the most commonly used for Bup drug screening. A urine sample is collected from the individual and tested for the presence of buprenorphine and its metabolites. Urine tests can detect buprenorphine use for up to several days after ingestion, depending on factors such as frequency of use and individual metabolism.
- Accuracy: Urine tests are generally considered reliable and are able to detect both buprenorphine and its metabolites. However, they are less effective in detecting recent use (within a few hours) and may have a longer detection window.
- Blood Drug Testing
- How It Works: Blood tests are typically used in more specialized or clinical situations. A blood sample is drawn from the individual and analyzed for buprenorphine and its metabolites. Blood tests offer a more immediate detection window and can indicate if the drug was recently used.
- Accuracy: Blood tests are highly accurate and can detect buprenorphine use within a much shorter time frame compared to urine tests. However, blood tests are less commonly used due to the invasive nature of the sample collection and their higher cost.
- Saliva Drug Testing
- How It Works: Saliva tests are less invasive and can be conducted on-site, which makes them convenient for employers or law enforcement agencies. A sample of saliva is collected, and buprenorphine and its metabolites are tested.
- Accuracy: Saliva tests are generally accurate for detecting recent use of buprenorphine, typically within a few hours to a day. They are less effective at detecting long-term use and may have a shorter detection window than urine tests.
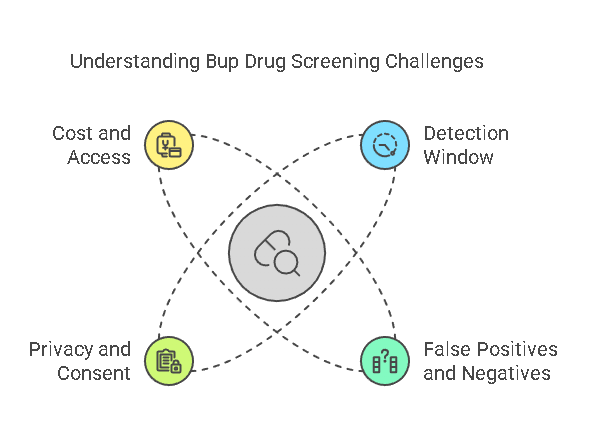
Accuracy and False Positives/Negatives
Bup drug screenings are not foolproof, and there is always a possibility of false positives or false negatives. A false positive occurs when a test indicates the presence of buprenorphine or its metabolites when they are not actually present. This can happen due to cross-reactivity with other substances or medications. A false negative, on the other hand, occurs when a test fails to detect buprenorphine or its metabolites despite their presence in the body.
To minimize the risk of false results, it’s important to follow proper testing protocols and, when necessary, confirmatory tests (such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry) can be used to verify initial screening results.