The Ultimate Guide to Pre-Employment Social Media Screening

The Growing Role of Pre-Employment Social Media Screening in Hiring Decisions
In today’s digital age, social media has become an integral part of our personal and professional lives. Employers are increasingly turning to pre-employment social media screening as a tool to make more informed hiring decisions. This process allows employers to gain insights into a candidate’s personality, behavior, and qualifications beyond what is outlined in resumes and interviews. In this article, we explore the importance of pre-employment social media screening, the benefits it provides, and the potential drawbacks that must be carefully managed.
What is Pre-Employment Social Media Screening?
Pre-employment social media screening refers to the process by which employers review a candidate’s online presence before offering them a job. Social media platforms such as LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram provide a wealth of personal and professional information that can help employers better understand a candidate’s character, qualifications, and suitability for a role.
This type of screening typically involves checking publicly accessible profiles, posts, comments, and interactions across social media platforms. In some cases, employers may also review content from personal blogs or other digital platforms where candidates share information. By evaluating this data, employers can assess how a potential hire behaves online, how they interact with others, and how well they may fit within the company culture.
Why is Pre-Employment Social Media Screening Important?
As technology continues to evolve, more and more people have an online presence. While resumes and interviews provide valuable insights into a candidate’s qualifications, they often fail to showcase a candidate’s true character, behavior, or interactions in real-world situations. Pre-employment social media screening offers a window into a candidate’s personal life that is difficult to assess through traditional recruitment methods.
1. Uncovering Red Flags and Risk Factors
Social media profiles can reveal a wealth of information that may not come up in an interview. For example, a candidate’s past posts may include offensive or inappropriate content, such as discriminatory remarks, hate speech, or evidence of unethical behavior. These red flags could indicate problematic behavior that may impact the workplace environment or harm the company’s reputation.
Additionally, social media screenings help employers identify warning signs of dishonesty or exaggeration on a candidate’s resume. For example, a candidate may claim to have attended a particular university, but their social media activity may suggest otherwise.
2. Verifying Qualifications and Professionalism
While resumes and cover letters can provide a glimpse of a candidate’s qualifications, they often do not tell the full story. Social media profiles—particularly professional networks like LinkedIn—offer a chance for employers to verify key details, such as job history, accomplishments, and professional skills. These profiles often include recommendations and endorsements from previous colleagues or employers, which can serve as valuable confirmation of a candidate’s qualifications.
By reviewing a candidate’s social media activity, employers can also gauge their professionalism and engagement in the industry. Do they regularly contribute to discussions about their field? Are they up-to-date on industry trends? This type of information can give employers an understanding of how seriously a candidate takes their profession and whether they are likely to add value to the organization.
The Benefits of Pre-Employment Social Media Screening
Pre-employment social media screening offers many benefits for employers seeking to make the best hiring decisions. Below are some of the key advantages of incorporating social media screening into the recruitment process:
1. Comprehensive Candidate Evaluation
Unlike traditional resume reviews or interviews, pre-employment social media screening gives employers a more well-rounded picture of a candidate. By reviewing both professional and personal profiles, employers can assess not only a candidate’s skills and qualifications but also their personality, character, and values. This comprehensive evaluation helps employers decide whether a candidate would be a good fit for the organization and its culture.
2. Enhanced Fraud Prevention
Social media screening can help prevent fraud and misrepresentation by revealing inconsistencies between a candidate’s resume and their online presence. For example, a candidate may claim to have extensive experience in a particular field, but a closer inspection of their social media profile might show that they have little to no involvement in relevant industry discussions. Detecting these discrepancies early in the hiring process helps prevent the risk of hiring someone who has falsified their qualifications.
3. Mitigating Risk and Workplace Issues
Pre-employment social media screening can uncover potential issues that could affect the workplace. For example, an applicant might display problematic behavior online, such as engaging in online bullying or sharing controversial opinions that could cause friction within the team. Identifying these behaviors early on helps employers assess the potential risks a candidate might bring to the company.
4. Faster Decision-Making
By adding social media screenings to the hiring process, employers can streamline their evaluation of candidates. In some cases, social media screening can provide a quicker and more efficient way to verify a candidate’s credentials and evaluate their personality than traditional background checks. This can speed up the hiring process and lead to faster decision-making.
Drawbacks and Concerns of Pre-Employment Social Media Screening
While pre-employment social media screening can be an effective tool for assessing candidates, it also comes with its own set of challenges and concerns. Employers must be mindful of the following drawbacks when using this method in the hiring process:
1. Privacy Concerns
One of the most significant issues surrounding pre-employment social media screening is privacy. Candidates may feel uncomfortable with the idea that their personal online activity is being scrutinized by potential employers, especially if the content in question has no bearing on their job qualifications. It is important for employers to respect candidates’ privacy and avoid reviewing private accounts unless explicit consent has been given.
Employers should also ensure that they only review publicly accessible information and avoid prying into a candidate’s private or personal life. To alleviate privacy concerns, employers should establish clear guidelines for social media screening and inform candidates about the process before it begins.
2. The Risk of Bias
Social media screenings can introduce bias into the hiring process. Employers may unconsciously form judgments about a candidate based on their social media activity, such as their political views, lifestyle choices, or personal opinions. This bias can lead to discrimination, particularly if employers make hiring decisions based on irrelevant or protected characteristics.
To avoid bias, employers must establish clear, objective criteria for what constitutes acceptable social media screening and ensure that all candidates are treated equally. Screening should focus only on factors that are relevant to the job and workplace culture, and not on personal characteristics unrelated to job performance.
3. Legal Implications
Pre-employment social media screening must be conducted in compliance with local, state, and federal laws. For example, in the United States, the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) governs how employers can conduct background checks, including social media screenings. The FCRA requires employers to obtain consent before conducting any background check, and candidates must be informed of how their information will be used.
Employers should be cautious about the legal implications of pre-employment social media screening and consult with legal experts to ensure they are complying with all relevant laws and regulations
How Pre-Employment Social Media Screening Works and Best Practices
As employers continue to incorporate pre-employment social media screening into their hiring processes, it’s important to understand how this screening works, the tools available, and the best practices for conducting it effectively and ethically. In this section, we will explore the step-by-step process of social media screening, discuss the tools and techniques involved, and highlight the best practices that employers should follow to ensure legal compliance and fair candidate evaluation.
How Does Pre-Employment Social Media Screening Work?
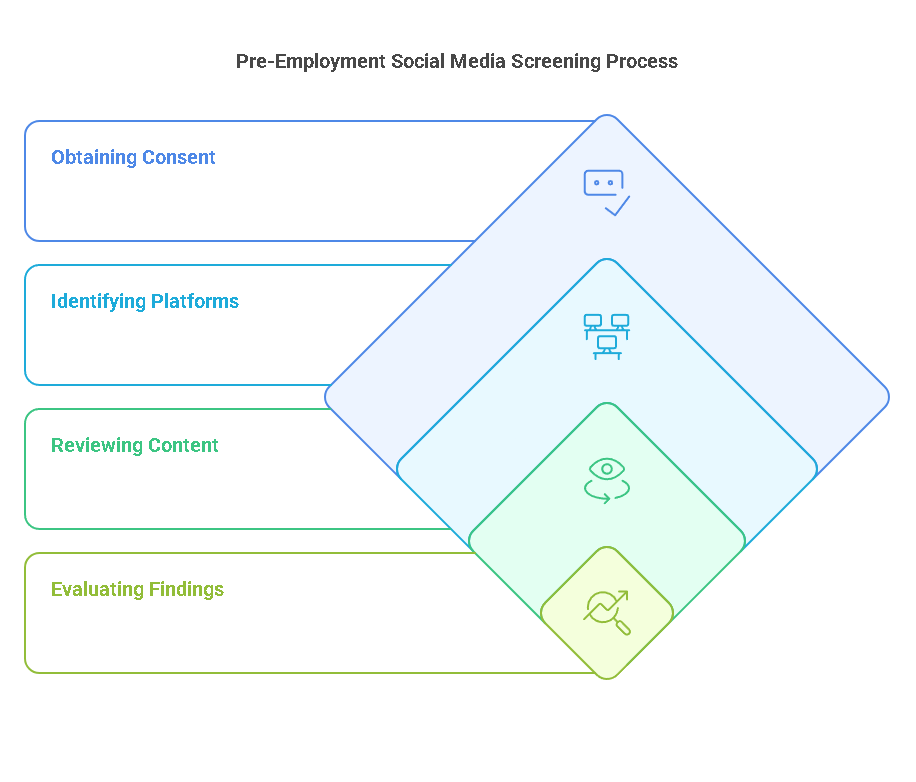
The process of pre-employment social media screening typically involves the following steps:
1. Obtaining Candidate Consent
Before initiating any form of social media screening, employers must first obtain explicit consent from the candidate. This is an important step in ensuring compliance with privacy laws and establishing transparency in the hiring process. In many countries, including the United States, the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) requires that candidates be informed about the background check process and that their consent is obtained before proceeding.
This consent should be documented in writing, and candidates should be made aware of the specific social media platforms and online activities that will be reviewed. Employers should also explain the purpose of the screening and how the information will be used in the hiring decision.
2. Identifying the Social Media Platforms to Screen
Once consent is obtained, employers typically focus on a few key social media platforms where candidates are likely to have professional profiles or public content. Common platforms include:
- LinkedIn: This is the most common platform for professional networking and showcasing career achievements. Employers use LinkedIn to verify job history, educational background, professional connections, and endorsements.
- Facebook: While primarily a personal platform, Facebook can provide insight into a candidate’s hobbies, family life, and social interactions. Employers may check Facebook profiles for any concerning behavior or content that could impact the company’s image.
- Twitter: Twitter can reveal a candidate’s opinions, engagement in industry conversations, and public persona. Employers may look for a candidate’s level of professionalism, the tone of their tweets, and their involvement in relevant discussions.
- Instagram: While Instagram is mainly used for personal photos, it may also reveal a candidate’s interests, values, and lifestyle choices. Employers may check for any posts or comments that could reflect negatively on the company or the candidate’s professional suitability.
- Other Platforms: Depending on the job role, employers might also look at other platforms like GitHub for developers, Behance for designers, or personal blogs for writers.
Employers should prioritize platforms where candidates are most likely to share relevant professional content or where they are publicly active.
3. Reviewing the Candidate’s Content
During the screening process, employers will review the content that candidates have made publicly available on social media platforms. The types of content typically reviewed include:
- Posts and Status Updates: Employers look for any posts that may contain inappropriate, offensive, or unprofessional content.
- Photos and Videos: Visual content can reveal a lot about a candidate’s personality, lifestyle, and values.
- Comments and Interactions: Employers may evaluate how candidates engage with others on social media, whether they exhibit positive communication skills or show signs of poor judgment.
- Group Memberships and Interests: Social media platforms often have groups or networks where users can join communities or share interests. Employers may review these to assess whether a candidate’s values align with the company’s culture.
Employers should ensure they are reviewing publicly accessible information only, avoiding private content such as direct messages, or private groups, to respect the candidate’s privacy.
4. Evaluating the Findings
After reviewing a candidate’s social media profiles, employers will evaluate the findings based on criteria that are relevant to the job role and company culture. The goal is to look for patterns or behaviors that indicate a good or poor fit for the organization.
Positive Indicators:
- Active participation in industry-related discussions
- Professionalism in posts and interactions
- Evidence of skills or knowledge related to the job position
- Positive or neutral opinions that align with the company’s values
Red Flags:
- Offensive or discriminatory language
- Inappropriate behavior, such as online bullying or harassment
- Posts that suggest illegal activities or poor judgment
- Content that contradicts the candidate’s professional claims (e.g., false job history)
Employers should always remain objective during the evaluation, ensuring that decisions are based on relevant factors that align with the job role.
Best Practices for Pre-Employment Social Media Screening
To ensure that pre-employment social media screening is effective, fair, and compliant with legal standards, employers should follow a set of best practices. These guidelines will help ensure that social media screenings are conducted ethically, minimizing the risks of bias or legal issues.
1. Set Clear Guidelines and Objectives
Employers should establish clear guidelines for social media screenings, including:
- Scope of Review: Define which platforms and types of content will be reviewed. Employers should focus on public-facing content related to professional behavior and avoid delving into private or personal information.
- Screening Criteria: Determine what constitutes acceptable content versus red flags. Employers should focus on finding information that is relevant to the candidate’s job qualifications or behavior in the workplace.
Having clear guidelines will help prevent unconscious bias and ensure that the screening process is consistent across all candidates.
2. Be Transparent with Candidates
Candidates should be informed about the social media screening process from the beginning. Employers should provide clear information about which platforms will be reviewed and explain the purpose of the screening. By being transparent, employers can foster trust with candidates and avoid any potential misunderstandings.
Additionally, employers should allow candidates to review their own social media profiles before screening takes place, ensuring that they are aware of what is publicly available.
3. Respect Candidate Privacy
Employers must respect candidates’ privacy rights by only reviewing publicly available content. Candidates should not be required to provide passwords or grant access to private social media accounts. Employers should also avoid reviewing any content that is irrelevant to the candidate’s qualifications or job suitability.
If candidates choose to delete certain content or adjust privacy settings before the screening process, employers should respect these choices.
4. Avoid Discrimination and Bias
To reduce the risk of discrimination, employers should focus solely on content that is relevant to the candidate’s qualifications or job performance. Employers must avoid basing hiring decisions on irrelevant personal characteristics such as political views, lifestyle choices, or personal beliefs.
By remaining objective and sticking to job-related criteria, employers can avoid biases that may lead to discrimination and ensure that the screening process is fair.
5. Document and Store Results Appropriately
Employers should maintain records of the social media screening process for transparency and compliance purposes. Any findings, decisions, and actions taken should be documented, and this information should be stored securely to protect candidate privacy.
This documentation can be useful in the event of a legal dispute or if a candidate requests feedback about the hiring process.
PreciseHire’s Role in Social Media Screening Services
At PreciseHire, we specialize in offering professional pre-employment social media screening services to help businesses stay compliant with privacy and anti-discrimination laws. By leveraging advanced screening tools and offering comprehensive candidate evaluations, we ensure that employers make informed decisions while maintaining fairness and respect for candidate privacy.
Our services include thorough social media profile reviews, helping you identify red flags and positive traits relevant to the position. We also provide tailored advice on what to look for and how to conduct screenings that comply with relevant laws like FCRA and GDPR. With PreciseHire, employers can ensure that their social media screening process is both effective and ethical.
Tools for Conducting Social Media Screening
Several tools and services can help employers streamline their pre-employment social media screening process. These tools often offer features like automated searches, comprehensive reports, and compliance with privacy regulations. Here are a few popular options:
| Tool | Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Social Intelligence | Provides deep social media background checks, including content screening and analysis. | Comprehensive social media screening with legal compliance. |
| Fama | Automated platform for screening social media accounts and generating reports on personality and behavior. | Screening candidates for personality traits and risk factors. |
| HireRight | Offers a range of background check services, including social media background checks. | Employers seeking comprehensive pre-employment screening. |
| Checkr | Provides background checks and social media screening services. | Employers looking for an easy-to-use screening platform. |
Employers should choose tools based on their specific needs and the scale of their hiring process.
By following these best practices and utilizing the right tools, employers can conduct pre-employment social media screenings that are ethical, effective, and legally compliant. In the next section, we will explore the legal aspects of social media screenings, answer frequently asked questions, and provide a comprehensive conclusion on the importance of this practice in today’s hiring process.
Legal Aspects, FAQs, and Conclusion on Pre-Employment Social Media Screening
As pre-employment social media screening becomes more common, it is crucial for employers to be aware of the legal and ethical considerations involved. Failing to adhere to privacy laws, discrimination regulations, and fairness standards can result in lawsuits, penalties, or damage to an organization’s reputation. In this section, we will delve into the legal aspects surrounding social media screening, address common questions employers and candidates have, and conclude with a summary of key takeaways.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Social Media Screening
When conducting pre-employment social media screening, employers must adhere to various legal and ethical guidelines to ensure they are operating within the law and maintaining fairness throughout the hiring process.
1. Privacy Laws and Candidate Consent
One of the most important legal considerations is privacy. Employers are required to obtain explicit consent from candidates before conducting social media screenings. This ensures that candidates are aware of the process and have agreed to it in writing. In the United States, this requirement is covered under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), which mandates that employers notify candidates when they are using a third-party service to conduct background checks, including social media screening.
While employers are allowed to review publicly accessible content, they are prohibited from accessing private social media accounts or requiring candidates to grant access to private profiles. This would constitute an invasion of privacy. Employers should always ensure that they are reviewing only publicly available content and should avoid asking candidates for login credentials to their social media accounts.
2. Discrimination Laws and Bias Concerns
Employers must be careful to avoid discrimination when reviewing social media profiles. Social media platforms often contain personal information that may not be relevant to a candidate’s qualifications, such as political opinions, religious beliefs, or lifestyle choices. Basing hiring decisions on such factors could expose employers to claims of discrimination based on protected characteristics (e.g., gender, race, religion, age).
To mitigate the risk of discrimination, employers should focus solely on content that pertains to the candidate’s ability to perform the job. They should also apply consistent criteria across all candidates, avoiding any biases that may arise from subjective judgments based on personal beliefs or characteristics.
3. Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) Compliance
In addition to anti-discrimination laws, employers must comply with Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) regulations, which prohibit hiring decisions based on factors like race, color, national origin, gender, and disability. By conducting pre-employment social media screening in an objective and non-discriminatory manner, employers can avoid violating EEO laws.
Employers should ensure that their social media screening process aligns with the EEO guidelines and does not inadvertently lead to biased hiring practices. For example, employers should avoid focusing on a candidate’s ethnic background or gender-related content, as these factors should not influence the hiring decision.
4. Global Regulations and Data Protection
For organizations hiring candidates across different countries, it’s essential to consider international regulations on data protection and privacy. In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) governs how companies handle personal data, including information obtained through social media. Under the GDPR, employers must have a valid legal basis for processing a candidate’s personal data and must respect the candidate’s right to privacy.
Employers should familiarize themselves with the privacy laws of the countries in which they are hiring to ensure compliance. For example, some countries may require employers to obtain explicit consent from candidates before reviewing their social media profiles, while others may impose restrictions on the types of content employers are allowed to access.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Pre-Employment Social Media Screening
What is the purpose of pre-employment social media screening?
Pre-employment social media screening helps employers assess a candidate's character, values, and overall fit for a role and the company’s culture. By reviewing publicly available content on social media platforms, employers can gain additional insights into a candidate’s behavior, professionalism, and qualifications, which may not be evident from the resume or interview alone.
Is it legal for employers to screen social media accounts of candidates?
Yes, it is legal for employers to screen public social media accounts of candidates, as long as the process is conducted within the boundaries of privacy laws. Employers must obtain consent from candidates before initiating any form of social media screening and ensure they only review publicly accessible content. Accessing private accounts or requiring candidates to provide login credentials would violate privacy laws.
What are the potential risks of pre-employment social media screening?
There are several risks associated with pre-employment social media screening, including the potential for unconscious bias, discrimination based on personal beliefs or lifestyle choices, and invasion of privacy. Employers must ensure that the screening process is objective, legally compliant, and focused on relevant information. Failure to do so could result in legal consequences and damage to the organization’s reputation.
Can an employer base their hiring decision solely on social media findings?
No, an employer should not base hiring decisions solely on social media screening. Social media content should be just one factor in the hiring process, alongside other assessments such as resumes, interviews, and references. Employers should avoid making decisions based on irrelevant or biased information and focus on how the candidate’s social media activity aligns with the job role and company values.
How can I ensure that my company is conducting social media screening legally?
To ensure your company is conducting social media screening legally, follow these best practices:
- Obtain explicit consent from candidates before conducting screenings.
- Focus only on publicly accessible content and avoid private or protected information.
- Ensure consistency in the criteria used to evaluate candidates.
- Comply with privacy laws like FCRA and GDPR, and avoid bias in the decision-making process.
- Document and store the screening results to maintain transparency and accountability.
Employing a third-party service such as PreciseHire for pre-employment social media screening can also help ensure that your process is legally compliant and aligned with industry standards.
Conclusion
Pre-employment social media screening offers a valuable tool for employers to assess candidates beyond resumes and interviews. When conducted ethically and legally, it provides employers with deeper insights into a candidate’s behavior, professionalism, and potential fit within the company culture.
However, employers must be diligent in adhering to privacy and discrimination laws to avoid legal issues and ensure fairness. By obtaining candidate consent, focusing on job-relevant content, and avoiding bias, employers can use social media screening responsibly and effectively.
As social media becomes increasingly integrated into our personal and professional lives, PreciseHire is here to help organizations streamline their screening processes while remaining fully compliant with legal and ethical standards. With our expertise in social media background checks and compliance guidelines, we ensure that employers can make informed, fair, and legally sound hiring decisions.
