Do Background Checks Show Education? Role of Education

Do Background Checks Show Education? Understanding the Role of Education Verification
Background checks are a crucial component of the hiring process, providing employers with a deeper understanding of a candidate’s history, qualifications, and character. In today’s competitive job market, ensuring the accuracy of an applicant’s resume and application is paramount. As part of the verification process, education background checks are often included to confirm that candidates possess the necessary academic qualifications. But the question arises: Do background checks show education? This article will explore how education verification fits into employment background checks, why it’s important for employers, and how this process is typically carried out.
Overview of Employment Background Checks
An employment background check is a comprehensive investigation conducted by employers to verify the details provided by candidates in their resumes and applications. It aims to identify any red flags that could impact an individual’s suitability for a role. Employment background checks cover a range of factors, including:
- Criminal History: Ensuring the candidate has no past criminal activity that would pose a risk to the workplace or others.
- Employment History: Verifying past employment, job titles, dates, and responsibilities to confirm the candidate’s work experience.
- Education: Checking the candidate’s educational qualifications to ensure they meet the requirements specified for the job.
Other background checks may involve assessing credit history, driving records, professional licenses, or social media activity. However, education verification specifically focuses on confirming the academic credentials claimed by a candidate. This is a vital aspect of the screening process because education qualifications are often a fundamental requirement for job roles.
Education Verification
Education verification refers to the process of confirming the academic qualifications a candidate claims to possess. This may include verifying the completion of a high school diploma, bachelor’s degree, or advanced degrees from accredited institutions. Education verification ensures that the candidate has the necessary knowledge and skills that the employer deems important for the position.
Why is education verification important? In many cases, employers rely on academic qualifications to determine whether a candidate has the foundational skills required for a job. For instance, a company hiring an engineer may require a degree in engineering to ensure the candidate has the technical expertise for the role. Inaccurate or exaggerated claims about academic achievements can lead to mismatches between the candidate and the job, affecting the employer’s decision-making process.
Do Background Checks Show Education?
The short answer is yes — background checks can show education. However, it’s important to clarify how this process works.
When employers conduct background checks, they typically request permission from the candidate to verify their educational background. Education verification itself is usually done in one of two ways:
- Direct Verification by the Employer:
Some employers may reach out directly to the educational institutions listed by the candidate to verify attendance, degrees awarded, and dates of graduation. However, this method can be time-consuming and may not always yield quick results. - Third-Party Background Screening Services:
Many employers choose to use third-party background screening services to verify education. These services have established connections with educational institutions, making the verification process more efficient. Third-party services can quickly confirm a candidate’s degree, major, and graduation year, reducing delays in the hiring process.
Regardless of the method used, education verification is an essential component of a comprehensive background check and is often one of the first steps an employer takes to ensure the candidate meets the necessary qualifications.
Importance for Employers

For employers, verifying education is not just about confirming that a candidate holds a degree; it’s about reducing the risk of hiring someone who may not be qualified for the job. Here are some key reasons why employers need to verify education during the hiring process:
- Preventing Resume Fraud:
Resume fraud is a growing concern, and one of the most common areas where candidates exaggerate is their educational background. Some candidates may falsely claim to have earned degrees or certifications they didn’t complete. By verifying education, employers can prevent hiring individuals who misrepresent their qualifications. - Ensuring the Right Skillset:
Employers typically require certain educational qualifications for specific positions. Verifying that a candidate has completed the required academic programs ensures they possess the necessary knowledge and skills for the job. - Reducing Legal Risks:
Failing to verify a candidate’s education could expose an employer to legal risks, especially if an employee is hired based on fraudulent credentials. For example, if an individual with a fake degree is hired for a high-level position that requires specific expertise, it could damage the company’s reputation or lead to liability issues. - Enhancing the Recruitment Process:
Education verification contributes to a thorough and transparent recruitment process. It helps employers build trust with candidates and ensures that only qualified individuals are considered for employment.
As part of a comprehensive background check, education verification is an essential step that protects both employers and their workforce. Understanding how it works and why it’s important is key for ensuring that the hiring process remains fair, transparent, and efficient.
Types of Education Verification
Education verification can be performed using several different methods, each with its advantages and challenges. The primary goal is to ensure the authenticity of the information provided by the candidate regarding their academic credentials. Here are the most common types of education verification methods:
- Direct Contact with Educational Institutions
The most traditional method of verifying education is for employers or hiring managers to contact the educational institutions listed by the candidate directly. This typically involves reaching out to the registrar’s office or the admissions department of the school to verify the degree, the field of study, and the dates of attendance or graduation. While this method ensures accuracy, it can be time-consuming, especially when dealing with a large volume of candidates or when schools are difficult to contact. - Third-Party Verification Services
Many employers prefer to use third-party background check providers to verify education. These services specialize in conducting thorough background checks, including education verification. By working with third-party companies, employers can save time and reduce the complexity of contacting educational institutions directly. These services have established partnerships with schools and can verify degrees quickly and efficiently. Additionally, they often have access to a larger database of educational records, improving the accuracy of the verification process. - Online Verification Databases
In some cases, certain universities, colleges, or other educational institutions have partnered with verification services to create online databases that can instantly confirm educational credentials. These systems allow background check services to instantly verify if a candidate attended the institution and received the degree they claim to have earned. This method is efficient and provides real-time results, although it may not be available for all institutions. - Verification through Public Records
Some countries or regions may make educational records accessible through government or public databases. For example, certain universities and colleges may have their records listed with government entities for easy access and verification. In this case, verification might be as simple as consulting a public record or using a government-based verification system. However, the availability of this information varies depending on the country or region and may not always cover private institutions.
How Employers Verify Education
Employers typically follow a structured process to verify education during the background check. Here’s an overview of the typical steps involved in verifying a candidate’s educational credentials:
- Obtaining Consent
Before initiating the background check, employers must first obtain consent from the candidate. This is usually part of the job application process, where candidates are asked to sign a consent form authorizing the employer or a third-party service to perform a background check. It’s important for employers to inform candidates that their educational background will be verified as part of the process. - Collecting Information from the Candidate
Once consent is obtained, employers may ask candidates to provide details about their educational history, such as the name of the institution, degree or diploma earned, dates of attendance, and any relevant certifications. This information serves as the basis for verifying the candidate’s educational credentials. - Verification by the Employer or Third-Party Service
After gathering the candidate’s educational details, the employer will either reach out to the educational institution directly or use a third-party verification service to verify the credentials. If using a third-party service, the company will input the candidate’s information into the service’s system, which will then handle the process of verifying the education. - Handling Discrepancies
If the background check reveals any discrepancies between the information provided by the candidate and what is found in the verification process, the employer may choose to follow up with the candidate for clarification. If the discrepancies are significant, it may impact the candidate’s eligibility for the job, depending on the employer’s policies and the severity of the misrepresentation. - Final Decision
Once the education verification is complete, and all other background checks have been conducted, the employer can make an informed decision about the candidate’s suitability for the position. If everything checks out, the candidate moves forward in the hiring process. If discrepancies or red flags are found, the employer may choose to disqualify the candidate from further consideration.
Role of Third-Party Services in Education Verification
While some employers may choose to handle education verification in-house, many prefer to work with third-party verification services, especially for larger organizations or those conducting mass hiring. Here’s how services like Precise Hire play a key role in streamlining the education verification process:
- Efficiency and Speed: Third-party services can quickly verify educational credentials, providing faster results than employers would typically receive if they were to contact educational institutions directly. This expedites the hiring process and prevents delays that could occur while waiting for responses from schools or universities.
- Expertise and Accuracy: Background screening companies specialize in education verification, meaning they are equipped to handle even complex cases. They have established relationships with educational institutions, which increases their ability to get accurate information promptly. Additionally, these services stay up-to-date with the latest verification procedures and legal guidelines, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
- Access to Databases: Third-party providers like Precise Hire often have access to extensive databases containing information from a wide range of institutions, which can be especially beneficial for verifying degrees from schools that do not have publicly accessible records or online verification systems. These services can cross-check education details against comprehensive databases to confirm that candidates’ degrees and credentials are valid.
- Compliance with Laws: Using third-party services also helps employers ensure they are complying with relevant legal regulations surrounding background checks, including the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) in the United States. These services handle the paperwork and ensure that background checks are carried out in accordance with privacy laws and regulations, mitigating any potential legal risks for employers.
- Scalability: For employers hiring large numbers of candidates, particularly during seasonal hiring periods, third-party verification services can scale their operations to handle high volumes of background checks. This allows businesses to manage a larger pool of candidates while ensuring that the verification process remains thorough and accurate.
Challenges in Education Verification
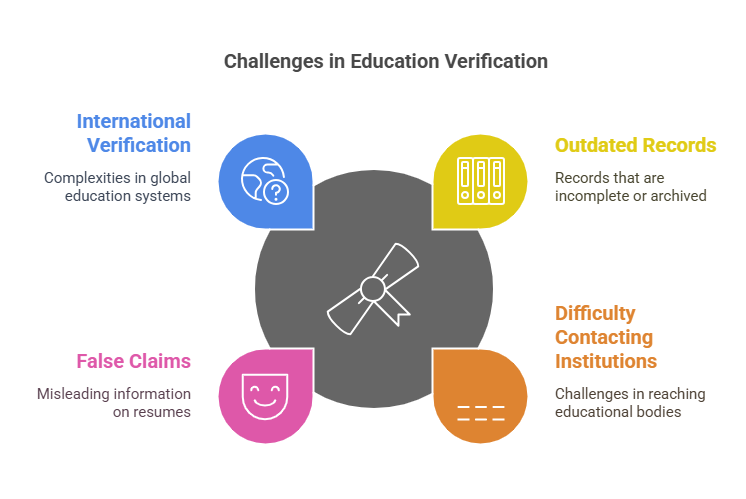
While education verification is crucial, there are several challenges that employers may face in the process:
- Outdated Records:
Some educational institutions may have outdated or incomplete records, particularly for alumni who graduated many years ago. This can make it difficult to verify degrees, especially when records are archived or stored in physical formats. - Difficulty Contacting Institutions:
Reaching out to educational institutions for verification can sometimes be a challenge. Certain schools may have limited staff or outdated contact information, and schools with large alumni networks may take longer to respond to requests. - False or Misleading Claims:
While education verification helps prevent resume fraud, some candidates may provide false information that is difficult to verify. For example, they may list a degree from a school that doesn’t exist or provide inaccurate graduation dates. Employers must be diligent in cross-checking details and handling discrepancies carefully. - International Education Verification:
Verifying education credentials from international institutions can be particularly challenging due to differences in educational systems, languages, and record-keeping methods. In these cases, third-party services with expertise in global education verification are often required.
Benefits of Education Verification
Despite the challenges, the benefits of verifying education during the hiring process far outweigh the drawbacks. Here’s why employers should prioritize education verification:
- Reducing Fraud:
Verifying education ensures that candidates are truthful about their academic qualifications, reducing the risk of hiring someone who misrepresents their educational background. - Ensuring Qualifications:
Education verification helps employers ensure that candidates possess the necessary qualifications for the job. For positions requiring specific degrees or certifications, verification is essential to confirm that applicants meet the job’s minimum requirements. - Protecting the Employer’s Reputation:
Hiring candidates with fraudulent educational backgrounds can damage a company’s reputation and potentially result in legal ramifications. Education verification helps safeguard the organization from these risks. - Improved Hiring Decisions:
Accurate education verification leads to better hiring decisions. By confirming that candidates possess the required academic qualifications, employers can make more informed choices, resulting in a more qualified and capable workforce.
Legal Aspects of Education Verification
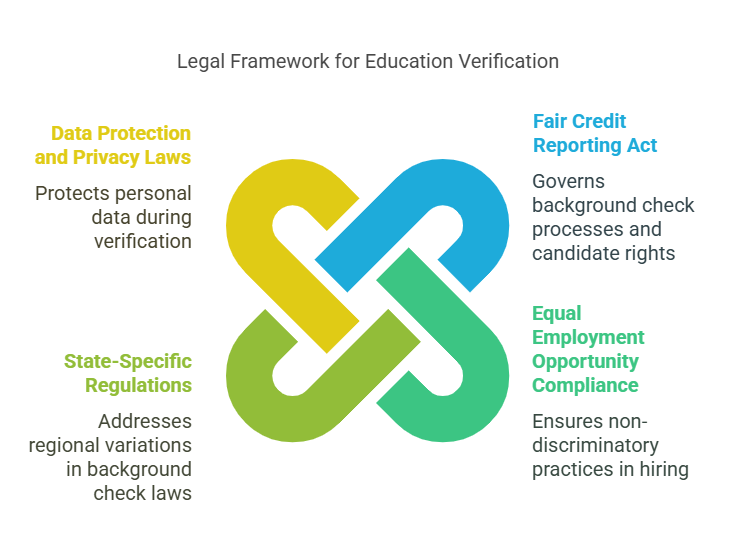
Education verification is an essential part of the background check process, and it’s governed by various legal standards and regulations. Employers must adhere to specific laws to ensure that the process is fair, transparent, and compliant with privacy standards. Below, we explore the most significant legal aspects of education verification in employment background checks.
- Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is a federal law in the United States that governs how background checks are conducted and how employers can use the information collected. The FCRA applies to third-party background screening companies and mandates that employers obtain written consent from candidates before conducting background checks, including education verification.Employers must also provide candidates with the right to dispute any inaccuracies found in their background check results. If an applicant’s educational background contains discrepancies or errors, they have the right to challenge those findings and request an investigation.
The FCRA also regulates the use of background check results, ensuring that employers do not make hiring decisions based on irrelevant or inaccurate information. This law aims to protect candidates’ privacy and prevent discrimination based on personal data that could be unfairly misinterpreted.
- Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) Compliance
Employers must also comply with Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) laws during the hiring process, including when verifying education. Discriminatory practices, such as rejecting candidates based on their educational background in a way that disproportionately impacts certain protected groups, can lead to legal challenges.Employers must ensure that their education verification processes are consistent and fair for all candidates, without bias. Additionally, it is crucial for employers to avoid using education verification as a tool for discrimination, particularly if educational requirements disproportionately exclude certain demographic groups.
- State-Specific Regulations
In addition to federal regulations, employers must also be aware of state-specific laws governing background checks. Many states have their own laws regarding employment screening, and some require employers to follow stricter guidelines than those outlined in the FCRA.For example, certain states mandate that employers must notify applicants before running a background check, or they may require additional consent for verification of educational credentials. Some states also limit how far back an employer can look into a candidate’s background, including education history.
Employers must stay informed about the specific legal requirements in their state or region to ensure compliance with local laws. Failing to do so can result in legal consequences or penalties.
- Data Protection and Privacy Laws
Since education verification involves handling personal information, employers must also consider data protection and privacy laws. In the European Union, for instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) applies to employers and third-party services involved in education verification for candidates from the EU.GDPR requires employers to handle personal data with the utmost care, ensuring it is used only for the intended purpose and stored securely. Employers must also provide candidates with clear information about how their data will be used and allow them to withdraw consent at any time.
For employers outside the EU, similar data protection laws may apply, depending on the jurisdiction. It’s essential for employers to be aware of these regulations to avoid potential violations of privacy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are five common questions related to education verification and background checks, along with detailed answers:
Do all employers verify education during the hiring process?
Not all employers verify education during the hiring process, but many do, especially for positions that require specific academic qualifications. While some employers may skip education verification for lower-level positions or roles that don’t require a degree, education verification is often crucial for higher-level roles or positions that involve specialized knowledge. Employers in fields such as healthcare, engineering, law, and finance are more likely to verify education to ensure candidates meet the necessary qualifications.
How do employers handle discrepancies between the candidate’s stated education and the results of the background check?
If a discrepancy is found between the candidate’s stated education and the results of the background check, employers typically contact the candidate for clarification. If the candidate provides a reasonable explanation or can offer additional documentation to support their claim, the issue may be resolved. However, if the discrepancy is significant or if the candidate is found to have falsified their educational background, the employer may choose to disqualify them from the hiring process.
Can an applicant challenge the results of an education verification?
Yes, an applicant can challenge the results of an education verification if they believe the information is inaccurate. Under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), applicants have the right to dispute errors found in background checks. If a candidate believes their education history has been misreported, they can file a dispute with the background screening company, which is required by law to investigate and correct any inaccuracies.
What happens if a candidate’s education information is found to be fraudulent?
If a candidate’s education information is found to be fraudulent during the background check, the employer may choose to reject the candidate’s application. Falsifying education credentials is a serious offense, and many employers have strict policies against hiring individuals who provide false or misleading information. In some cases, fraudulent claims about education can lead to legal consequences for the candidate, including potential lawsuits or criminal charges for fraud.
How far back can education verification go in a background check?
Education verification typically goes as far back as the highest level of education the candidate claims to have completed. Employers usually verify the most recent educational attainment, such as a college degree or professional certification. However, some employers may choose to verify earlier levels of education, such as high school diplomas, depending on the requirements of the role. The timeframe for how far back education verification goes varies depending on the employer’s policies and the relevance of earlier educational achievements to the position.
Conclusion
Education verification is a vital step in the background check process, helping employers ensure that candidates possess the necessary academic qualifications for the job. It not only prevents fraudulent claims but also helps organizations hire qualified individuals who can perform their roles effectively. By using third-party services like Precise Hire, employers can streamline the verification process, ensuring accuracy and compliance with legal regulations.
As we’ve discussed, employers must navigate a complex landscape of legal requirements, including the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), state-specific regulations, and privacy laws. It’s crucial to remain informed and follow best practices to ensure that education verification is conducted fairly, transparently, and in compliance with all applicable laws.
The key takeaway for employers is that education verification is an essential tool in the hiring process. It helps protect organizations from the risks associated with resume fraud, ensures candidates meet job requirements, and contributes to building a trustworthy and qualified workforce.
