Understanding Form I-9: Employment Eligibility Verification and Compliance

Introduction to Form I-9 and Employment Eligibility Verification
What is Form I-9?
Form I-9, officially known as the “Employment Eligibility Verification” form, is a crucial document mandated by the U.S. federal government. Its primary purpose is to verify the identity and employment eligibility of individuals hired to work in the United States. The form was introduced as part of the Immigration Reform and Control Act (IRCA) of 1986, which aimed to prevent illegal immigration by ensuring that employers hire only individuals who are legally authorized to work in the U.S. Employers must complete Form I-9 for each new hire, regardless of nationality or citizenship status, to confirm the employee’s legal right to work.
Why is Form I-9 Important?
Form I-9 plays a critical role in preventing the employment of unauthorized workers. By requiring employers to verify the employment eligibility of their employees, it helps safeguard the integrity of the U.S. labor market. This form is an essential tool for enforcing U.S. immigration laws and maintaining compliance with federal regulations. The information collected on Form I-9 is used to ensure that employees are legally authorized to work, and it helps prevent fraudulent employment practices.
The importance of Form I-9 extends beyond preventing illegal employment; it also protects both employees and employers from potential legal and financial consequences. Employers who fail to properly complete or retain Form I-9 may face significant fines, especially if it is found that they knowingly employed individuals without proper work authorization. In addition, employees may experience delays or complications in their employment status if they are unable to present appropriate documentation for verification.
Employer Responsibility and Legal Compliance
Employers are legally required to complete Form I-9 for each new employee, regardless of whether the employee is a U.S. citizen, permanent resident, or foreign national. The responsibility for completing the form lies with the employer, who must review the employee’s documentation and ensure that it meets the criteria for employment eligibility. Employers must retain these forms for a specified period and make them available for inspection by authorized government agencies, such as the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) or Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE).
Failure to comply with Form I-9 regulations can lead to penalties ranging from fines to more severe legal consequences. This reinforces the critical role the form plays in maintaining a legally compliant workforce. Employers must not only complete Form I-9 correctly but also ensure that their practices align with the laws governing work authorization.
Form I-9’s Role in Immigration Compliance
Form I-9 also plays a vital role in U.S. immigration enforcement. By requiring the submission of valid documentation, the form helps the government track and monitor the workforce, ensuring that only those who are legally authorized to work are employed. Over time, this has helped reduce unauthorized immigration and employment, contributing to stronger border control and labor market regulations.
Additionally, the form is part of a broader compliance effort to address illegal immigration, and it is regularly updated to ensure it remains consistent with current immigration laws and policies. This includes adding or removing acceptable documents and refining the process of verifying eligibility.
As the U.S. government increases its enforcement of immigration laws, Form I-9 remains a cornerstone in ensuring businesses comply with regulations. It protects the U.S. labor market from exploitation while ensuring that individuals have the opportunity to work legally within the country. Therefore, completing Form I-9 accurately and timely is crucial for employers, as it helps to prevent any legal complications related to employment eligibility.
Steps Involved in Completing Form I-9 and Required Documentation
How to Complete Form I-9
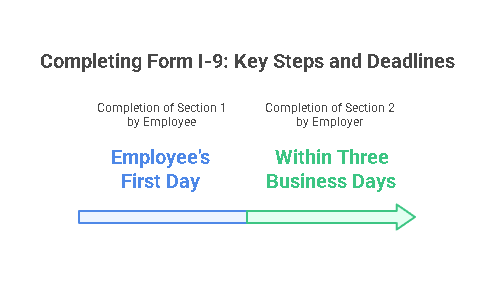
The completion of Form I-9 involves several key steps that employers must follow to verify the identity and employment eligibility of their employees. These steps ensure compliance with federal regulations and help businesses avoid potential penalties. The process of completing Form I-9 can be broken down into two main sections: the employee section and the employer section.
1. Employee Section
The employee is responsible for filling out Section 1 of Form I-9 on their first day of employment, but no later than the end of their first workday. The following details must be provided:
- Personal Information: The employee must provide their full name, address, date of birth, and Social Security number (if applicable). For employees who are not U.S. citizens, they must also indicate their citizenship status, such as whether they are a U.S. citizen, lawful permanent resident, or alien authorized to work in the United States.
- Signature and Date: The employee must sign and date the form, certifying that the information they provided is accurate. This section also includes a statement where the employee affirms their eligibility to work in the U.S.
2. Employer Section
The employer’s responsibility is to complete Section 2 of Form I-9 within three business days of the employee’s first day of employment. In this section, the employer must:
- Review the Employee’s Documents: The employer must verify that the employee has provided valid documents to establish both their identity and employment eligibility. This involves reviewing the original documents provided by the employee and ensuring they meet the criteria outlined in the form.
- Record Document Details: The employer must record the document information, including the document title, issuing authority, document number, and expiration date (if applicable). The employer must also sign and date the form, confirming that they have reviewed the employee’s documents and attested to their authenticity.
Employers must ensure that they complete the employer section of Form I-9 accurately and within the specified time frame to avoid non-compliance penalties.
Types of Acceptable Documents for Verification
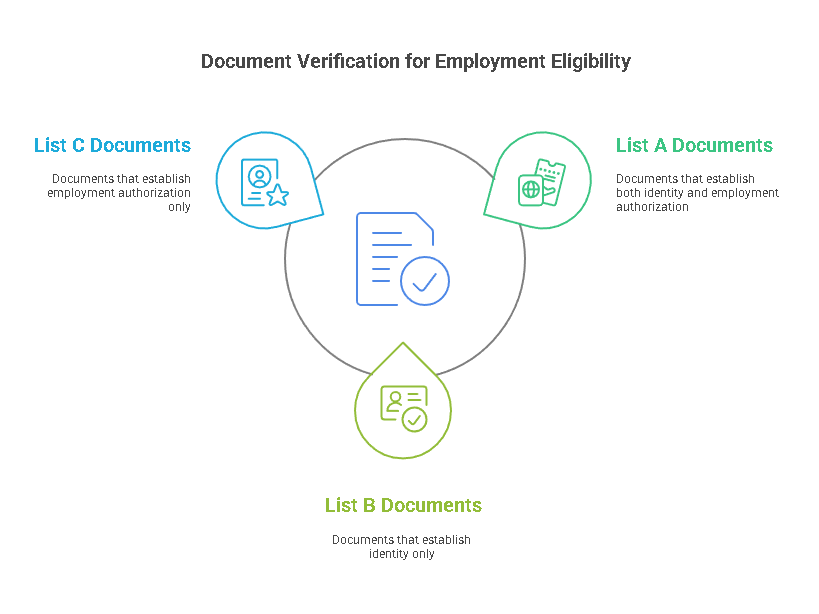
Employees must provide certain documents that prove their identity and eligibility to work. The documents fall into three categories: List A, List B, and List C. Employees can present one document from List A, or one from List B and one from List C.
- List A (Documents that Establish Both Identity and Employment Authorization):
- U.S. Passport or Passport Card
- Permanent Resident Card or Alien Registration Receipt Card (Form I-551)
- Foreign Passport with a Form I-94 or Form I-94A indicating work authorization
- List B (Documents that Establish Identity Only):
- Driver’s License or ID card issued by a state
- School ID with a photograph
- Voter’s Registration Card
- List C (Documents that Establish Employment Authorization Only):
- Social Security card
- Birth Certificate issued by a U.S. state or outlying possession
- Employment Authorization Document (EAD)
Employees may provide a combination of documents from List B and List C if they cannot provide a List A document. However, it is important to note that employers cannot specify which documents employees must present, and they should never refuse a valid document.
Precisehire’s Support in Employment Eligibility Verification
Precisehire offers specialized services to help employers ensure that they are compliant with employment eligibility verification requirements. By leveraging advanced technologies, Precisehire assists companies in conducting thorough background checks and ensuring that the documents provided by employees are valid. With experience in dealing with Form I-9 compliance, Precisehire helps businesses streamline the verification process, ensuring they meet legal obligations while minimizing the risk of errors or non-compliance.
Data Table: Acceptable Documents for Form I-9
| Document Type | Category | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| U.S. Passport or Passport Card | List A | U.S. Passport, U.S. Passport Card |
| Permanent Resident Card (Green Card) | List A | Form I-551, Alien Registration Receipt Card |
| Driver’s License or State-issued ID | List B | Driver’s License, State-issued ID |
| Social Security Card | List C | Social Security Card |
| U.S. Birth Certificate | List C | Birth Certificate issued by U.S. state or possession |
Importance of Correct Documentation
It is essential that employers verify the authenticity of the documents provided by employees. Accepting fraudulent documents can lead to severe penalties for employers, including fines or even criminal charges. Employers must ensure that the documents presented appear genuine and are on the list of approved documents.
Precisehire’s Role in Document Verification
By utilizing Precisehire’s services, employers can ensure that the documents presented by their employees meet the required standards for identity and employment eligibility. Precisehire’s advanced verification system helps reduce the risk of accepting fraudulent documents, allowing businesses to remain compliant with federal regulations.
Legal Aspects of Form I-9 Employment Eligibility Verification
Compliance with Immigration Laws
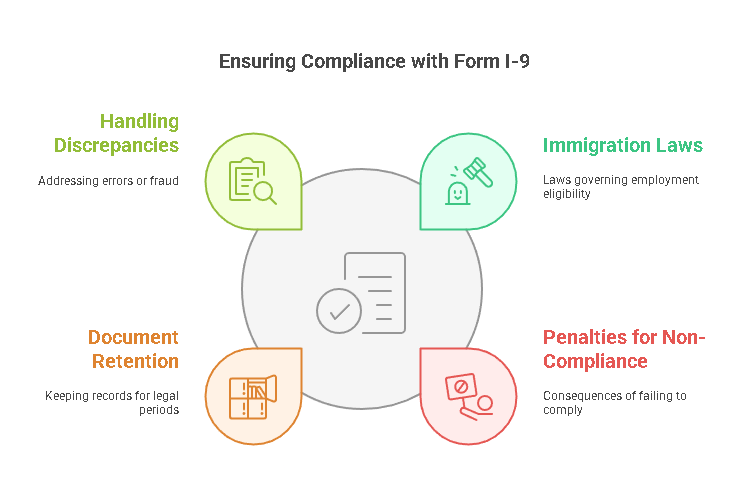
Form I-9 is a critical document used to comply with U.S. immigration laws, primarily the Immigration and Nationality Act (INA). The form helps employers verify the identity and employment eligibility of individuals hired to work in the United States. Compliance with these laws is essential for businesses to avoid penalties and potential legal issues.
Employers must ensure that they complete Form I-9 accurately and on time for every new hire. Failure to do so can result in civil penalties, ranging from fines for incomplete or missing forms to severe penalties for knowingly hiring unauthorized workers.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Employers who fail to properly complete Form I-9 can face serious consequences. The penalties for non-compliance can vary depending on the number of violations and whether the employer has a history of violations. Penalties may include:
- Civil Penalties: Employers can face fines ranging from $250 to $2,500 per form for failing to complete Form I-9 correctly or failing to retain it for the required period.
- Criminal Penalties: In cases of knowingly hiring unauthorized workers or creating false documents, employers can face criminal prosecution, which may lead to additional fines and potential imprisonment.
Document Retention Requirements
Employers are required to retain Form I-9 for a certain period after an employee’s termination. The form must be kept for three years after the date of hire or for one year after the date of employment ends, whichever is later. The form must be available for inspection by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and other relevant authorities if requested.
Handling Discrepancies
If there are discrepancies between the information provided by the employee and the documentation they present, the employer is obligated to address these issues promptly. Employers cannot knowingly accept fraudulent or altered documents. If an employee cannot provide acceptable documentation or if the documentation appears to be fraudulent, the employer must notify the employee and take appropriate action.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if Form I-9 is not completed correctly?
If Form I-9 is not completed correctly, the employer may face penalties from the U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE). Employers are required to ensure the form is completed correctly and within the required timeframe. Mistakes can lead to fines or legal action. In some cases, employers may be able to correct errors, but it's essential to act quickly.
Can an employee work before their I-9 is completed?
No, an employee cannot legally begin working until Form I-9 is completed. The law mandates that the employee complete Section 1 of the form on their first day of employment, and the employer must complete Section 2 by the end of the employee's third day of employment. Failing to complete the form before the employee begins work can result in fines for the employer.
How long do employers need to keep Form I-9 on file?
Employers must retain Form I-9 for three years after the date of hire or one year after the employee’s employment ends, whichever is later. The form must be available for inspection by authorized government officials if requested.
What should employers do if they suspect an employee’s documents are fraudulent?
Employers should not accept any documents that appear to be fraudulent. If an employer suspects that an employee’s documents are not authentic, they should inform the employee and request alternative documentation. If the employee cannot provide valid documentation, the employer must refrain from hiring them. Employers are also encouraged to report suspected fraudulent activity to the appropriate authorities.
How often should employers update I-9 forms for their employees?
Employers are not required to update Form I-9 unless there is a specific reason, such as when an employee’s work authorization status changes. In cases where an employee’s work authorization expires, the employer must update the form to reflect the new status. Employers should also review their records periodically to ensure they remain in compliance.
Conclusion
Form I-9 plays a vital role in ensuring that employers comply with U.S. immigration laws by verifying the identity and employment eligibility of employees. Proper completion and retention of the form are essential to avoid penalties and maintain a lawful workforce. Employers must be diligent in reviewing documents, addressing discrepancies, and keeping accurate records to ensure compliance.
Precisehire offers valuable services to help employers navigate the complexities of Form I-9 compliance, offering support in document verification and background screening. By working with a trusted partner like Precisehire, employers can reduce the risk of errors and stay up-to-date with the latest regulations, ensuring their hiring processes remain legally sound.
In conclusion, maintaining accurate and compliant employment eligibility verification processes is crucial for businesses operating in the United States. The responsibility of properly completing Form I-9 lies with the employer, and adherence to immigration laws is not only legally required but also essential for protecting the integrity of the workforce.
