Vendor Risk Mitigation Explained: A Strategic Approach to Managing Third-Party Risks

Introduction to Vendor Risk Mitigation
In today’s interconnected global economy, businesses increasingly rely on third-party vendors to support and enhance their operations. These vendors provide essential services such as IT infrastructure, supply chain management, and customer support. However, this reliance on external vendors introduces a range of risks that could potentially harm a company’s financial stability, operations, and reputation. To mitigate these risks, businesses must adopt robust vendor risk mitigation strategies—practices designed to identify, assess, and manage the risks posed by vendors.
What is Vendor Risk Mitigation?
Vendor risk mitigation refers to the systematic process of identifying, evaluating, and addressing risks associated with third-party vendors. The goal of this process is to reduce potential risks that could disrupt business operations, harm an organization’s reputation, or lead to financial losses. Vendor risk mitigation encompasses various strategies, such as thorough vendor selection, ongoing performance monitoring, and risk assessments, that help businesses navigate the complexities of vendor relationships.
The Importance of Vendor Risk Mitigation
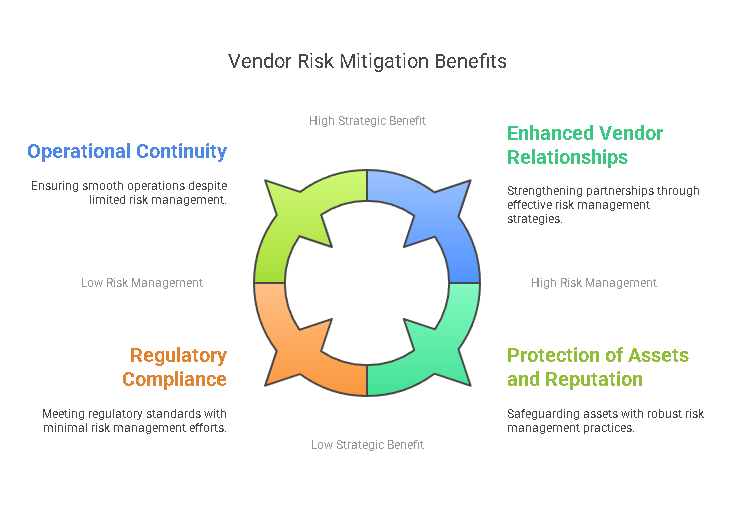
The significance of vendor risk mitigation has grown in tandem with the increasing dependence on third-party vendors. As businesses expand their vendor networks, the complexity of managing these relationships also increases. Vendors may introduce various types of risks, including financial instability, operational inefficiencies, cybersecurity threats, and compliance violations. If left unaddressed, these risks can lead to severe consequences, such as data breaches, regulatory fines, supply chain disruptions, or damage to the company’s brand and customer trust.
Implementing an effective vendor risk mitigation strategy offers businesses several advantages, including:
- Protection of Assets and Reputation: Vendor failures or mismanagement can result in financial loss, legal consequences, and reputational damage. Mitigating these risks helps safeguard the company’s assets and reputation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are subject to strict regulatory standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Vendor risk mitigation ensures that vendors are compliant with applicable regulations, preventing the company from facing legal or financial penalties.
- Operational Continuity: By assessing potential risks early on, businesses can develop contingency plans to ensure that disruptions in the vendor relationship do not affect their operations or lead to downtime.
- Enhanced Vendor Relationships: Vendor risk mitigation strategies often improve communication and understanding between businesses and their vendors, resulting in stronger, more transparent partnerships.
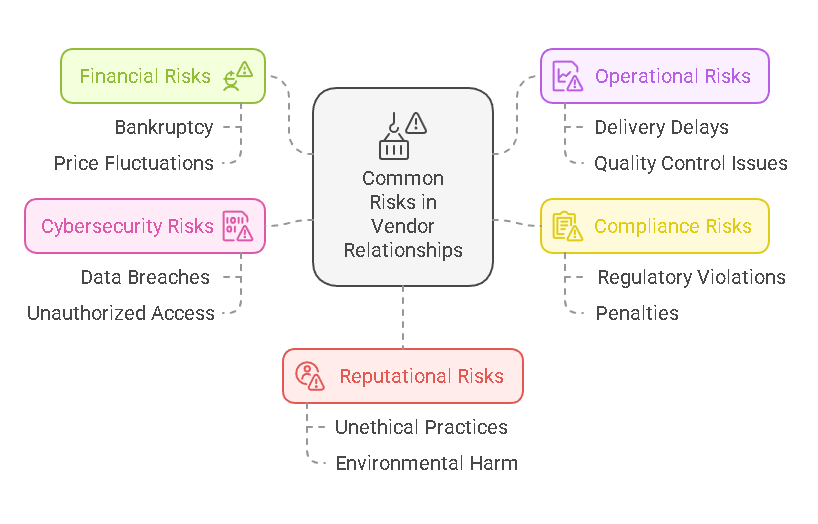
Common Risks Associated with Vendor Relationships
Vendor relationships can present a wide variety of risks, each of which has the potential to negatively impact a business. These risks can vary depending on the industry, vendor role, and the nature of the relationship. The most common risks associated with vendor relationships include:
1. Financial Risks
Financial risks occur when a vendor faces financial instability or fails to meet their financial obligations. This may include a vendor’s inability to deliver products or services due to bankruptcy, insolvency, or other financial challenges. Financial risks can also include price fluctuations or the failure to pay subcontractors, which may delay project timelines and impact overall service delivery.
2. Operational Risks
Operational risks refer to disruptions in business operations caused by vendor issues. This could include delays in product deliveries, poor quality control, or vendor inefficiencies that affect the company’s performance. Operational risks may also arise from failure to meet agreed-upon service levels, resulting in missed deadlines and substandard service delivery.
3. Compliance Risks
Many industries face strict regulatory requirements, such as data protection laws, environmental regulations, and industry-specific standards. Compliance risks occur when vendors fail to meet these regulatory requirements, placing the business at risk of non-compliance penalties. For example, a healthcare provider’s vendor may fail to comply with HIPAA regulations, resulting in significant fines and damage to the provider’s reputation.
4. Cybersecurity Risks
As digital transformation continues to shape the way businesses operate, cybersecurity risks associated with vendors have become a growing concern. A third-party vendor’s cybersecurity weaknesses could expose the business to data breaches, unauthorized access to sensitive information, or loss of intellectual property. This is especially true for vendors that have access to business-critical data or IT infrastructure.
5. Reputational Risks
Vendors can directly impact a business’s reputation, either positively or negatively. If a vendor is found to be engaged in unethical practices—such as labor violations, environmental harm, or fraud—the reputation of the business that partners with them can suffer. Similarly, vendor failures, such as delays or product defects, can tarnish the business’s reputation if customers or clients are affected.
Industries That Rely Heavily on Vendor Relationships
Certain industries are particularly dependent on third-party vendors to sustain operations. In these sectors, the impact of vendor risks is even more pronounced, making vendor risk mitigation strategies essential. The following industries rely heavily on vendor relationships:
1. Technology
The technology industry is one of the most vendor-reliant sectors. Companies depend on external vendors for hardware, software, cloud services, cybersecurity measures, and technical support. Given the fast-moving nature of the tech sector, vendor risk mitigation in this industry is crucial to avoid delays, security breaches, and failure to comply with industry standards.
2. Manufacturing
In manufacturing, businesses rely on vendors for raw materials, components, and outsourced labor. These vendors play a critical role in the supply chain, and any disruption can have a ripple effect on production timelines and product quality. Vendor risk mitigation is essential to ensure that materials are delivered on time, meet quality standards, and comply with environmental regulations.
3. Healthcare
Healthcare organizations depend on vendors for medical equipment, pharmaceuticals, IT services, and patient management systems. In this highly regulated industry, vendor risk mitigation is especially important to ensure that vendors adhere to compliance standards such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and protect patient data from cyber threats.
4. Retail
Retail businesses rely on vendors for the production, supply, and distribution of goods. Delays in inventory or quality control issues can have a significant impact on the retail business. Vendor risk mitigation in retail ensures that products are delivered on time, meet quality standards, and comply with product safety regulations.
5. Finance
The financial services industry depends on third-party vendors for software systems, compliance services, and customer support. Given the sensitive nature of financial data, cybersecurity and compliance risks are a major concern. Financial institutions must mitigate vendor risks to avoid exposure to fraud, data breaches, and regulatory violations.
Why Vendor Risk Mitigation is Critical
Given the extensive reliance on third-party vendors, vendor risk mitigation is crucial for businesses in any sector. Vendor-related risks, if not addressed, can lead to significant financial losses, legal issues, and operational disruptions. Additionally, vendor risks can have a cascading effect across an organization, affecting not just the direct business relationship with the vendor but also customer satisfaction, brand reputation, and regulatory compliance.
Challenges Businesses Face in Implementing Vendor Risk Mitigation
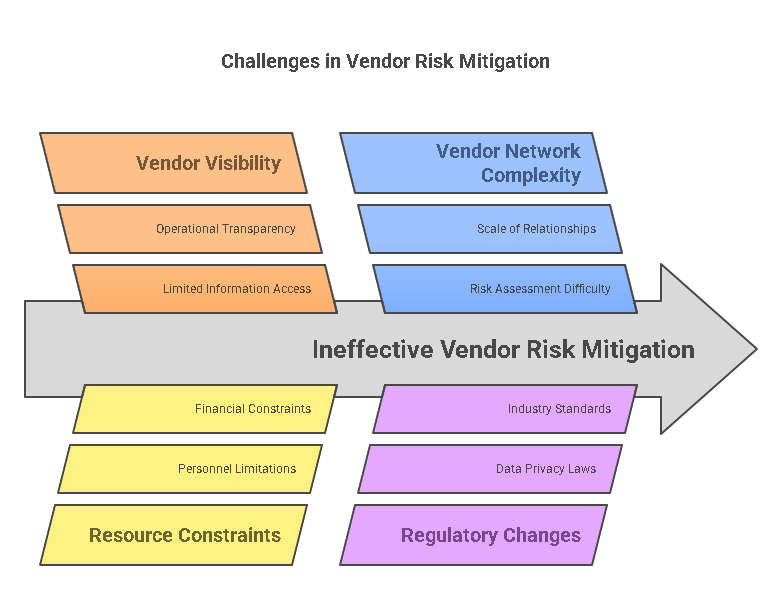
While vendor risk mitigation is essential, businesses often encounter several challenges when implementing these strategies:
- Lack of Vendor Visibility: Gaining complete visibility into a vendor’s operations, financial health, and compliance status is often challenging. Many businesses have limited access to critical information that would allow them to effectively assess potential risks.
- Resource Constraints: Implementing comprehensive vendor risk management programs requires dedicated resources, both in terms of personnel and financial investment. Smaller businesses may struggle with allocating the necessary resources.
- Complex Vendor Networks: For large companies, managing risks across a network of hundreds or thousands of vendors can be complex. The sheer scale of vendor relationships can make it difficult to assess and monitor every risk.
- Evolving Regulations: Regulations regarding data privacy, security, and industry standards frequently change. Businesses must ensure that their vendor risk management strategies remain up-to-date and compliant with these evolving requirements.
- Inconsistent Vendor Performance: Vendors may not always meet expectations, and businesses may struggle to manage vendor relationships when performance issues arise. Resolving such issues requires clear communication, escalation protocols, and defined contract terms.
This section has explored the significance of vendor risk mitigation and outlined the key risks businesses face when working with vendors. Understanding these risks and challenges is essential for developing effective strategies to protect a business’s assets, operations, and reputation. In the next section, we will delve deeper into the effective strategies for mitigating these risks and highlight how companies can proactively manage their vendor relationships to ensure long-term success.
Effective Strategies for Vendor Risk Mitigation
Vendor risk mitigation involves a series of well-defined strategies and practices that help organizations proactively manage the risks posed by their third-party vendors. These strategies aim to identify, assess, and control various risks associated with vendor relationships, such as financial instability, operational inefficiencies, cybersecurity threats, and compliance violations. By implementing a robust risk mitigation strategy, businesses can protect their assets, ensure compliance, and maintain strong vendor relationships.
Key Components of an Effective Vendor Risk Mitigation Strategy
An effective vendor risk mitigation strategy incorporates several key components. These components work together to create a comprehensive approach to managing vendor risks. The primary elements of a vendor risk mitigation strategy include vendor selection, ongoing monitoring, risk assessments, and contract management.
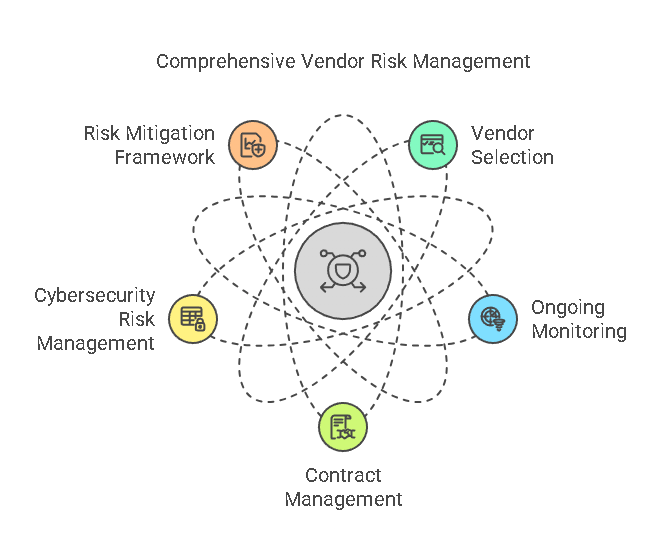
1. Vendor Selection and Due Diligence
The first and most critical step in mitigating vendor risk is selecting the right vendors. A thorough vendor selection process, supported by robust due diligence, is essential for identifying potential risks before engaging in a business relationship. Due diligence involves assessing a vendor’s financial stability, operational capabilities, compliance with industry regulations, and cybersecurity posture.
Key considerations during the vendor selection process include:
- Financial Health: Review the vendor’s financial records, credit reports, and financial stability. Financially unstable vendors pose a significant risk to business operations, as their inability to fulfill obligations can lead to disruptions.
- Reputation and Track Record: Investigate the vendor’s reputation in the market. A vendor with a history of performance issues, legal disputes, or non-compliance with industry standards may present greater risks.
- Compliance and Regulatory Standing: Ensure that the vendor complies with relevant laws and industry regulations, such as data protection laws, environmental regulations, and labor standards. This helps reduce compliance risks that could lead to legal penalties.
- Cybersecurity: Vendors with access to sensitive business data or IT infrastructure should have a robust cybersecurity framework in place. Ensure the vendor follows best practices for data protection, encryption, and network security.
A well-designed due diligence process ensures that businesses partner with trustworthy vendors who meet regulatory requirements and have the financial capacity to deliver on their obligations.
2. Ongoing Monitoring and Risk Assessment
Vendor risk is not static; it evolves over time. Ongoing monitoring and regular risk assessments are crucial for identifying new or emerging risks in existing vendor relationships. This continuous monitoring process helps organizations stay informed about their vendors’ performance, financial health, compliance status, and cybersecurity practices.
Key elements of ongoing monitoring include:
- Regular Audits: Conducting periodic audits to evaluate the vendor’s performance, financial stability, and adherence to contract terms. Audits provide valuable insights into how well the vendor is meeting agreed-upon standards.
- Risk Reviews: Regularly reviewing and reassessing the vendor’s risk profile, including updates on their financial health, cybersecurity practices, and compliance with laws and regulations. Businesses should remain vigilant to changes in vendor operations that could impact risk levels.
- Performance Metrics: Setting up key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure vendor performance and ensure that service levels are consistently met. This can include tracking on-time delivery, quality control, and customer satisfaction.
- Incident Reporting and Resolution: Having a system in place for vendors to report incidents, such as data breaches, service disruptions, or compliance violations, allows businesses to respond quickly and effectively. Prompt reporting and resolution of issues minimize the impact of potential risks.
3. Contract Management
A well-crafted contract is one of the most powerful tools in mitigating vendor risks. Clear and detailed contract terms set expectations for both parties, define performance standards, and outline the consequences of non-compliance. Contract management is critical in ensuring that vendors understand their obligations and the penalties they may face if they fail to meet these obligations.
Key aspects of contract management for vendor risk mitigation include:
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Include SLAs in contracts to clearly define the expectations for vendor performance, such as delivery timelines, quality standards, and customer support. SLAs hold vendors accountable for their actions and provide a legal basis for recourse if performance falls short.
- Termination Clauses: Ensure that contracts include provisions for termination in the event of vendor non-compliance, financial instability, or failure to meet agreed-upon terms. This allows businesses to quickly disengage from underperforming vendors.
- Indemnification and Liability: Include clauses that specify the vendor’s responsibility for indemnifying the business in case of damages resulting from vendor failures, such as data breaches or compliance violations.
- Compliance Clauses: Include clauses that require vendors to comply with relevant laws and industry regulations. These clauses help ensure that vendors adhere to legal requirements, reducing the risk of regulatory violations for the business.
A strong contract management system ensures that both parties understand their rights, responsibilities, and potential risks, and it provides the necessary legal framework to enforce compliance.
4. Cybersecurity Risk Management
In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity risks are among the most pressing concerns in vendor risk management. Third-party vendors often have access to sensitive business data, IT infrastructure, and customer information, making them potential targets for cybercriminals. A data breach or cybersecurity incident involving a vendor can have severe consequences, including financial losses, regulatory fines, and reputational damage.
Cybersecurity risk management in the context of vendor relationships involves:
- Vendor Security Assessments: Regularly evaluating a vendor’s cybersecurity posture through assessments or audits. This includes reviewing the vendor’s security controls, protocols, and incident response procedures.
- Data Encryption and Access Controls: Ensuring that vendors implement strong data encryption practices and strict access controls to protect sensitive information. This includes securing data in transit and at rest.
- Third-Party Risk Assessments: Evaluating the risks associated with third-party service providers or subcontractors that the primary vendor may use. These third-party relationships can introduce additional vulnerabilities.
- Cybersecurity Training: Ensuring that vendors’ employees undergo regular cybersecurity training to recognize and mitigate risks such as phishing attacks, malware, and other cyber threats.
By incorporating robust cybersecurity measures into vendor risk mitigation strategies, businesses can significantly reduce the likelihood of data breaches or cyberattacks involving their vendors.
5. Developing a Vendor Risk Mitigation Framework
A comprehensive vendor risk mitigation framework provides a structured approach to managing vendor risks. This framework includes processes, tools, and guidelines that guide organizations in assessing, managing, and mitigating vendor risks. Key steps in creating a vendor risk mitigation framework include:
- Risk Identification: Identifying potential risks across the vendor relationship, including financial, operational, cybersecurity, and compliance risks.
- Risk Assessment: Assessing the likelihood and impact of identified risks. This helps businesses prioritize risk mitigation efforts based on the severity of potential consequences.
- Risk Response: Developing strategies to respond to identified risks, such as diversifying the vendor base, improving vendor performance, or implementing risk-sharing agreements.
- Risk Monitoring: Continuously monitoring vendor performance, financial health, and compliance status to detect any new or emerging risks.
The development and implementation of a vendor risk mitigation framework ensures that businesses can proactively address potential risks before they materialize and disrupt operations.
Risk Mitigation Strategies for Different Types of Risks
Different types of risks require tailored mitigation strategies. Below is a table summarizing common risk categories and corresponding mitigation strategies.
| Risk Type | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Financial Risks | Conduct thorough due diligence on vendor financials. Monitor vendor financial health regularly. Use performance bonds or insurance. |
| Operational Risks | Set clear service level agreements (SLAs). Regularly audit vendor performance. Diversify vendor sources to reduce dependency on a single vendor. |
| Cybersecurity Risks | Assess vendor cybersecurity protocols. Ensure data encryption and strong access controls. Conduct regular cybersecurity training for vendors. |
| Compliance Risks | Require vendors to adhere to relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Conduct periodic audits and compliance checks. |
| Reputational Risks | Vet vendors for ethical practices and past legal issues. Include reputation management clauses in contracts. |
Precisehire’s Role in Vendor Risk Mitigation
At Precisehire, we provide comprehensive solutions to help businesses assess and mitigate risks when working with vendors. As part of our background screening and compliance services, we assist businesses in evaluating potential vendors for financial stability, regulatory compliance, and reputational integrity. Our background checks help organizations make informed decisions when selecting vendors, ensuring that they partner with trustworthy, reliable, and compliant companies. By using Precisehire’s services, businesses can identify risks early in the vendor selection process and develop stronger, more secure vendor relationships.
Legal Aspects, FAQs, and Conclusion
In the context of vendor risk mitigation, businesses must not only manage operational risks but also navigate a complex legal landscape. Compliance with industry regulations, data protection laws, and contractual obligations is essential to ensure that both parties uphold their responsibilities. This section will discuss the legal implications of vendor risk mitigation, address frequently asked questions, and conclude with key takeaways on how businesses can enhance their vendor risk mitigation strategies.
Legal Aspects of Vendor Risk Mitigation
Vendor risk mitigation is closely tied to several legal considerations that businesses must account for to protect themselves and maintain compliance with applicable laws. These legal aspects encompass compliance with industry regulations, data protection, contractual obligations, and the legal consequences of vendor failures.
1. Compliance with Industry Regulations
Many industries are subject to specific regulations that govern how businesses interact with their vendors. For example:
- Healthcare: The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires healthcare organizations to ensure that their vendors comply with privacy and security standards when handling protected health information (PHI).
- Finance: The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) requires financial institutions to protect customers’ personal financial information and ensure that their vendors adhere to similar security standards.
- Retail and Consumer Goods: The Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act (CPSIA) mandates that suppliers adhere to safety standards in the manufacturing of consumer products, particularly for children’s products.
Failure to comply with these regulations can result in severe penalties, including fines, litigation, and damage to a business’s reputation. By ensuring that vendors are compliant with relevant laws, businesses can mitigate the risks associated with non-compliance.
2. Data Protection and Privacy Laws
As data security becomes increasingly important, businesses must take care to comply with data protection laws when working with vendors. These laws typically govern the collection, processing, and storage of personal data. Notable regulations include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This European Union regulation sets strict rules for how businesses handle personal data of EU citizens, and it requires vendors who process such data to meet specific standards for data security and privacy.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): This state law gives California residents the right to access, delete, and control their personal information, impacting how businesses engage with vendors who handle consumer data.
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Regulations: In the U.S., the FTC enforces data protection regulations that affect vendors involved in marketing, advertising, and consumer data collection.
It is crucial for businesses to establish clear data protection clauses in vendor contracts that mandate vendors’ compliance with applicable data protection laws. Vendors must also implement appropriate cybersecurity measures to safeguard sensitive data and prevent breaches that could expose both parties to legal and financial consequences.
3. Contractual Obligations and Legal Remedies
Contracts serve as the foundation of vendor relationships and provide the legal framework to enforce compliance with agreed-upon terms. Vendor contracts should include clauses that:
- Define Expectations: Clearly outline the responsibilities of both parties, including performance standards, timelines, and deliverables.
- Specify Penalties for Non-Compliance: Define penalties or consequences for failure to meet the terms of the contract, such as late delivery, substandard quality, or failure to meet regulatory requirements.
- Address Indemnification: Include indemnification clauses that specify how the vendor will compensate the business for damages resulting from their failure to meet contractual obligations.
- Outline Dispute Resolution Procedures: Include provisions for dispute resolution, such as arbitration or mediation, to resolve conflicts without resorting to costly litigation.
By incorporating these legal protections into contracts, businesses can ensure that they have the legal tools needed to manage vendor risk and seek compensation or remedies when issues arise.
4. Legal Consequences of Vendor Failures
When a vendor fails to fulfill their contractual obligations, it can lead to serious legal and financial consequences. Potential repercussions include:
- Breach of Contract: If a vendor fails to meet the terms of the contract, businesses may be entitled to compensation or damages. For example, if a vendor’s cybersecurity failure leads to a data breach, the business may have grounds to sue for negligence.
- Regulatory Fines and Penalties: Non-compliance with industry regulations can lead to regulatory investigations and fines. For example, a vendor who fails to adhere to GDPR requirements could trigger substantial fines for the business.
- Reputational Damage: A vendor’s failure to meet performance expectations or regulatory requirements can tarnish a business’s reputation, leading to lost customers, diminished brand equity, and legal consequences.
By maintaining strong contractual relationships and monitoring vendor compliance, businesses can avoid or mitigate the impact of these legal consequences.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Most Common Risks Associated with Vendors?
The most common risks associated with vendors include:
- Financial Risk: Vendors may face financial instability, which can affect their ability to fulfill their obligations.
- Operational Risk: Vendors may fail to meet service level agreements (SLAs) or may not have the necessary capacity to deliver on commitments.
- Cybersecurity Risk: Data breaches, hacking, or other cybersecurity incidents involving vendors can expose sensitive business data.
- Compliance Risk: Vendors may fail to meet industry-specific regulations, leading to legal penalties for the business.
How Can Businesses Assess Vendor Risk Effectively?
Businesses can assess vendor risk through:
- Due Diligence: Conducting comprehensive background checks, financial assessments, and regulatory compliance reviews.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regularly auditing vendor performance and cybersecurity practices.
- Risk Assessments: Identifying potential risks based on vendor performance metrics and historical data.
What Role Do Contracts Play in Vendor Risk Mitigation?
Contracts serve as the primary tool for mitigating vendor risk. They establish clear expectations, define performance standards, and outline legal remedies in case of non-compliance. A well-structured contract can protect businesses from financial loss and legal consequences by ensuring that vendors adhere to agreed-upon terms.
What Tools or Technologies Can Businesses Use to Manage Vendor Risks?
Businesses can use a variety of tools to manage vendor risks, including:
- Vendor Risk Management Software: These tools automate the process of assessing, monitoring, and mitigating vendor risks.
- Contract Management Systems: These systems help businesses manage contracts, track compliance, and ensure that terms are met.
- Cybersecurity Tools: Tools such as vulnerability scanners and encryption software help assess and manage cybersecurity risks posed by vendors.
How Can Vendors Protect Themselves from Risks While Working with Clients?
Vendors can protect themselves by:
- Maintaining Compliance: Adhering to relevant industry regulations and standards.
- Establishing Clear Contracts: Ensuring that contracts clearly define responsibilities, liabilities, and performance standards.
- Implementing Robust Cybersecurity Practices: Ensuring that their systems and data are secure to prevent breaches that could affect both parties.
Conclusion
Vendor risk mitigation is a critical aspect of modern business operations. By selecting the right vendors, conducting due diligence, establishing clear contracts, and continuously monitoring vendor performance, businesses can minimize the risks associated with vendor relationships. Legal considerations, including compliance with industry regulations and data protection laws, further highlight the importance of a structured approach to vendor risk management.
Incorporating best practices for vendor risk mitigation is not only essential for business continuity but also for protecting valuable assets and maintaining a positive reputation in the marketplace. As businesses face increasing challenges related to vendor relationships, leveraging services such as those offered by Precisehire can significantly enhance risk management efforts. With background checks, compliance solutions, and continuous monitoring, Precisehire helps businesses make informed decisions and mitigate vendor risks effectively. By partnering with trusted vendors, businesses can strengthen their operations and reduce vulnerabilities, ensuring long-term success and sustainability.
