What Does a Fingerprint Background Check Show? A Comprehensive Guide

What is a Fingerprint Background Check?
A fingerprint background check is a type of criminal background check that uses an individual’s fingerprints to verify their criminal history. Unlike other background checks that rely on name-based searches, fingerprint background checks offer a more accurate and detailed method of identification. They are typically conducted by law enforcement agencies, employers, or other organizations that need to ensure an individual’s background is thoroughly vetted.
Fingerprint background checks are essential tools in identifying individuals with prior criminal activity, as fingerprints are unique to every person and remain the same throughout their life. This ensures that even if an individual changes their name or other personal details, their fingerprints will still uniquely identify them.
How Does a Fingerprint Background Check Work?
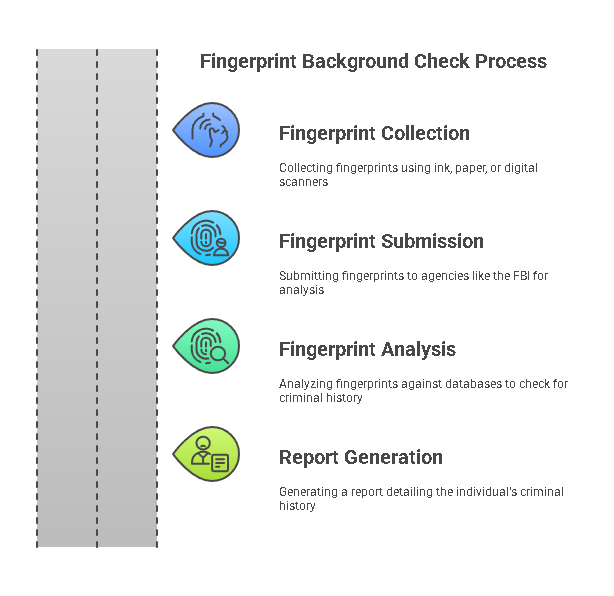
Fingerprint background checks involve a multi-step process that includes the collection, submission, and analysis of fingerprints. Here’s a general overview of how it works:
- Fingerprint Collection
The process starts by collecting fingerprints from the individual. This is typically done using ink and paper or more commonly now with digital scanners. Digital fingerprinting, also known as livescan, captures high-resolution prints electronically and transmits them to the relevant authorities, making the process faster and more efficient. - Fingerprint Submission
After collection, the fingerprints are submitted to appropriate agencies for analysis. This could be the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), state law enforcement agencies, or local police departments. These agencies have databases that house fingerprint records linked to criminal histories, and they use them to verify the identity of individuals undergoing background checks. - Fingerprint Analysis
Once the fingerprints are submitted, they are compared against the databases to search for any matching records. The results will show whether the individual has any history of criminal activity, such as arrests, charges, convictions, or other legal issues. The fingerprint analysis ensures that the criminal record tied to the individual is accurate and verifiable. - Report Generation
After the fingerprint analysis is complete, a report is generated that provides detailed information on the individual’s criminal history (if any). This report can be shared with employers, law enforcement, or other relevant parties, depending on the purpose of the check.
Difference Between Fingerprint and Name-Based Background Checks
While both name-based background checks and fingerprint background checks aim to reveal an individual’s criminal history, there are significant differences in their accuracy and scope.
- Name-Based Background Checks: These checks use personal information like an individual’s name, date of birth, and Social Security number to search for criminal records in various databases. However, they are more susceptible to errors, such as false positives (where an individual with a similar name is flagged) or false negatives (where records are missed due to variations in name spelling or incomplete information).
- Fingerprint Background Checks: Fingerprints are unique identifiers, which means they are much more reliable and accurate in confirming someone’s criminal history. Even if an individual has a common name or has used multiple aliases, their fingerprints will still point to the correct criminal record (if applicable).
For example, if two people share the same name, a name-based search could produce incorrect results, but a fingerprint background check will correctly identify each person due to the uniqueness of their fingerprints.
The Purpose of Fingerprint Background Checks
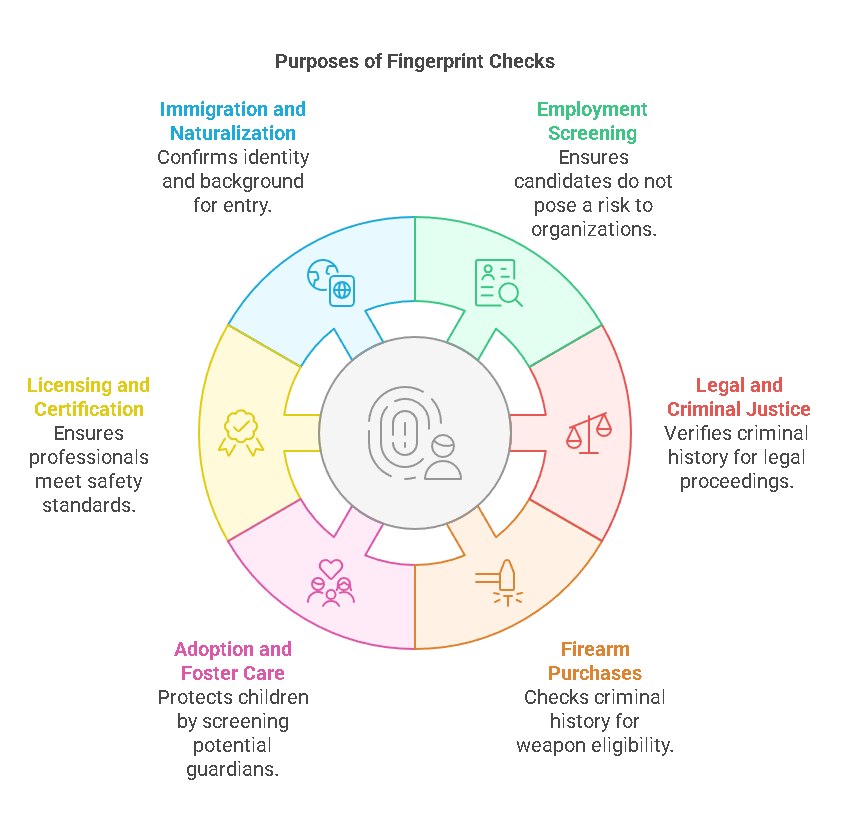
Fingerprint background checks serve several purposes across different industries, including:
- Employment Screening
Many employers require fingerprint background checks as part of their hiring process, especially in industries that deal with sensitive information, vulnerable populations (such as children or the elderly), or high-security positions. These checks help employers assess whether a candidate’s criminal history might pose a risk to the organization or its clients. - Legal and Criminal Justice Purposes
Fingerprint checks are often used in the legal field to verify an individual’s criminal history. They may be required when someone is involved in a legal matter, such as a court case, or to confirm their identity in relation to criminal investigations. - Firearm Purchases
When purchasing firearms, individuals are often required to undergo fingerprint background checks to ensure they do not have a criminal record that would disqualify them from purchasing weapons. The FBI runs these checks through the National Instant Criminal Background Check System (NICS). - Adoption and Foster Care
Fingerprint background checks are frequently required for individuals applying to adopt or foster children. These checks help ensure the safety of children by verifying that applicants do not have a criminal history that might endanger a child’s welfare. - Licensing and Certification
Certain professions, such as healthcare, childcare, education, and security, may require fingerprint checks as part of the licensing or certification process. This ensures that professionals in these fields do not have criminal histories that could affect their ability to work in these sensitive areas. - Immigration and Naturalization
Fingerprint background checks are also a standard part of the immigration and naturalization process. Applicants for citizenship or visas are often required to submit fingerprints as part of the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) background check process.
Where Are Fingerprint Background Checks Commonly Used?
Fingerprint background checks are widely used across various sectors and for a range of purposes, including:
- Employment: For jobs in healthcare, security, government, education, and other sectors that require a high level of trust.
- Law Enforcement: To verify the identity of suspects, convicts, or individuals being processed in the criminal justice system.
- Firearm Purchases: To ensure individuals buying firearms are legally allowed to own them.
- Adoption and Child Welfare: To safeguard children by confirming that adoptive or foster parents do not have a criminal record.
- Immigration and Naturalization: To ensure that individuals applying for citizenship or immigration visas do not have criminal backgrounds that could disqualify them.
- Licensing for Regulated Professions: Professions such as healthcare, finance, education, and real estate require background checks to verify the applicant’s suitability for the role.
Fingerprint background checks are also crucial in other scenarios where an individual’s criminal history needs to be verified for legal, safety, or regulatory purposes.
What Information Does a Fingerprint Background Check Show?
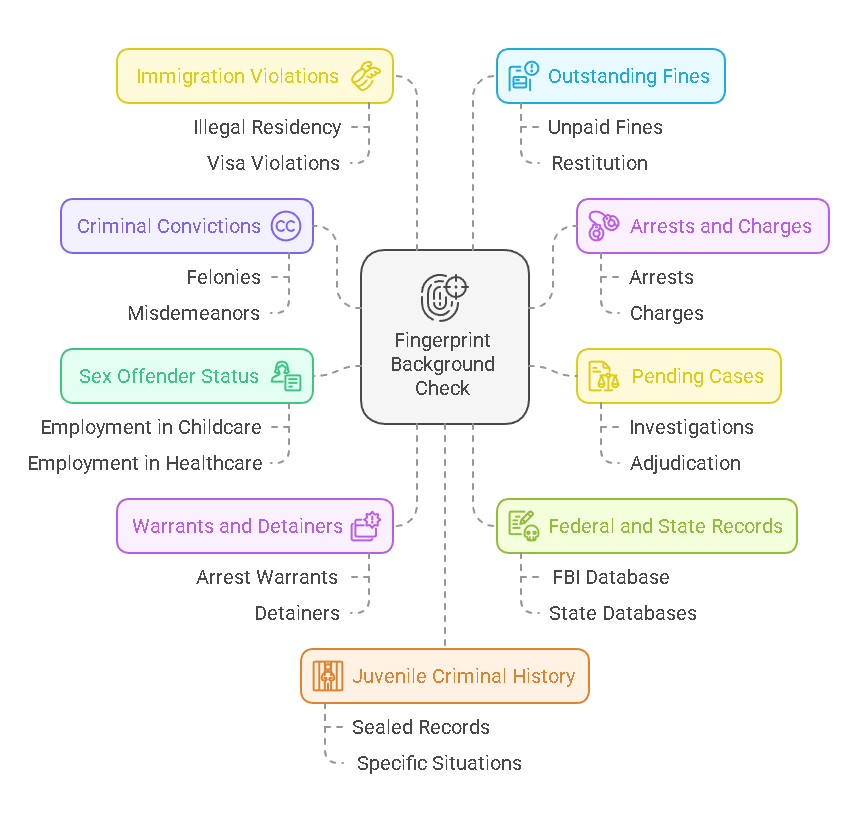
A fingerprint background check provides a comprehensive and reliable overview of an individual’s criminal history, revealing a range of important information. This can include details about arrests, convictions, charges, and even dismissed cases. Since fingerprint checks are tied to an individual’s unique biometric data, they offer a much more accurate and thorough representation of a person’s criminal background than name-based searches.
Here are the key pieces of information that a fingerprint background check can uncover:
- Criminal Convictions
One of the primary pieces of information that fingerprint background checks provide is a list of criminal convictions. This includes felonies, misdemeanors, and other charges that led to a conviction. Convictions are typically categorized by the seriousness of the crime, with felonies being more serious than misdemeanors. The report will indicate whether the conviction resulted in a prison sentence, probation, fines, or other penalties. - Arrests and Charges
Even if an individual was not convicted of a crime, a fingerprint background check will show if they were ever arrested or charged with a crime. These records will indicate the nature of the charge and whether it resulted in a dismissal, plea bargain, or other resolution. It’s important to note that arrest records alone do not imply guilt but may be used as part of a larger investigation into an individual’s background. - Dismissed or Expunged Charges
In some cases, fingerprint background checks can reveal charges that were dismissed or expunged. If an individual was arrested but never convicted, or if they had charges dropped or expunged from their record, this information may still appear. However, the impact of such records can vary based on the jurisdiction and the laws governing expungement. In some cases, individuals may be able to petition to have their criminal record sealed or erased entirely. - Pending Cases
If there are any ongoing legal proceedings or pending cases against an individual, a fingerprint background check may show that charges are still under investigation or in the process of being adjudicated. This is an important detail for employers or legal authorities to know, as pending cases could influence an individual’s eligibility for certain positions or activities. - Sex Offender Status
Some fingerprint background checks, particularly those required for employment in sensitive positions (such as childcare or healthcare), may include information about whether an individual is listed in a sex offender registry. This is a key consideration for employers hiring individuals who will have access to vulnerable populations. - Warrants and Detainers
A fingerprint background check may also reveal whether there are any active warrants or detainers against an individual. If law enforcement is seeking to arrest someone based on a warrant or if they are under investigation for a crime, this information will appear in the report. Employers or authorities may take this into account when making decisions about an individual’s suitability for a role or other legal matters. - Federal and State Criminal Records
Depending on the jurisdiction, a fingerprint background check can uncover both federal and state-level criminal records. For example, the FBI maintains a database of national criminal records, while individual states have their own databases that focus on state-specific crimes. This means a fingerprint check can provide a broader and more complete picture of an individual’s criminal history. - Immigration Violations
In some cases, fingerprint background checks may reveal immigration violations, such as being in the country illegally or violating visa terms. This is particularly relevant for individuals applying for immigration or naturalization, as these violations can affect their eligibility for certain immigration benefits. - Outstanding Fines or Restitution
Certain background checks may also highlight any outstanding financial obligations, such as unpaid fines, court costs, or restitution owed as part of a criminal case. These details can be relevant when assessing an individual’s legal and financial standing, especially in industries that require financial responsibility or fiduciary duties. - Criminal History for Juveniles
While juvenile records are generally sealed or protected by law, some jurisdictions may still allow certain information about juvenile criminal records to be revealed in fingerprint background checks, especially for specific situations (such as when applying for law enforcement or military positions). However, juvenile records are typically less accessible than adult criminal records.
How the FBI, State Agencies, and Local Authorities Use Fingerprints
Fingerprint background checks rely heavily on databases maintained by the FBI, state law enforcement agencies, and local authorities. Here’s how these agencies use fingerprint data to verify an individual’s criminal history:
- FBI Criminal History Database
The FBI maintains the National Crime Information Center (NCIC), a comprehensive database that contains fingerprint records from individuals who have been arrested at the federal, state, or local levels. This database allows agencies across the country to check fingerprints against a national database to identify individuals with criminal histories. - State and Local Databases
In addition to the FBI’s database, each state and local jurisdiction may have its own database of criminal records. These records typically include arrests, charges, convictions, and other legal information specific to that jurisdiction. Fingerprint background checks often involve searching both federal and state databases to ensure that no criminal records are overlooked. - Livescan Technology
Livescan, or digital fingerprinting, is increasingly used to capture and transmit fingerprints to law enforcement agencies in real-time. This technology improves the accuracy of background checks by providing high-quality digital images of fingerprints that can be processed more quickly than traditional ink-based prints.
Precisehire Fingerprint Background Check Services
At Precisehire, we offer efficient and thorough fingerprint background check services for businesses and individuals alike. Our services include fast processing times, high-quality digital fingerprinting, and access to national and state-level criminal records databases. Whether you need background checks for employment, legal purposes, firearm purchases, or any other reason, we ensure a smooth and accurate process.
We understand the importance of timely and accurate results, and our team is dedicated to providing exceptional service every step of the way.
Table: Information Revealed by Fingerprint Background Checks
| Type of Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Criminal Convictions | Felonies, misdemeanors, and other convictions resulting in a sentence. |
| Arrests and Charges | Arrest records and charges, whether or not the individual was convicted. |
| Dismissed or Expunged Charges | Information on charges that were dismissed or expunged from the record. |
| Pending Cases | Ongoing legal proceedings or cases that are still under investigation. |
| Sex Offender Status | Whether the individual is listed in a sex offender registry. |
| Warrants and Detainers | Active warrants or detainers issued for an individual’s arrest. |
| Federal and State Criminal Records | Criminal records maintained by federal and state agencies. |
| Immigration Violations | Violations of immigration laws or visa terms. |
| Outstanding Fines/Restitution | Financial obligations owed by the individual as part of a criminal case. |
| Juvenile Criminal History | Some information about juvenile criminal records, depending on jurisdiction. |